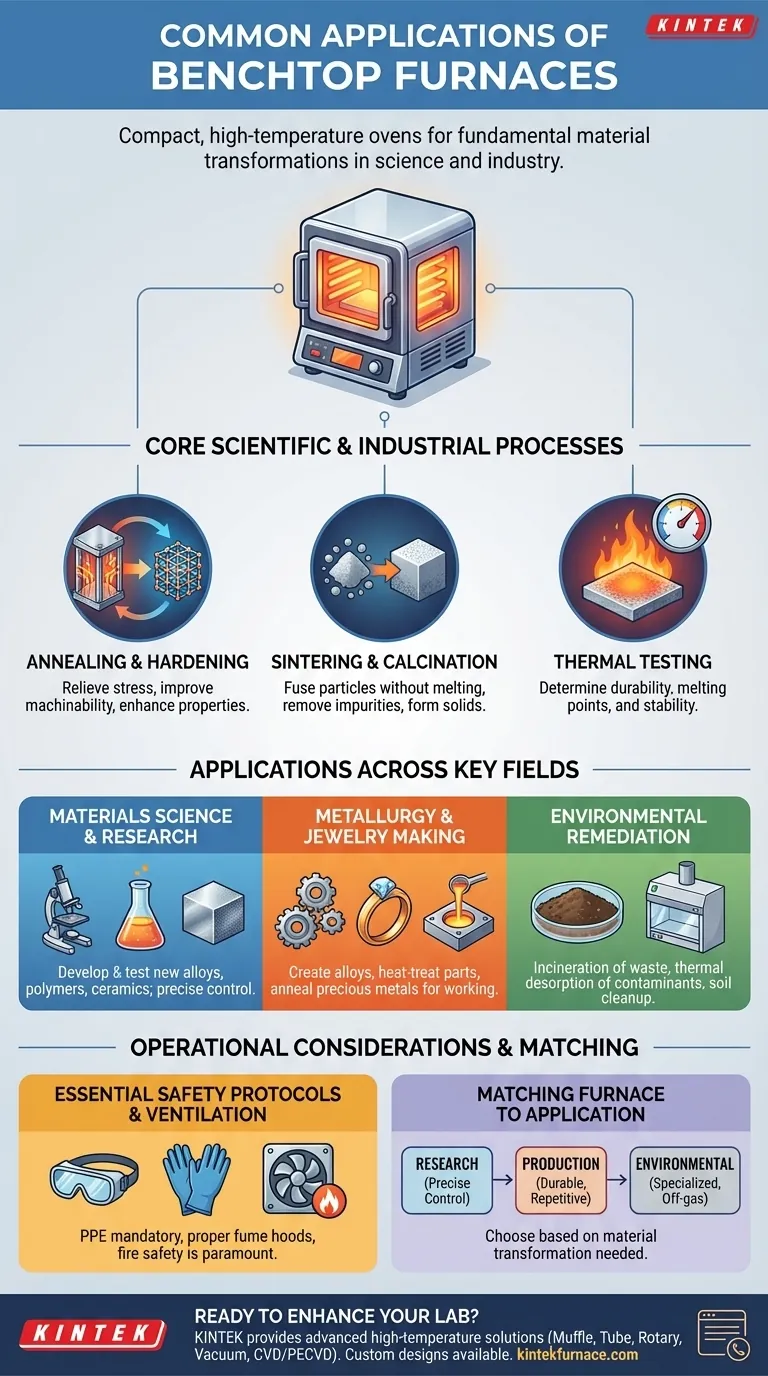
In essence, benchtop furnaces are compact, high-temperature ovens used across scientific and industrial fields to fundamentally alter the properties of materials. Their applications range from materials science research and metallurgy to jewelry making and environmental remediation, enabling precise thermal processes like annealing, sintering, and thermal testing in a small-footprint device.
A benchtop furnace's core function is to provide a controlled, high-heat environment. This capability is not just about heating things up; it's about enabling specific chemical and physical transformations in materials, making it a cornerstone tool for innovation and production.

Core Scientific and Industrial Processes
The versatility of a benchtop furnace stems from its ability to execute several fundamental thermal processes with high precision. Understanding these processes is key to understanding their applications.
Annealing and Hardening
Annealing is a heat treatment process that alters a material's microstructure to make it more ductile and less hard. The material is heated above its recrystallization temperature, held there for a specific time, and then cooled slowly.
This process is critical for relieving internal stresses, improving machinability, and enhancing electrical conductivity in metals and alloys.
Sintering and Calcination
Sintering uses heat to fuse particles together without melting them, forming a solid, coherent mass. This is fundamental in creating ceramics, metal components from powders (powder metallurgy), and other composite materials.
Calcination involves heating a material to a high temperature in the absence of air to cause thermal decomposition or a phase transition. This process is often used to remove impurities or create more stable, reactive materials for industrial use.
Thermal Testing
Researchers use benchtop furnaces to subject materials to extreme temperatures and observe their response. This thermal testing is vital for determining a material's durability, melting point, and stability under harsh conditions.
This data is crucial for developing new alloys, polymers, and ceramics for demanding applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Applications Across Key Fields
These core processes find application in a diverse range of professional fields, each leveraging the furnace's controlled environment for specific goals.
Materials Science and Research
In laboratories, benchtop furnaces are indispensable tools for developing and testing new materials. Researchers can precisely control heating and cooling cycles to study material behavior and create novel substances with desired properties.
Metallurgy and Jewelry Making
Metallurgists use these furnaces for creating alloys, heat-treating small metal parts, and conducting failure analysis. Similarly, jewelers rely on them for annealing precious metals to make them workable, as well as for casting and soldering.
Environmental Remediation
Specialized benchtop furnaces play a role in environmental cleanup. They can be used for the incineration of small batches of hazardous waste or the thermal desorption of contaminants from soil samples, restoring soil quality on a lab scale.
They are also used in upgrading phosphate ores by heating them to enhance purity, which is essential for producing effective fertilizers.
Understanding Operational Considerations
While incredibly useful, operating a high-temperature furnace requires a strict commitment to safety protocols. Misuse can lead to severe personal injury and equipment damage.
Essential Safety Protocols
Users must be trained on the specific furnace type and its associated hazards. Following established safety protocols is not optional.
This includes always wearing appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), such as heat-resistant gloves, safety glasses, and proper lab attire.
Ensuring Proper Ventilation
Many thermal processes can release harmful fumes or off-gas volatile compounds. The furnace must be operated in a well-ventilated area, often under a fume hood, to prevent the buildup of toxic or flammable gases.
Fire safety is also paramount. An appropriate fire extinguisher must be accessible, and the area surrounding the furnace must be clear of all flammable materials.
Matching the Furnace to Your Application
Choosing the right approach depends entirely on your end goal. The furnace is a tool, and its application must be matched to the specific material transformation you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is materials research: You require a furnace capable of precise temperature control and programmable heating/cooling cycles for testing and development.
- If your primary focus is small-scale production (e.g., jewelry): You need a durable furnace designed for repetitive processes like annealing, casting, and hardening specific metals.
- If your primary focus is environmental analysis: You need a specialized furnace equipped for processes like incineration or thermal desorption, often with integrated off-gas management.
Ultimately, a benchtop furnace empowers you to precisely control the fundamental properties of materials.
Summary Table:
| Application Field | Key Processes | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Science | Annealing, Sintering, Thermal Testing | Research and development of new materials |
| Metallurgy & Jewelry | Annealing, Hardening, Casting | Heat-treating metals, creating alloys, jewelry making |
| Environmental Remediation | Incineration, Thermal Desorption | Hazardous waste treatment, soil decontamination |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom benchtop furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization to meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in materials science, metallurgy, or environmental work, we can help you achieve precise thermal processes efficiently. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















