At their core, decomposing tube furnaces offer a powerful combination of precise process control, high thermal efficiency, and operational simplicity. This makes them exceptionally well-suited for applications like chemical cracking, where they can achieve high yields of specific products, such as ethylene and propylene, from various feedstocks in a continuous and highly controllable manner.
The fundamental advantage of a tube furnace is not a single feature, but its ability to create a highly isolated and precisely controlled thermal environment. This synergy of control and flexibility enables superior efficiency, process repeatability, and product quality across applications ranging from laboratory research to large-scale industrial decomposition.
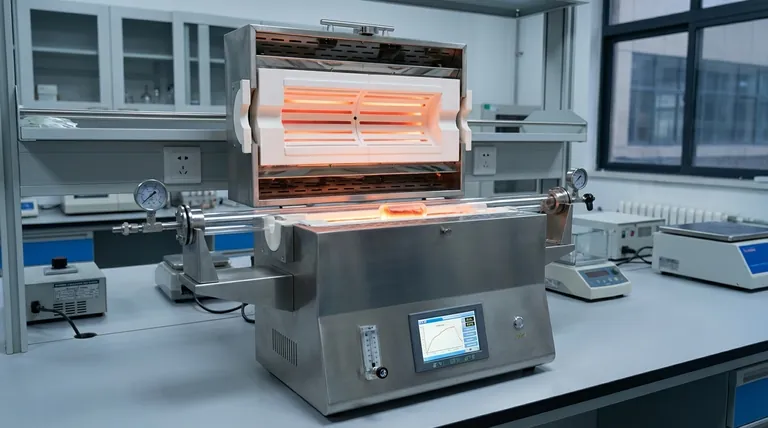

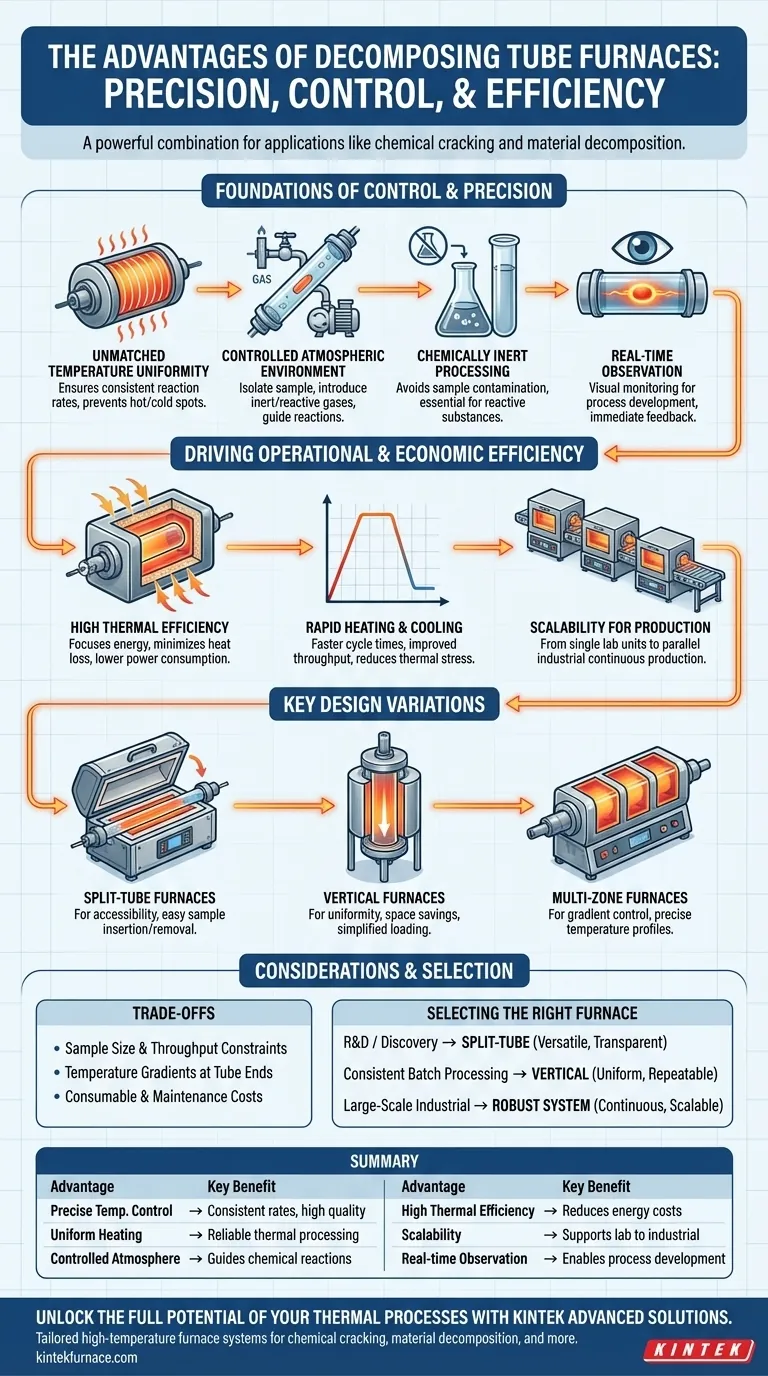
The Foundations of Control and Precision
The primary value of a tube furnace stems from its ability to precisely manage every critical parameter of a thermal process. This control is the basis for achieving consistent and predictable results.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical geometry of a tube furnace is inherently suited for providing uniform heating around the circumference of the sample. This ensures the entire material experiences the same thermal conditions, which is critical for consistent reaction rates and preventing hot or cold spots that could compromise the final product.
Controlled Atmospheric Environment
By its nature, a tube furnace isolates the sample from the outside environment. This allows you to maintain a vacuum or introduce a specific gas atmosphere—whether inert (like argon) or reactive (like hydrogen)—to guide the chemical reaction. This level of atmospheric control is essential for preventing unwanted oxidation and directing the decomposition pathway.
Chemically Inert Processing
Process tubes are often made from materials like high-purity quartz or alumina. These materials are chemically inert even at high temperatures, ensuring that the tube itself does not react with or contaminate the sample. For highly reactive substances, this is a non-negotiable requirement.
Real-time Process Observation
Many designs utilize a transparent quartz process tube. This provides a direct window into the reaction, allowing for real-time visual observation of phenomena like color changes, melting, or gas evolution. This immediate feedback is invaluable for process development and troubleshooting.
Driving Operational and Economic Efficiency
Beyond precision, tube furnaces are designed for efficient operation, impacting everything from energy costs to production throughput.
High Thermal Efficiency
Insulating materials and a compact heating chamber focus energy directly onto the process tube, minimizing heat loss to the surrounding environment. This results in lower power consumption and high thermal efficiency, making it an economically sound choice for energy-intensive processes.
Rapid Heating and Cooling
Modern furnaces often feature rapid heating rates, allowing them to reach the desired process temperature quickly and reduce cycle time. Similarly, forced cooling capabilities can reduce the time needed to safely handle the product, improving overall throughput and minimizing thermal stress that can cause material defects.
Scalability for Production
The fundamental design is highly scalable. While single furnaces are common in labs, industrial applications can link multiple furnaces in parallel. This allows for massive, continuous production while retaining the precise control characteristic of a single unit.
Understanding Key Design Variations
Not all tube furnaces are the same. The specific design dramatically impacts its suitability for a given task.
Split-Tube Furnaces: For Accessibility
These furnaces are hinged and can be opened along their length. This design greatly simplifies the insertion and removal of the process tube and sample holders, which is especially useful when the setup includes complex flanges or multiple connections that you wish to leave undisturbed.
Vertical Furnaces: For Uniformity and Space Savings
Orienting the tube vertically leverages gravity for sample loading and can improve temperature uniformity, as convection currents are more predictable. This design also has a smaller physical footprint, making it ideal for crowded laboratories.
Multi-Zone Furnaces: For Gradient Control
For long samples or complex processes, a single heating zone may not be sufficient. Multi-zone furnaces feature several independent heating elements along the length of the tube. This allows for precise control over the temperature profile, enabling the creation of specific thermal gradients required for processes like crystal growth or specialized chemical vapor deposition.
The Trade-offs: Limitations and Considerations
While powerful, tube furnaces are not without limitations. Acknowledging these is key to making an informed decision.
Sample Size and Throughput Constraints
The diameter of the process tube inherently limits the size of the sample that can be processed. For bulk material processing, the throughput of a single furnace may be a limiting factor compared to other industrial furnace types.
Temperature Gradients at Tube Ends
Achieving perfect temperature uniformity across the entire length of the tube is challenging. The ends of the tube, which are often less insulated or exposed to the outside, tend to be cooler than the center. This "end effect" must be accounted for in process design, often by ensuring the sample resides entirely within the central hot zone.
Consumable and Maintenance Costs
High-performance components like high-purity process tubes and heating elements are consumables with a finite lifespan, especially under extreme temperatures or reactive atmospheres. The cost and downtime associated with replacing these parts should be factored into the total cost of ownership.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your final choice should be dictated by your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is R&D or material discovery: Prioritize a versatile split-tube furnace with a transparent quartz tube to maximize accessibility and process observation.
- If your primary focus is consistent batch processing: A vertical furnace often provides superior temperature uniformity and simplified loading for repeatable, high-quality results.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial decomposition: Seek a robust system designed for continuous operation, high thermal efficiency, and the ability to scale by adding more units.
Ultimately, understanding these core advantages empowers you to select a tube furnace not just as a piece of equipment, but as a precise tool tailored to your specific process goals.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Precise Temperature Control | Ensures consistent reaction rates and high product quality |
| Uniform Heating | Prevents hot/cold spots for reliable thermal processing |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Allows inert or reactive gases to guide chemical reactions |
| High Thermal Efficiency | Reduces energy costs and improves operational economy |
| Scalability | Supports applications from lab research to industrial production |
| Real-time Observation | Enables visual monitoring for process development and troubleshooting |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced tube furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs—whether for chemical cracking, material decomposition, or other high-temperature applications. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your efficiency, control, and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















