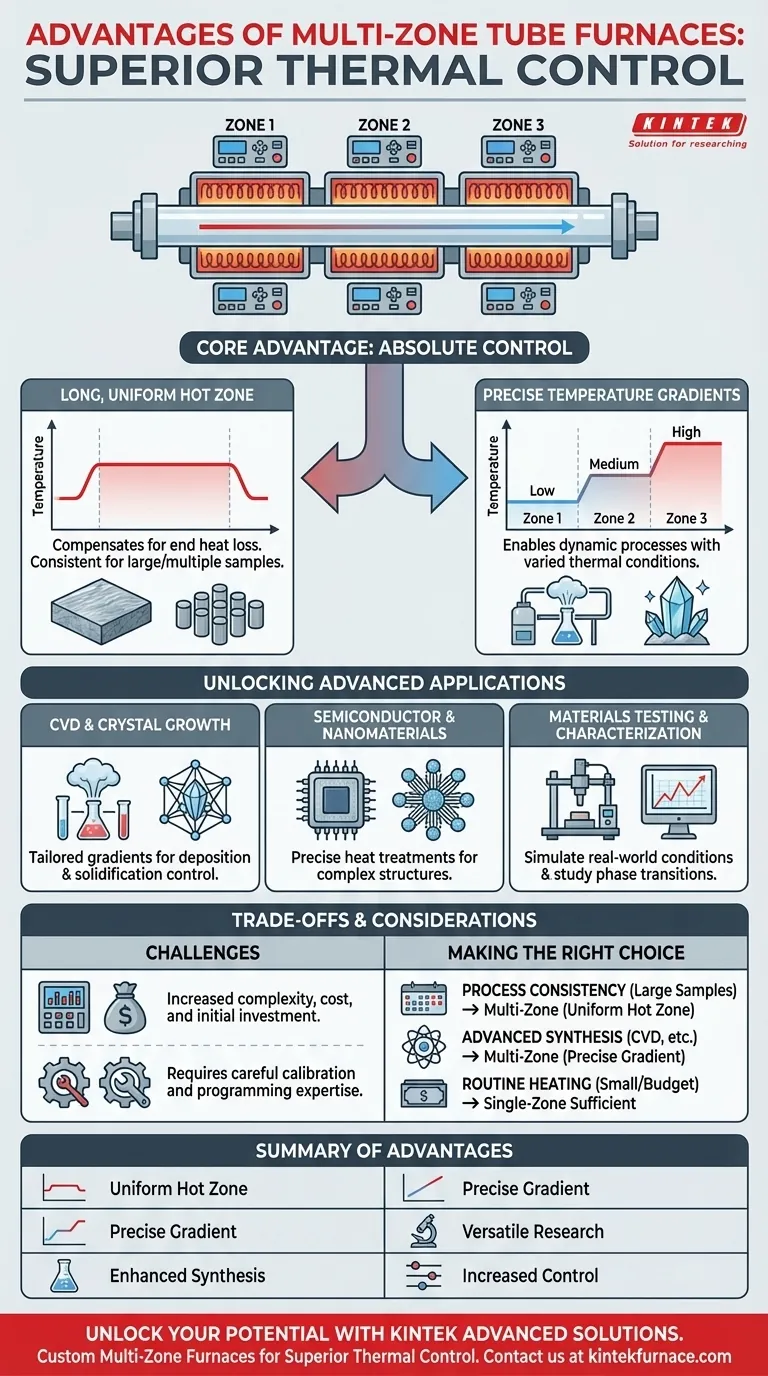
In short, a multi-zone tube furnace gives you superior control over the temperature profile along the length of the process tube. This control manifests in two primary advantages: the ability to create an exceptionally long and uniform hot zone for consistent processing, or the ability to establish a precise, stable temperature gradient for more advanced applications like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
The fundamental advantage of a multi-zone furnace is not just heat, but control. It transforms the furnace from a simple oven into a precise instrument for engineering thermal environments, enabling processes that are impossible with a single heat source.
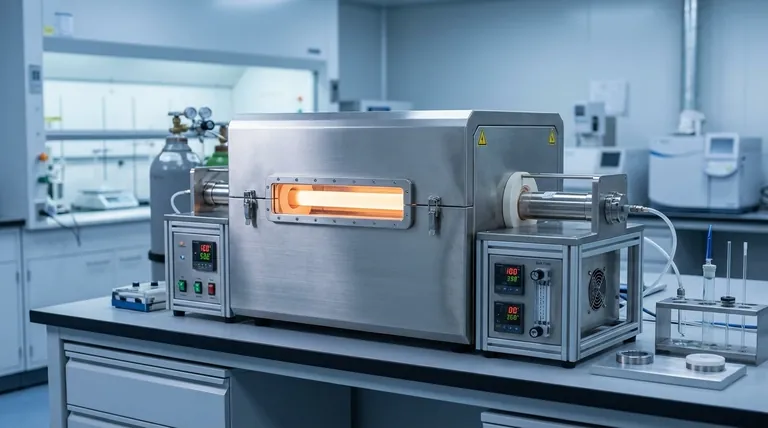

The Core Advantage: Absolute Control Over the Thermal Profile
A single-zone furnace is effective but limited; it heats the center well, but temperature naturally drops off toward the ends. A multi-zone furnace overcomes this by dividing the heating elements into independently controlled sections.
Creating a Longer, More Uniform Hot Zone
In a single-zone furnace, heat loss at the ends of the tube is unavoidable, resulting in a relatively short area of true temperature uniformity.
Multi-zone designs solve this by allowing you to slightly overheat the end zones. This compensates for natural heat loss and creates a significantly longer, flatter temperature profile across the central zones. This is critical for ensuring consistent thermal treatment for larger samples or for processing multiple smaller samples in a single batch.
Engineering Precise Temperature Gradients
The most powerful feature of a multi-zone furnace is the ability to set each zone to a different temperature. This creates a controlled and stable temperature gradient along the process tube.
This capability is essential for dynamic processes where different stages of a reaction or synthesis require different thermal conditions within the same operation.
Unlocking Advanced Material Processing Capabilities
This enhanced control over the thermal profile is not just a minor improvement; it is an enabling technology for a range of sophisticated applications.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Crystal Growth
Many CVD processes require a specific temperature gradient to control the vaporization of precursor materials in one zone and their subsequent deposition onto a substrate in a hotter or cooler zone.
Similarly, controlled crystal growth often relies on slowly moving a sample through a precise temperature gradient to manage the solidification process, which is made simple and repeatable with a multi-zone furnace.
Semiconductor and Nanomaterial Synthesis
In semiconductor manufacturing, the precise control of dopant diffusion and thin-film characteristics is paramount. Multi-zone furnaces provide the thermal accuracy needed to achieve these results.
For synthesizing complex nanomaterials or ceramics, the ability to create tailored heat treatments at different stages of formation allows for the creation of intricate and highly specific structures.
Materials Testing and Characterization
These furnaces are invaluable for research. Scientists can study a material's phase transitions, mechanical properties, or electrical behavior as it passes through various temperatures in a single test.
This is also used to simulate real-world operating conditions for components like battery materials, accelerating the development and optimization of new energy technologies.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, a multi-zone furnace is not always the default best choice. Its advantages come with inherent complexities.
Increased Complexity and Cost
The addition of multiple controllers, thermocouples, and power relays makes a multi-zone furnace inherently more complex and expensive than its single-zone counterpart. The initial investment is significantly higher.
Calibration and Programming
Achieving a truly uniform profile or a precise gradient requires careful calibration and programming. The user must understand the thermal dynamics of their system to program each zone correctly, as the zones inevitably influence each other.
When a Single-Zone is Sufficient
For many routine applications, such as simple annealing or calcination of a small, centrally-placed sample, the uniformity of a high-quality single-zone furnace is perfectly adequate. If your process does not require an exceptionally long hot zone or a temperature gradient, the added complexity of a multi-zone system may be unnecessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision must be driven by the specific demands of your process, not by a desire for the most features.
- If your primary focus is process consistency for larger samples: A multi-zone furnace's ability to create a long, uniform hot zone is your key advantage.
- If your primary focus is advanced synthesis or process development (like CVD): The ability to create and control precise temperature gradients is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is routine heating of small samples on a budget: A single-zone furnace is often the most practical and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is about matching the tool's capabilities directly to your scientific or production goals.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Long Uniform Hot Zone | Compensates for heat loss, ensuring consistent processing for larger samples. |
| Precise Temperature Gradient | Enables advanced applications like CVD and crystal growth with stable thermal profiles. |
| Enhanced Material Synthesis | Supports semiconductor manufacturing, nanomaterials, and ceramics with tailored heat treatments. |
| Versatile Research Applications | Ideal for materials testing, phase transitions, and simulating real-world conditions. |
| Increased Process Control | Independent zone control transforms the furnace into a precise thermal engineering tool. |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions!
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide multi-zone tube furnaces and other products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior thermal control for applications in materials science, semiconductor processing, and energy research.
Ready to enhance your process efficiency and achieve groundbreaking results? Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















