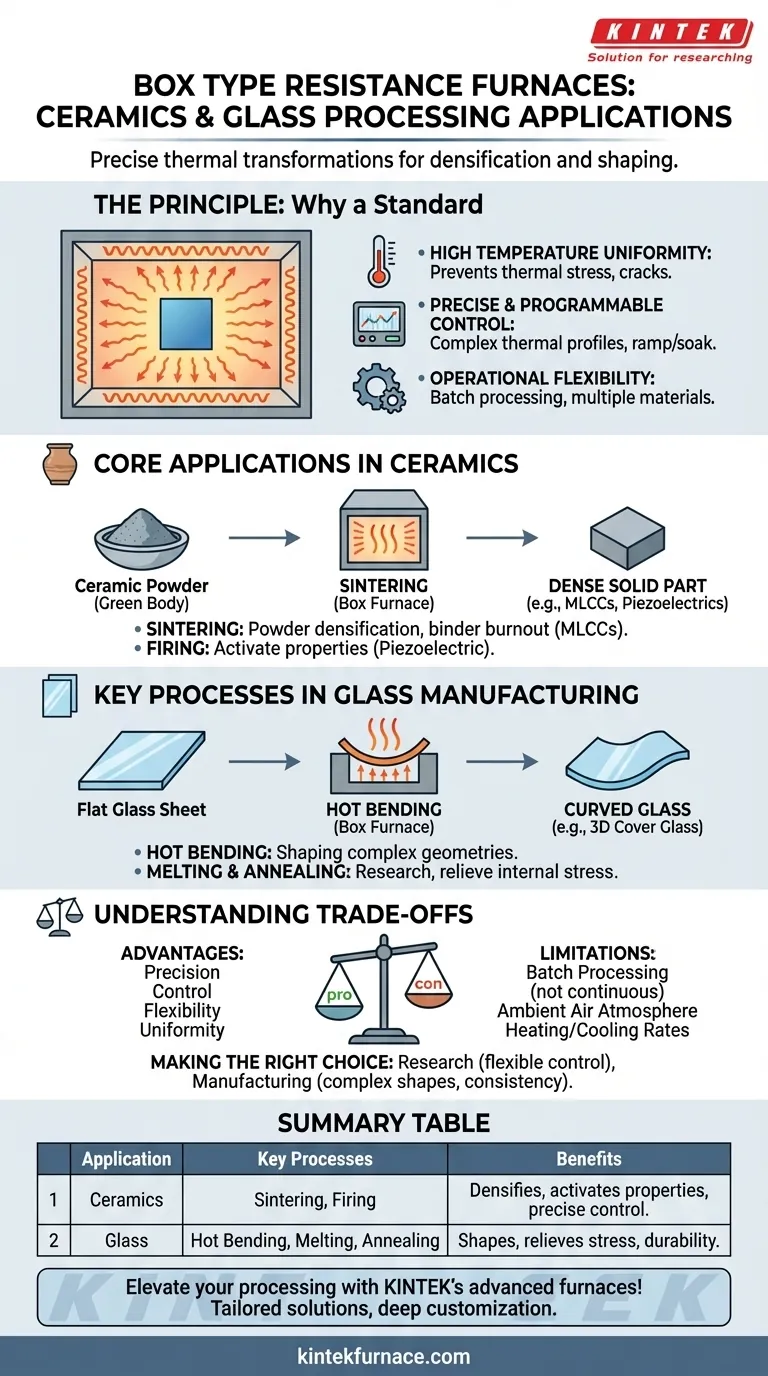
In ceramics and glass processing, the box-type resistance furnace is a fundamental tool for thermal transformation. It is primarily used for sintering to densify ceramic powders into solid components and for hot bending to shape flat glass into complex curved forms. These applications rely on the furnace's ability to deliver precise, uniform high-temperature environments.
The core value of a box-type resistance furnace lies not just in its ability to get hot, but in its capacity for controlled, uniform heating. This precision is what allows engineers and researchers to reliably transform raw glass and ceramic materials into finished products with specific structural and functional properties.
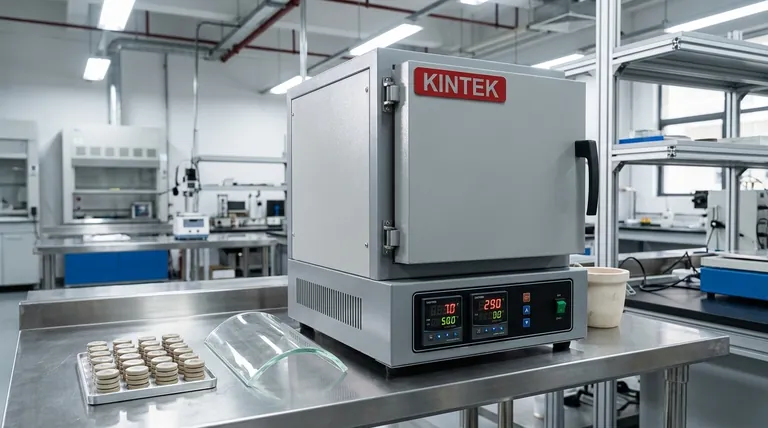

The Principle: Why Box Furnaces Are a Standard
A box-type resistance furnace is a deceptively simple piece of equipment. It uses resistive heating elements, typically wires or rods, to generate heat within an insulated chamber. This heat is transferred to the workpiece primarily through thermal radiation, ensuring excellent temperature uniformity.
High Temperature Uniformity
The enclosed, chamber-like design allows heat to radiate evenly from all sides. This uniformity is critical for preventing thermal stress, cracks, or warping in both ceramic and glass components during processing.
Precise and Programmable Control
Modern box furnaces feature sophisticated controllers that allow operators to program specific temperature profiles. This includes controlled ramp-up rates, extended soak times at a target temperature, and controlled cooling, which are essential for complex processes like multi-stage sintering or glass bending.
Operational Simplicity and Flexibility
Their straightforward design makes box furnaces reliable and easy to operate. Because they are not designed for a single, continuous process, they offer the flexibility to run different materials and thermal cycles, making them ideal for both production and research environments.
Core Applications in Ceramics Processing
In ceramics, the goal is often to convert a shaped "green" body, typically made of compressed powder, into a dense, hard, and durable final part. The box furnace is central to this transformation.
Sintering: From Powder to Solid Form
Sintering is the process of heating a compacted powder material to a high temperature (below its melting point) until its particles bond together. A box furnace provides the ideal environment for densifying materials like alumina or for specialized processes like the adhesive sintering of Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs), where organic binders must be carefully burned out before the ceramic layers are fused.
Firing: Activating Material Properties
Beyond densification, firing in a box furnace can activate unique properties. For instance, piezoelectric ceramics are heat-treated after polarization to lock in their ability to generate an electric charge in response to mechanical stress. This critical heat treatment step relies on the furnace's precise temperature control.
Key Processes in Glass Manufacturing
For glass, thermal processing is used to shape the material or to alter its internal stresses to improve strength and durability.
Hot Bending: Shaping Complex Geometries
Hot bending involves heating a flat sheet of glass until it becomes soft enough to sag and conform to the shape of a mold. Box furnaces are widely used for this, especially in producing items like the 3D curved cover glass for smartphones, where uniform heating is essential for a flawless, optically clear surface.
Melting and Annealing: For Research and Stability
In laboratory settings, smaller box furnaces are used for experimental glass melting to develop new formulations. They are also used for annealing, a process where glass is heated and then slowly cooled to relieve internal stresses, significantly increasing its strength and durability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While versatile, the box furnace is not the optimal solution for every thermal processing need. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Batch Processing vs. Continuous Flow
The primary characteristic of a box furnace is its suitability for batch processing. You load a part or batch of parts, run a cycle, and then unload them. This is less efficient for high-volume, standardized production compared to continuous-flow equipment like a tunnel kiln.
Atmosphere Control
A standard box furnace operates in an ambient air atmosphere. While sufficient for many applications, processes requiring a specific inert gas (like argon) or a vacuum to prevent oxidation demand more specialized and costly furnace designs.
Heating and Cooling Rates
While highly controllable, the thermal mass of a box furnace generally limits its maximum heating and cooling rates. For applications requiring extremely rapid thermal cycling, other specialized systems may be more appropriate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements will determine how you leverage a box furnace.
- If your primary focus is developing new materials: A box furnace is an indispensable laboratory tool for experimental sintering and heat treatment due to its precise, repeatable, and flexible thermal control.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing complex curved glass: The programmable heating and superior temperature uniformity of a box furnace are critical for achieving consistent hot bending results without optical defects.
- If your primary focus is producing specialized electronic components: A box furnace is essential for the multi-stage thermal profiles required for sintering advanced ceramics like MLCCs, ensuring proper binder burnout and final densification.
Ultimately, the box furnace is a cornerstone technology, enabling the precise thermal transformations required to create advanced ceramic and glass products.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramics Processing | Sintering, Firing (e.g., MLCCs, piezoelectric ceramics) | Densifies powders, activates properties with precise temperature control |
| Glass Manufacturing | Hot Bending (e.g., smartphone glass), Melting, Annealing | Shapes complex geometries, relieves stresses for durability |
Elevate your ceramics and glass processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise fit for your unique experimental needs in sintering, hot bending, and more. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















