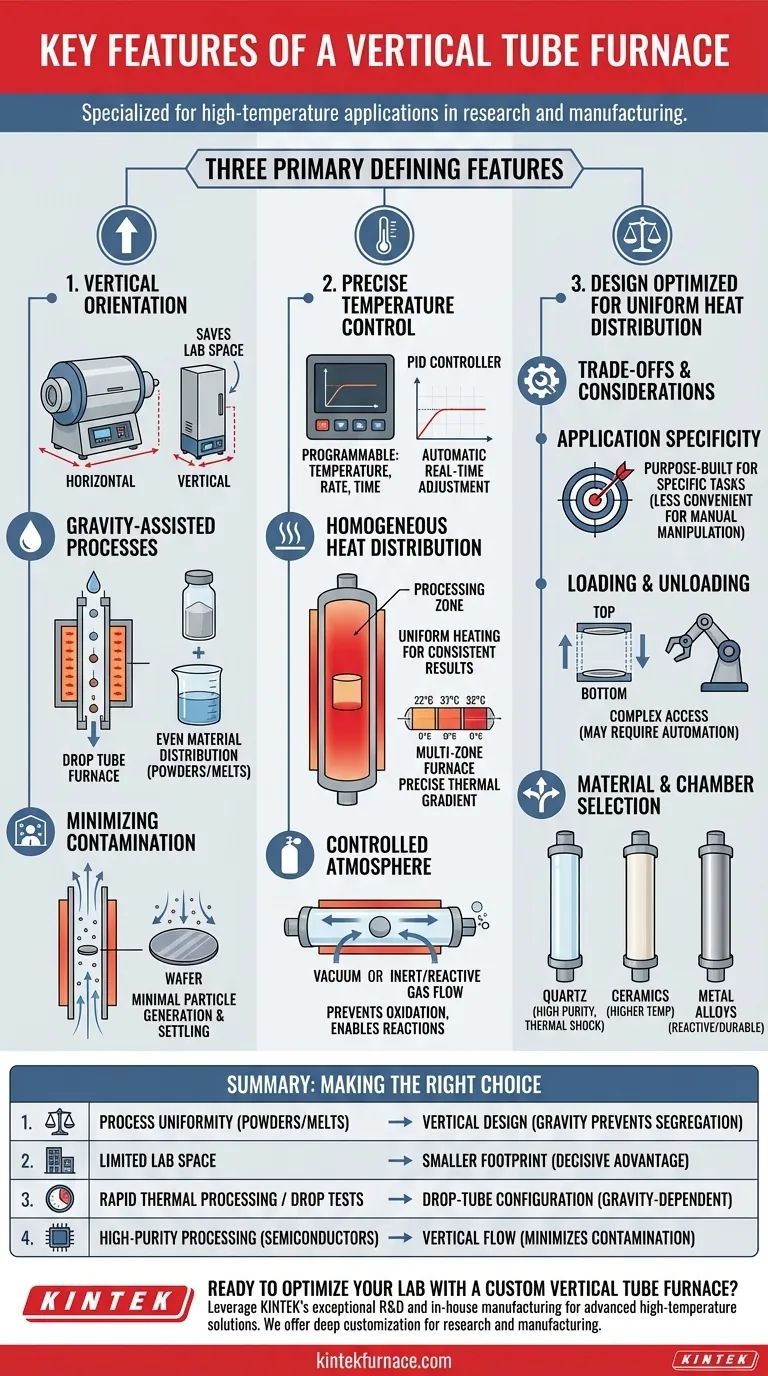
At its core, a vertical tube furnace is defined by three primary features: a vertical orientation that saves space and enables gravity-assisted processes, highly precise temperature control for repeatable results, and a design optimized for uniform heat distribution. These characteristics make it a specialized tool for specific high-temperature applications in research and manufacturing.
The most critical takeaway is that the vertical design is not merely a space-saving alternative to a horizontal furnace. It is an intentional engineering choice that fundamentally enables processes dependent on gravity, such as drop testing or achieving uniform heating for powders and melts, which are difficult or impossible in other configurations.

The Defining Feature: Vertical Orientation
The orientation of the furnace is its most significant and impactful characteristic, influencing everything from lab layout to the types of processes it can perform.
Maximizing Laboratory Space
A vertical tube furnace has a significantly smaller footprint compared to a horizontal model of similar capacity. This makes it an ideal solution for laboratories where floor space is at a premium, allowing for more efficient use of the available area.
Enabling Gravity-Assisted Processes
The vertical setup is essential for processes where gravity plays a crucial role. In applications like a drop tube furnace, materials are dropped through the heated zone, facilitating rapid thermal processing or specific reaction studies.
This orientation also helps ensure even material distribution for powders or liquids, preventing settling or separation that might occur in a horizontal tube.
Minimizing Contamination
The vertical design can lead to minimal particle generation and contamination. Gravity helps keep particulates from settling on the sample, which is a critical advantage in high-purity applications like semiconductor wafer processing.
Precision and Uniformity in Operation
Beyond its physical orientation, a vertical tube furnace is engineered for exceptional control and consistency, which is vital for sensitive thermal processes.
Advanced Temperature Control
Modern vertical tube furnaces employ advanced control systems, often using PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers. This allows users to precisely program the heating temperature, heating rate, and holding time.
The PID system automatically adjusts heating power in real-time to maintain a highly stable and accurate temperature, compensating for any fluctuations.
Ensuring Homogeneous Heat Distribution
A key performance metric is the ability to provide uniform heating throughout the entire processing zone. This consistency is crucial for achieving homogeneous heat treatment, ensuring that the entire sample experiences the exact same thermal conditions.
In multi-zone furnaces, separate controls for different heating sections allow for the creation of a precise thermal gradient or an even more finely-tuned uniform zone.
Controlled Atmosphere Environments
These furnaces are designed for excellent atmosphere control. The sealed tube allows for processing in a vacuum or under a specific inert or reactive gas, preventing oxidation and enabling specific chemical reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Considerations
While powerful, a vertical tube furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to successful implementation.
Application Specificity
The primary advantage—gravity assistance—is also its main constraint. This design is purpose-built for specific tasks. It may be less convenient for processes that require manual manipulation of a sample horizontally or for simple batch annealing of large, flat objects.
Loading and Unloading
Depending on the setup (top-loading vs. bottom-loading), accessing the sample can be more complex than with a simple horizontal furnace. Systems for large-scale production often require automated boat or wafer transfer mechanisms to be practical.
Material and Chamber Selection
The furnace tube material is a critical choice that dictates the furnace's capabilities.
- Quartz is common for its high purity and thermal shock resistance but has temperature limitations.
- Ceramics (like Alumina) offer higher temperature operation.
- Metal alloys are used for specific reactive environments or when durability is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace requires matching its features to your primary process goal.
- If your primary focus is process uniformity for powders or melts: The vertical design uses gravity to prevent segregation and ensure even heating throughout the material.
- If your primary focus is limited lab space: The smaller footprint is a decisive advantage over a comparable horizontal furnace.
- If your primary focus is rapid thermal processing or drop tests: The drop-tube configuration is the only design specifically engineered for these gravity-dependent tasks.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing (e.g., semiconductors): The vertical flow minimizes particle settling on the sample and provides superior atmosphere control.
Ultimately, the decision to use a vertical tube furnace should be driven by the specific demands of your process, not just its specifications.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Vertical Orientation | Saves lab space and enables gravity-assisted processes like drop testing. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Uses PID controllers for stable, accurate heating and programmable cycles. |
| Uniform Heat Distribution | Ensures homogeneous heating across the sample for consistent results. |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Supports vacuum or gas environments to prevent oxidation and aid reactions. |
| Application Specificity | Ideal for powders, melts, and high-purity tasks like semiconductor processing. |
Ready to optimize your lab with a custom vertical tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in research or manufacturing, we can help you achieve precise, efficient thermal processing. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















