In short, the key heat treatment processes performed in horizontal furnaces are annealing, hardening, tempering, and sintering. These thermal cycles are fundamental to metallurgy, as they precisely modify the internal microstructure of materials to achieve desired mechanical properties like strength, ductility, and hardness.
A horizontal furnace is a foundational tool for materials engineering. Its value lies not in a single function, but in its versatility to execute a range of controlled heating and cooling cycles that fundamentally alter a material's properties to fit a specific application.
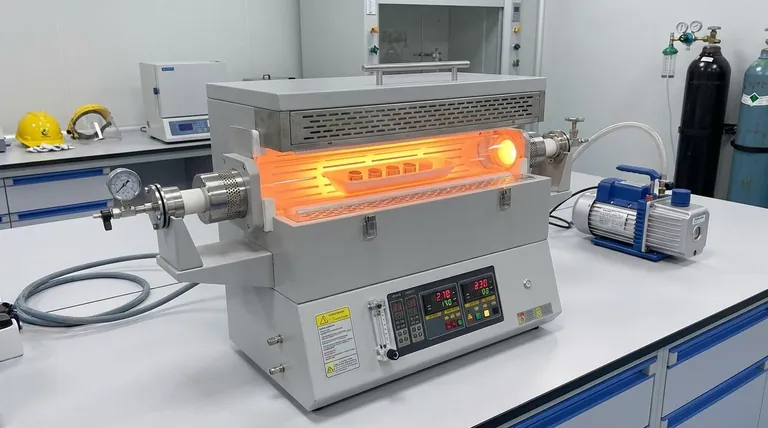

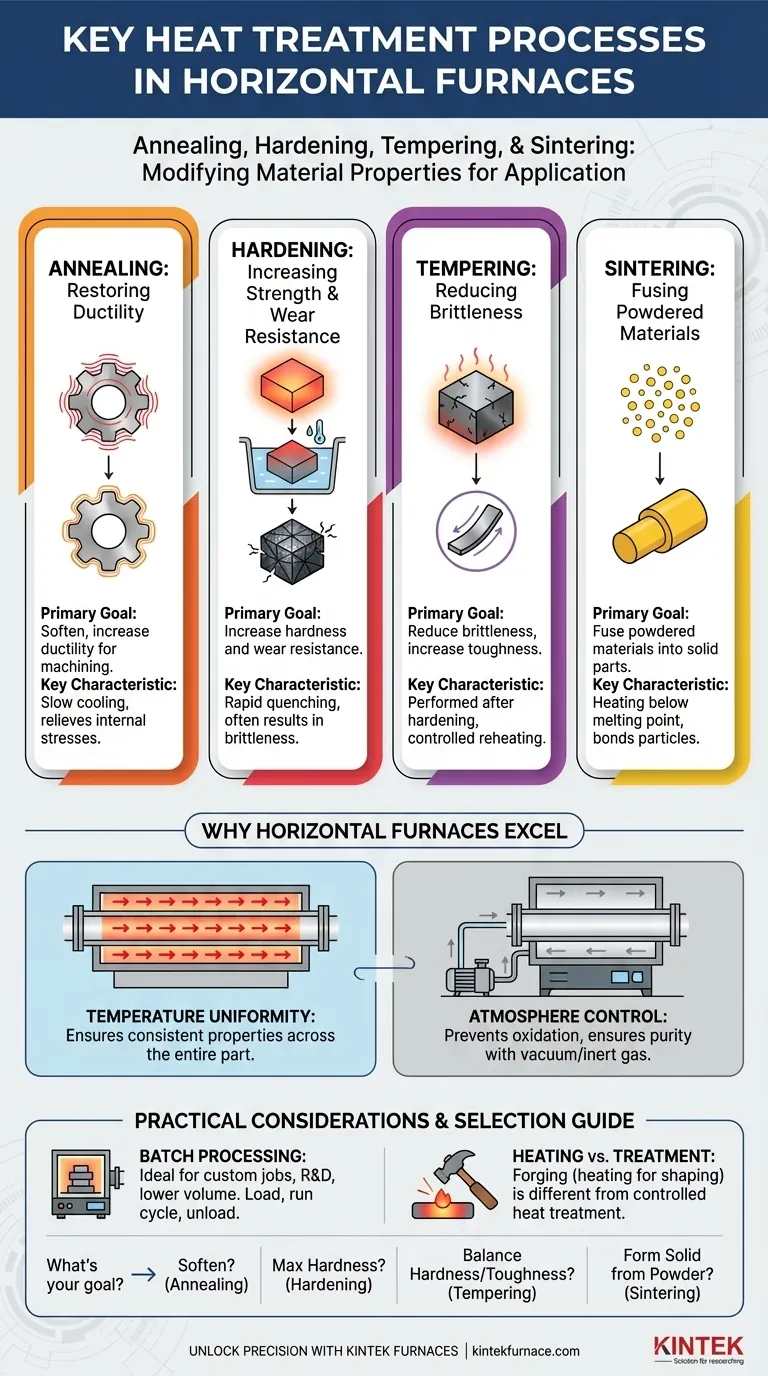
The Core Heat Treatment Processes Explained
Each process involves a distinct thermal profile—a specific sequence of heating, holding, and cooling—designed to produce a unique change in the material's microstructure.
Annealing: Restoring Ductility
Annealing is a process that involves heating a metal to a specific temperature and then cooling it slowly. This slow cooling allows the material's internal grain structure to reform, relieving internal stresses.
The primary goal is to soften the material, making it more ductile and easier to machine or form. It essentially resets the material to a more workable state after it has been hardened by processes like cold working.
Hardening: Increasing Strength and Wear Resistance
Hardening is achieved by heating a metal (typically steel) to a high temperature and then cooling it rapidly, a process known as quenching. This rapid cooling traps the material in a very hard, brittle microstructural state.
This process significantly increases the material's hardness and wear resistance. However, it almost always comes at the cost of reduced toughness, making the part susceptible to fracture.
Tempering: Reducing Brittleness
Tempering is a secondary heat treatment that is almost always performed after hardening. The hardened part is reheated to a lower temperature and held for a specific time.
This process reduces the extreme brittleness introduced by hardening, trading a small amount of hardness for a significant gain in toughness. The final balance between hardness and toughness can be precisely controlled by adjusting the tempering temperature.
Sintering: Fusing Powdered Materials
Sintering is used to create solid objects from metal or ceramic powders. The compacted powder is heated in the furnace to a temperature below its melting point.
At this temperature, the individual particles bond and fuse together, forming a solid, dense part. This is a common manufacturing method for creating complex shapes or components from materials with very high melting points.
Why Horizontal Furnaces Excel at These Tasks
The design of a horizontal furnace is particularly well-suited for these precise thermal operations, primarily due to its ability to control two critical variables: temperature and atmosphere.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
For any heat treatment to be successful, the entire part must experience the exact same temperature profile. Horizontal furnaces, especially tube furnaces, are designed to create a long, stable, and uniform hot zone.
This uniformity ensures that one end of the part doesn't become harder or softer than the other, preventing internal stresses and guaranteeing consistent, predictable mechanical properties throughout.
Atmosphere Control for Purity
Many heat treatment processes require a controlled environment to prevent unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation, on the material's surface.
Horizontal furnaces can be sealed and operated with an inert gas (like argon) or under a vacuum. A vacuum environment is especially effective as it removes virtually all contaminants, ensuring the material's surface remains pure and free from discoloration or scaling, leading to a higher quality final product.
Understanding the Practical Considerations
While versatile, the horizontal furnace is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness depends on the production scale and the nature of the material being processed.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Horizontal furnaces are ideal for batch processing. You can load one or several parts, run the thermal cycle, and then unload them. This is perfect for custom jobs, research and development, or low-to-medium volume production.
They are generally less efficient for high-volume, continuous production, where a conveyor-style furnace might be more appropriate.
Heating for Forging vs. Heat Treatment
It is crucial to distinguish between heating for forming and heat treatment. A furnace is used to heat a billet of metal before it is forged (shaped with a hammer or press). This is simply a heating step.
Heat treatment processes like annealing or tempering are distinct, controlled cycles performed after shaping to refine the final mechanical properties. A single furnace can be used for both tasks, but the processes themselves are fundamentally different.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Goal
The choice of heat treatment is dictated entirely by the desired final properties of the component.
- If your primary focus is to soften a material for easier machining or forming: Annealing is the correct process to restore ductility and relieve internal stress.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: Hardening through heating and rapid quenching is the essential first step.
- If your primary focus is to toughen a previously hardened part so it doesn't shatter: Tempering is the necessary follow-up process to balance hardness with durability.
- If your primary focus is to create a solid, dense part from metal powder: Sintering is the method used to bond the particles into a cohesive whole.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment is about using the furnace as a precise tool to engineer the exact material performance your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften material, increase ductility | Slow cooling, relieves internal stresses |
| Hardening | Increase hardness and wear resistance | Rapid quenching (quenching), often brittle |
| Tempering | Reduce brittleness, increase toughness | Performed after hardening, controlled temperature |
| Sintering | Fuse powdered materials into solid parts | Heating below melting point, bonds particles |
Unlock Precision in Your Heat Treatment Processes with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're optimizing annealing, hardening, tempering, or sintering, our furnaces ensure uniform heating, precise atmosphere control, and reliable performance for materials like metals and ceramics.
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior material properties? Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















