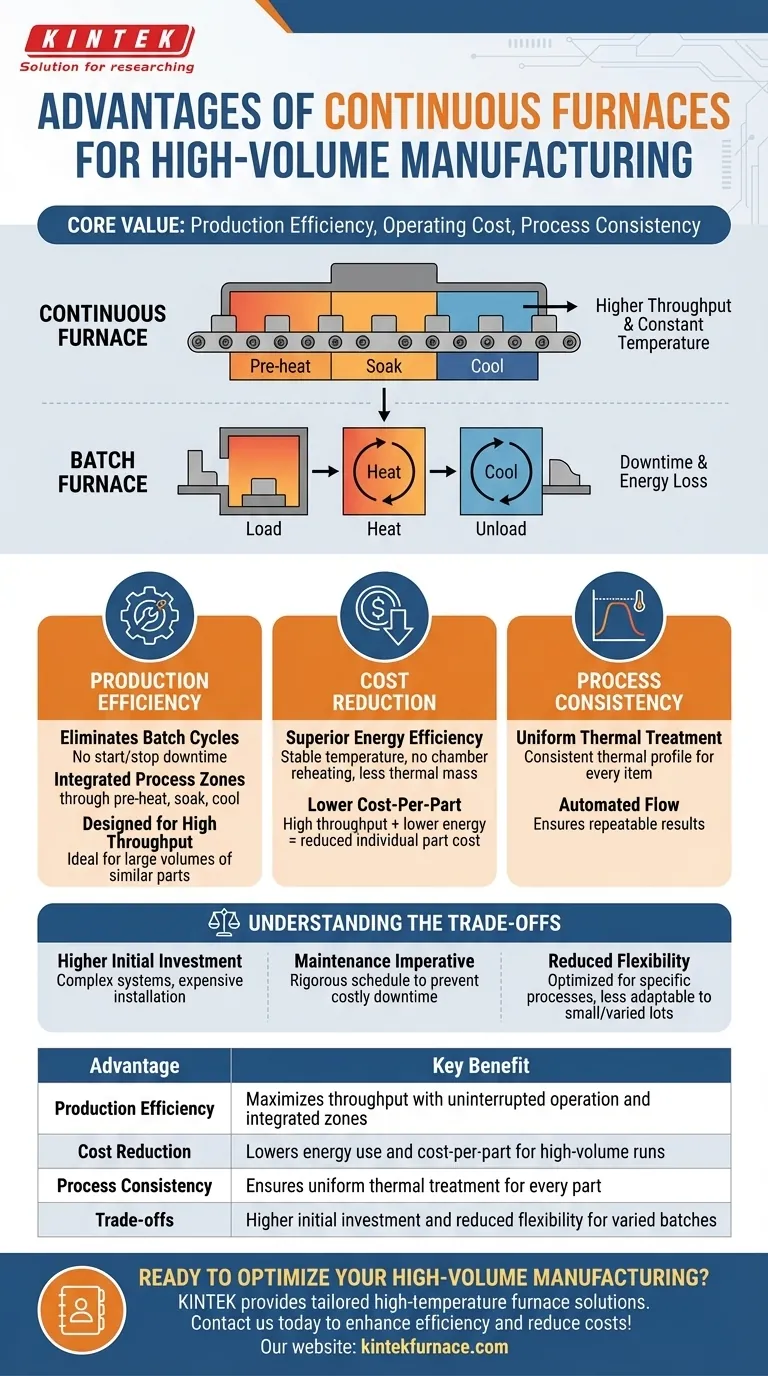
At their core, continuous furnaces provide significant advantages in production efficiency, operating cost, and process consistency for high-volume manufacturing. Unlike batch furnaces that heat and cool in cycles, continuous furnaces maintain a constant operating temperature and process parts in an uninterrupted flow. This design streamlines the heat treatment process, leading to higher throughput and lower energy consumption per part.
The fundamental trade-off is one of scale. While continuous furnaces require a higher initial investment and are less flexible, they dramatically lower the per-part cost in high-volume, repetitive manufacturing environments by optimizing energy use and maximizing throughput.

The Primary Driver: Production Efficiency
The most significant advantage of a continuous furnace is its ability to maximize output. This is achieved through a design philosophy centered on uninterrupted operation.
Eliminating the Batch Cycle
Continuous furnaces operate without stopping, processing a steady stream of products. This eliminates the downtime inherent in batch systems, where the furnace must be loaded, heated, cooled, and unloaded for each cycle.
Integrated Process Zones
These furnaces are often designed with multiple zones for pre-heating, soaking, and cooling. Parts move automatically through each stage, which shortens the total processing time and ensures a consistent thermal profile for every item.
Designed for High Throughput
The combination of continuous operation and rapid processing cycles makes these furnaces the ideal solution for high-volume manufacturing. They are engineered to handle a large quantity of similar parts with maximum efficiency.
A Deeper Look at Cost Reduction
Beyond speed, the design of a continuous furnace directly translates into lower long-term operating costs in the right application.
Superior Energy Efficiency
A continuous furnace maintains a stable temperature in its heating zones, avoiding the massive energy loss of repeatedly heating and cooling an entire furnace chamber. Furthermore, they often do not require heavy fixtures like baskets or racks, which reduces the total thermal mass that needs to be heated with each part.
Lower Cost-Per-Part
By combining high throughput with lower energy consumption, the operational cost attributed to each individual part is significantly reduced. This makes continuous furnaces a highly cost-effective choice for mass production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is a universal solution. The advantages of a continuous furnace come with specific limitations that make it unsuitable for certain operations.
Higher Initial Investment
Continuous furnaces are complex systems that are more expensive to purchase, install, and commission compared to their batch counterparts. This high upfront cost is a primary consideration.
The Maintenance Imperative
To ensure reliable, continuous operation and prevent costly downtime, these furnaces require a rigorous and often more frequent maintenance schedule. Their complexity can also make repairs more involved.
Reduced Flexibility
A continuous furnace is typically optimized for a specific process and part type. They lack the flexibility of batch furnaces to easily handle small, varied lots or frequent changes in processing requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on your production goals and operational realities.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repetitive production: A continuous furnace offers the lowest cost-per-part and the highest throughput, making it the superior long-term investment.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse, low-volume batches: A batch furnace provides essential flexibility and a much lower initial cost, making it the more practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is process cleanliness and environmental compliance: A continuous vacuum furnace provides a sealed, controlled environment that prevents contamination and meets stringent regulatory standards.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is a strategic decision that directly impacts your operational efficiency and final product quality.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Production Efficiency | Maximizes throughput with uninterrupted operation and integrated zones |
| Cost Reduction | Lowers energy use and cost-per-part for high-volume runs |
| Process Consistency | Ensures uniform thermal treatment for every part |
| Trade-offs | Higher initial investment and reduced flexibility for varied batches |
Ready to optimize your high-volume manufacturing with advanced furnace solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and reduce costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput



















