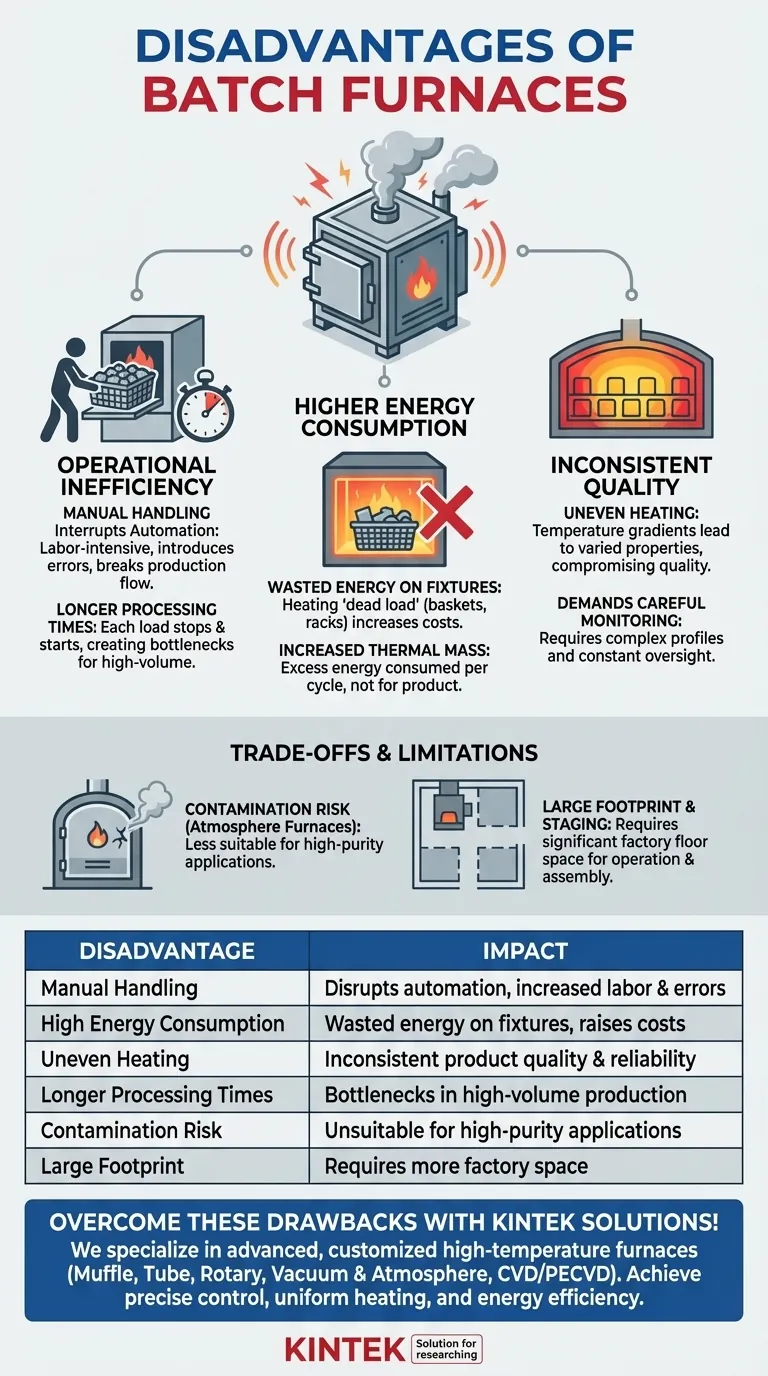
The primary disadvantages of batch furnaces are operational inefficiency due to manual handling, higher energy consumption from heating fixtures, and inconsistent product quality caused by uneven heating. These factors make them less suitable for high-volume, automated production environments where process uniformity and energy efficiency are critical.
While batch furnaces offer flexibility for varied production runs, their inherent design introduces significant trade-offs. The core challenge lies in balancing this flexibility against inherent drawbacks in process consistency, energy efficiency, and integration with modern, automated production lines.

Inefficiency in Production Flow and Energy Use
A key set of disadvantages stems from the fundamental "batch" nature of the operation. Unlike a continuous process, work must stop and start with each load, creating bottlenecks and consuming excess energy.
Manual Handling Interrupts Automation
In a typical production line, parts must be removed and manually grouped together for processing in a batch furnace. Operators load parts onto fixtures like baskets or racks, which are then placed inside the furnace.
This manual step breaks the flow of an automated production line, introducing labor costs and potential for handling errors.
Increased Energy Consumption
The fixtures required to hold the parts—the baskets, racks, and carts—also represent a significant thermal mass. This "dead load" must be heated and cooled along with the product for every single cycle.
This process consumes a substantial amount of energy that does not go into treating the product, increasing overall operating costs.
Longer Overall Processing Times
Processing parts one batch at a time can be slower than using a continuous furnace, where product is constantly moving through the heat treatment cycle.
For high-volume production, the time spent loading, unloading, heating, and cooling individual batches can quickly become a major production bottleneck.
The Challenge of Process Consistency
Achieving a uniform result across every part in a large batch is a persistent engineering challenge with these furnaces.
High Risk of Uneven Heating
Parts located near the furnace's heat source will inevitably heat up faster and reach a higher temperature than parts in the center of the load.
This temperature gradient can lead to inconsistent metallurgical properties, hardness, or curing across the batch, potentially compromising product quality and reliability.
Demands Careful Monitoring
Because of the risk of non-uniform heating, batch furnaces require careful monitoring to ensure all components receive the proper thermal treatment.
This is especially critical for large or complex parts, where temperature differences between sections can be significant and require specifically optimized temperature profiles to manage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Beyond the primary issues of efficiency and consistency, certain designs and applications introduce further drawbacks that must be considered.
Contamination Risk in Atmosphere Furnaces
For processes requiring a controlled atmosphere, such as those using low-vacuum batch furnaces, there can be a higher risk of contamination compared to high-vacuum systems.
This limitation makes them less suitable for applications demanding extreme purity, such as in the semiconductor or advanced materials industries.
Physical Footprint and Staging Area
Batch furnaces, particularly large horizontal models, can require a significant amount of factory floor space.
Beyond the unit itself, you must also allocate space for staging areas where batches are assembled before loading and disassembled after cooling, further increasing the operational footprint.
Is a Batch Furnace Right for Your Application?
Choosing the correct furnace requires weighing its flexibility against its inherent limitations. Your production goals should be the deciding factor.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: A continuous furnace is likely a better investment to maximize throughput and ensure process consistency.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse, low-volume, or complex parts: A batch furnace offers necessary flexibility, but you must engineer your process to mitigate uneven heating and account for higher energy costs.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing: A standard batch furnace may introduce unacceptable contamination, and a specialized high-vacuum system may be required.
Understanding these drawbacks allows you to select the right thermal processing technology that aligns with your specific operational needs and quality standards.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Impact |
|---|---|
| Manual Handling | Disrupts automation, increases labor costs and errors |
| High Energy Consumption | Wasted energy on fixtures, raises operating costs |
| Uneven Heating | Leads to inconsistent product quality and reliability |
| Longer Processing Times | Causes bottlenecks in high-volume production |
| Contamination Risk | Unsuitable for high-purity applications like semiconductors |
| Large Footprint | Requires more factory space for staging and operation |
Struggling with batch furnace inefficiencies? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems with strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in materials science, manufacturing, or research, our solutions ensure precise temperature control, uniform heating, and energy efficiency to overcome batch furnace drawbacks. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processing with reliable, customized equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between an alumina tube furnace and a quartz tube furnace? Choose the Right Tube Furnace for Your Lab
- What technical requirements affect the external thermal strength of furnace tubes? Optimize for High-Temp Performance
- What are the key features of a quartz tube furnace? Discover High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- How should a quartz tube furnace be cleaned? Essential Steps for Safe, Contamination-Free Maintenance
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a quartz tube furnace? Ensure Reliable High-Temperature Processing



















