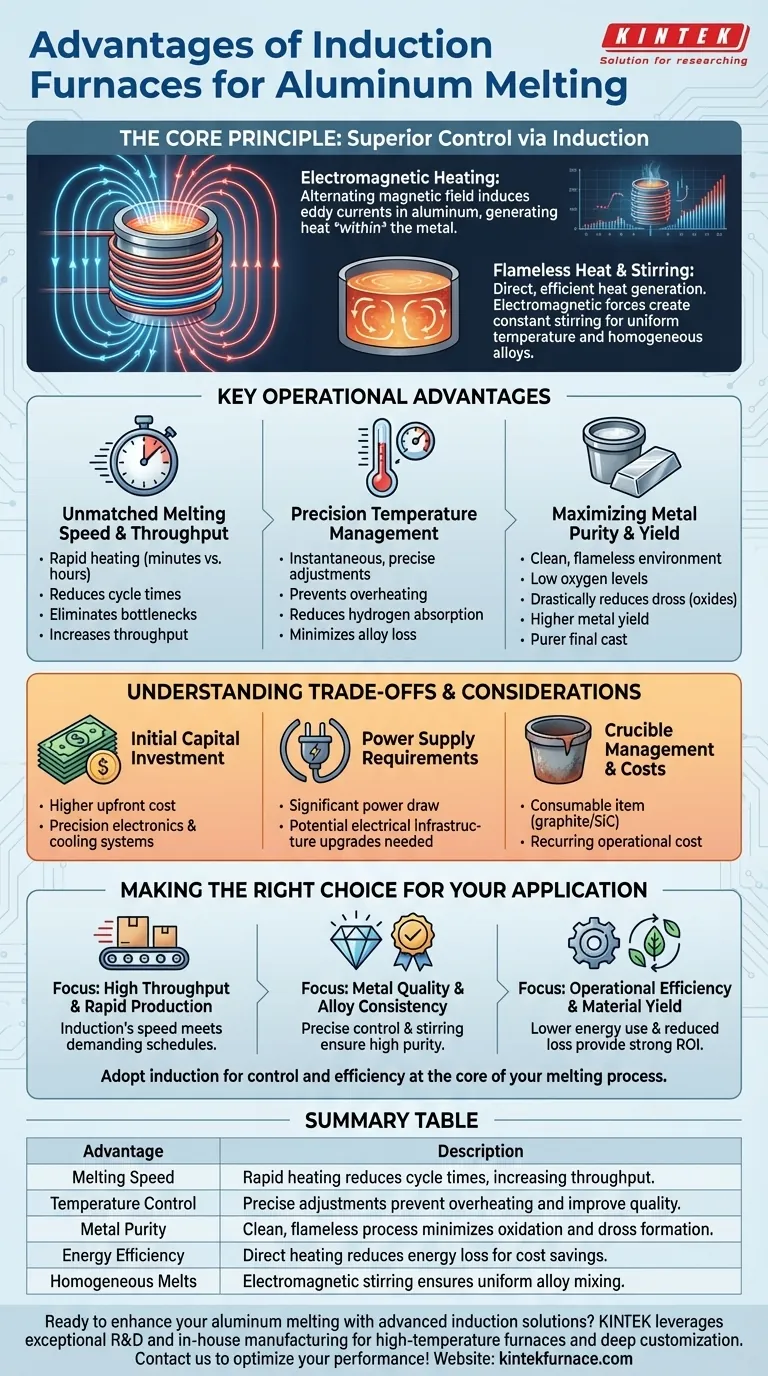
For melting aluminum, induction furnaces offer a combination of speed, efficiency, and quality control that is difficult to match with traditional methods. By generating heat directly within the metal itself, this technology provides rapid melting rates, precise temperature management, and a cleaner environment that preserves the integrity of the final product.
The primary advantage of induction furnaces is not just a list of benefits, but a fundamental shift in how heat is applied. By using electromagnetic fields instead of external combustion, you gain direct control over the melting process, which translates into higher quality, greater speed, and improved cost-effectiveness.
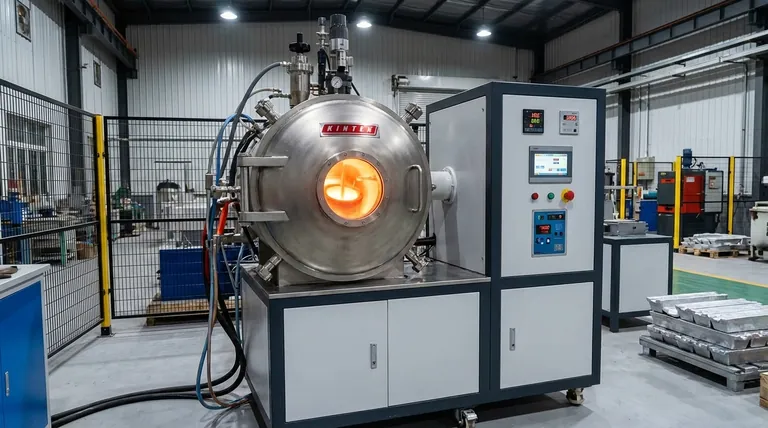

The Core Principle: How Induction Delivers Superior Control
To understand the advantages, you must first understand the mechanism. Induction furnaces do not burn fuel to create heat; they use electricity to generate it directly inside the material being melted.
Electromagnetic Heating Explained
An induction furnace uses a powerful coil to create a rapidly alternating magnetic field. When conductive material like aluminum is placed within this field, it induces strong electrical currents, known as eddy currents, to flow within the metal. The aluminum's natural resistance to these currents generates intense, rapid heat.
The Benefit of Flameless, Contact-Free Heat
Because heat is generated within the aluminum, the process is incredibly fast and efficient. There is no need to heat the chamber or crucible first and wait for that heat to transfer to the charge. This direct heating method minimizes energy loss to the surrounding environment.
Inherent Stirring for Homogeneous Melts
The same electromagnetic forces that generate heat also create a stirring action within the molten metal. This constant, gentle circulation ensures a uniform temperature throughout the melt and automatically mixes in alloys, leading to a highly consistent and homogeneous final product without mechanical stirrers.
Key Operational Advantages for Aluminum Foundries
The unique heating principle of induction translates directly into tangible operational benefits that address common challenges in aluminum melting.
Unmatched Melting Speed and Throughput
Induction systems can bring a charge to its melting point in minutes, sometimes seconds, rather than hours. This dramatic reduction in cycle time allows for a more continuous workflow, eliminates production bottlenecks, and significantly increases the overall throughput of a facility.
Precision Temperature Management
Induction allows for nearly instantaneous and highly precise temperature adjustments. This control is critical for aluminum, as it prevents overheating, which can lead to increased hydrogen absorption, dross formation, and the loss of valuable alloying elements.
Maximizing Metal Purity and Yield
Since there is no combustion, the melting environment is exceptionally clean and has very low oxygen levels. This drastically reduces the formation of oxides (dross), resulting in a higher metal yield from your charge material and a purer final cast. The specialized ceramic or graphite crucibles used also prevent contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, induction technology is not a universal solution without its own set of considerations. Acknowledging these is key to making a sound investment decision.
Initial Capital Investment
Induction furnace systems typically require a higher upfront capital expenditure compared to traditional gas-fired furnaces. The precision electronics, power supplies, and cooling systems contribute to this initial cost.
Power Supply Requirements
These furnaces draw a significant amount of electrical power. Facilities may need to upgrade their electrical infrastructure to support the system's demands, which can be an additional and substantial project cost.
Crucible Management and Costs
The crucible, which holds the molten aluminum, is a consumable item with a finite lifespan. Made from materials like graphite or silicon carbide, these crucibles represent a recurring operational cost that must be factored into any total cost of ownership analysis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Aluminum Application
The decision to use an induction furnace should be aligned with your specific production goals and priorities.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and rapid production: Induction's unparalleled melting speed is its defining advantage for meeting demanding production schedules.
- If your primary focus is metal quality and alloy consistency: The precise temperature control and inherent electromagnetic stirring of induction are critical for creating high-purity, homogeneous melts.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and material yield: The lower energy consumption and significantly reduced metal loss from oxidation often provide a strong return on the initial investment.
Ultimately, adopting induction technology is a strategic decision to prioritize control and efficiency at the core of your melting process.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Melting Speed | Rapid heating reduces cycle times, increasing throughput. |
| Temperature Control | Precise adjustments prevent overheating and improve quality. |
| Metal Purity | Clean, flameless process minimizes oxidation and dross formation. |
| Energy Efficiency | Direct heating reduces energy loss for cost savings. |
| Homogeneous Melts | Electromagnetic stirring ensures uniform alloy mixing. |
Ready to enhance your aluminum melting process with advanced induction furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique needs, delivering higher throughput, superior metal quality, and operational efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















