In essence, the primary disadvantages of a standard rotary kiln are its relatively low thermal efficiency and the inherent difficulty in achieving perfectly uniform product quality. These issues stem directly from its fundamental design as a large, rotating cylinder, which creates challenges in heat transfer and material mixing that require careful engineering and operational control to overcome.
While powerful for the continuous processing of bulk materials, the core mechanics of a rotary kiln often lead to significant heat loss and inconsistent material heating. Understanding these limitations is critical for evaluating if it's the right technology for your specific process and quality requirements.

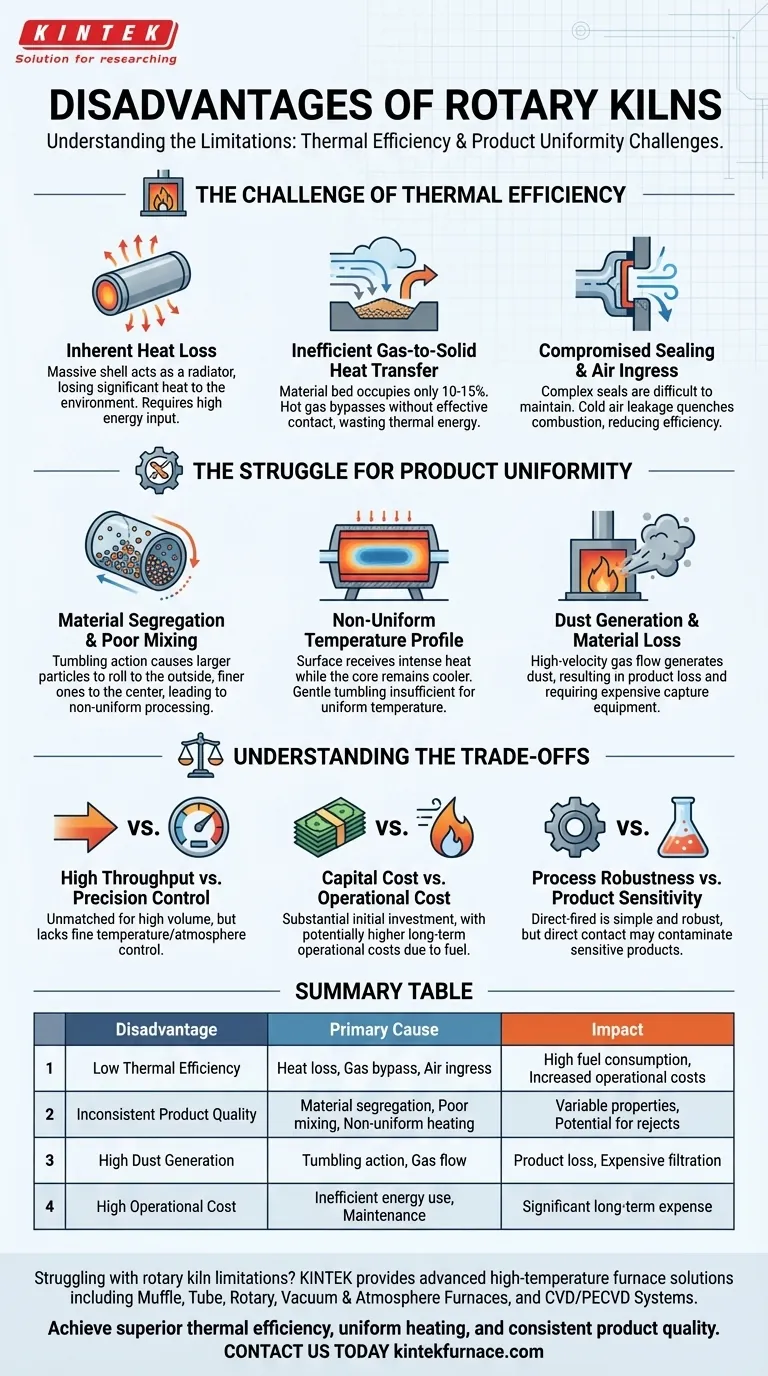
The Challenge of Thermal Efficiency
A rotary kiln's massive size and simple, direct-fired design make it a workhorse, but this often comes at the cost of high energy consumption. Several factors contribute to this inefficiency.
Inherent Heat Loss
The kiln itself is a massive steel shell that acts as a radiator. While an internal refractory lining protects the steel from extreme process temperatures, a significant amount of heat is still lost to the surrounding environment through the shell's large surface area.
This continuous heat loss requires a constant, high-energy input from the burner simply to maintain the target temperature, directly increasing fuel consumption and operational costs.
Inefficient Gas-to-Solid Heat Transfer
The material being processed, known as the "bed," typically occupies only 10-15% of the kiln's internal volume. Hot gas from the burner can flow over the top of this material bed without making effective contact.
This "gas bypass" means a substantial portion of the hot exhaust gas can exit the kiln without efficiently transferring its thermal energy to the solids, representing a major source of wasted energy.
Compromised Sealing and Air Ingress
Rotary kilns require complex seals at the feed and discharge ends to contain hot gases while allowing the shell to rotate. These seals are subject to wear and thermal stress, making them notoriously difficult to keep perfectly airtight.
Cold air leaking into the kiln can quench the combustion process, lower the internal temperature, and force the burner to work harder, dramatically reducing overall thermal efficiency.
The Struggle for Product Uniformity
The same tumbling motion that transports material through the kiln can also be a source of inconsistent product quality. Achieving a homogenous final product requires overcoming several mixing and heating challenges.
Material Segregation and Poor Mixing
As the kiln rotates, the material tumbles in a pattern that is often not ideal for perfect mixing. Larger particles have a tendency to roll to the outside of the bed, while finer particles sift toward the center.
This segregation can lead to different residence times for different particle sizes, resulting in a non-uniform product where some material is over-processed and some is under-processed.
Non-Uniform Temperature Profile
The material bed receives intense radiant heat on its surface but remains much cooler in its core. The kiln's gentle tumbling action is often insufficient to fully mix the bed and create a uniform temperature throughout its cross-section.
This temperature gradient means particles on the surface can be overheated while particles in the center remain too cool, leading to variations in chemical reactions and physical properties in the final product.
Dust Generation and Material Loss
The combination of tumbling material and high-velocity gas flow can generate significant amounts of dust. These fine particles can become entrained in the exhaust gas and be carried out of the kiln before they are fully processed.
This not only results in a loss of valuable product but also requires extensive downstream equipment like baghouses or cyclones to capture the dust, adding to the system's capital and maintenance costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The disadvantages of a rotary kiln are best understood as trade-offs inherent to its design. It excels in certain areas at the expense of others.
High Throughput vs. Precision Control
Rotary kilns are unmatched for the continuous, high-volume processing of bulk solids. However, this scale comes at the cost of the fine temperature and atmosphere control found in smaller batch kilns or more specialized furnace technologies.
Capital Cost vs. Operational Cost
While the initial capital investment for a large rotary kiln system is substantial, its low thermal efficiency can lead to even more significant long-term operational costs due to high and often volatile fuel prices.
Process Robustness vs. Product Sensitivity
A direct-fired rotary kiln is a robust and relatively simple piece of equipment. However, the direct contact between the combustion gases and the process material can be a source of contamination, making it unsuitable for highly sensitive or pure products without moving to a more complex and expensive indirect-fired or electric design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use a rotary kiln depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume bulk processing: A rotary kiln is a powerful tool, but be prepared to invest in robust seals, high-quality refractory, and advanced process controls to manage efficiency and product consistency.
- If your primary focus is absolute product uniformity: You should evaluate alternative technologies like batch kilns, fluidized bed reactors, or multi-hearth furnaces that offer superior mixing and more precise temperature control.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational costs and emissions: Explore modern, high-efficiency kiln designs that incorporate preheaters and advanced seals, or consider an electrically heated kiln if your material and process are compatible.
Recognizing these inherent disadvantages empowers you to select the right technology and engineer a process that delivers on your operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Primary Cause | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Low Thermal Efficiency | Heat loss through shell, gas bypass, air ingress | High fuel consumption, increased operational costs |
| Inconsistent Product Quality | Material segregation, poor mixing, non-uniform heating | Variable product properties, potential for rejects |
| High Dust Generation | Tumbling action and gas flow | Product loss, need for expensive filtration systems |
| High Operational Cost | Inefficient energy use and maintenance needs | Significant long-term expense despite high throughput |
Struggling with the limitations of your rotary kiln? KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions are engineered to overcome these challenges. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with precise, efficient alternatives. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Achieve superior thermal efficiency, uniform heating, and consistent product quality. Contact us today (#ContactForm) to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your process and reduce operational costs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing



















