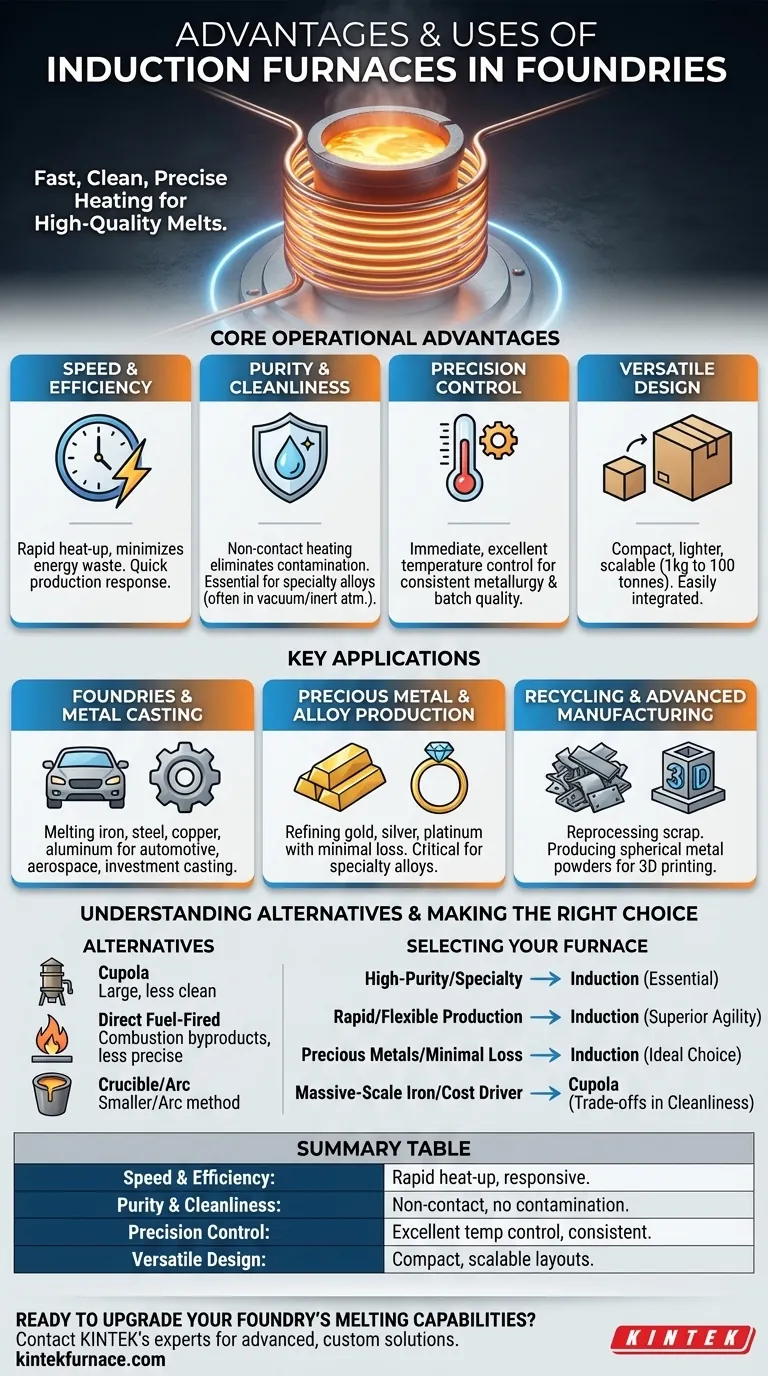
The primary advantages of induction furnaces in foundries are their exceptional speed, cleanliness, and precise temperature control. This clean, non-contact heating process allows for the production of high-quality, consistent metal melts for a wide range of materials, including iron, steel, copper, aluminum, and precious metals.
Induction furnaces offer a superior melting solution for modern foundries by using electromagnetic induction for fast, clean, and highly controllable heating. This eliminates combustion byproducts and direct contact with heating elements, resulting in higher purity alloys and greater operational efficiency.

Core Operational Advantages of Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces represent a significant technological leap over traditional melting methods. Their benefits stem directly from the fundamental physics of how they generate heat.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
An induction furnace's ability to generate heat directly within the metal itself leads to very quick heat-up times.
This rapid melting capability minimizes energy waste during startup and allows foundries to respond quickly to production demands, boosting overall efficiency.
Superior Purity and Cleanliness
The heating process is non-contact, meaning no heating element or flame touches the metal. This eliminates contamination from combustion byproducts like gas or soot.
This cleanliness is critical when producing specialty steels and alloys that would oxidize or become contaminated if heated in the presence of air. This is why they are often used in a vacuum or inert atmosphere.
Precision Temperature Control
The electromagnetic process allows for excellent and immediate temperature control.
This precision is vital for achieving consistent metallurgical properties and casting quality, batch after batch. It reduces the risk of overheating and ensures alloys meet exact specifications.
Compact and Versatile Design
Compared to older furnace types, induction furnaces are often smaller and lighter.
This makes them easier to install and integrate into various foundry layouts. Their design is also highly scalable, with sizes available to melt anything from one kilogram to one hundred tonnes.
Key Applications in Foundries and Beyond
The unique advantages of induction furnaces make them suitable for a wide range of critical applications where quality and consistency are paramount.
Foundries and Metal Casting
Induction furnaces are the standard in modern foundries for melting iron, steel, copper, and aluminum.
They are used to produce high-purity components for demanding sectors like the automotive, aerospace, and machinery industries. They are also a common choice for investment casting processes.
Precious Metal and Alloy Production
In refining gold, silver, and platinum, the efficiency of induction heating ensures minimal material loss.
The clean melting environment is also essential for manufacturing specialty alloys, where even minor impurities can compromise the final product's performance.
Recycling and Advanced Manufacturing
These furnaces are highly effective in reprocessing scrap metal due to their fast melting capabilities.
In advanced applications, they are integrated with other technologies to produce specialized materials, such as spherical metal powders for 3D printing and thermal spraying.
Understanding the Alternatives
To fully appreciate the role of induction furnaces, it's helpful to understand how they compare to other common furnace types used in foundries.
The Traditional Cupola Furnace
Cupolas are large, cylindrical furnaces that burn coke to melt iron. They are workhorses for very large-scale casting operations but are a less clean method compared to induction.
Direct Fuel-Fired Furnaces
These furnaces use natural gas, oil, or propane as a direct heat source. While versatile, they introduce combustion byproducts and offer less precise temperature control.
Crucible and Electric-Arc Furnaces
Crucible furnaces are simple and ideal for smaller-scale operations or precious metals. Electric-arc furnaces (EAFs) are also highly efficient and precise, but they use a high-energy electric arc rather than induction to melt the metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your specific production requirements for purity, volume, and material.
- If your primary focus is high-purity specialty alloys: The clean, non-contact nature and vacuum compatibility of an induction furnace are essential.
- If your primary focus is rapid, flexible production of various metals: The fast heat-up times and precise control of induction furnaces provide superior operational agility.
- If your primary focus is melting precious metals with minimal loss: The efficiency and contained nature of an induction furnace make it the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is massive-scale iron melting where initial cost is the driver: A traditional cupola furnace may still be a consideration, though with clear trade-offs in cleanliness.
Ultimately, adopting induction furnace technology empowers a foundry with the control, cleanliness, and efficiency required to meet modern manufacturing demands.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit for Foundries |
|---|---|
| Speed & Efficiency | Rapid heat-up times and quick melting for responsive production. |
| Purity & Cleanliness | Non-contact heating prevents contamination for high-quality alloys. |
| Precision Control | Excellent temperature control ensures consistent metallurgical properties. |
| Versatile Design | Compact and scalable for various foundry layouts and metal volumes. |
Ready to upgrade your foundry's melting capabilities?
KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions, backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, are designed to meet the demanding requirements of modern metal production. Whether you are melting specialty alloys, precious metals, or reprocessing scrap, our deep customization capabilities ensure a perfect fit for your unique operational goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace technology can bring superior efficiency, purity, and control to your production line.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















