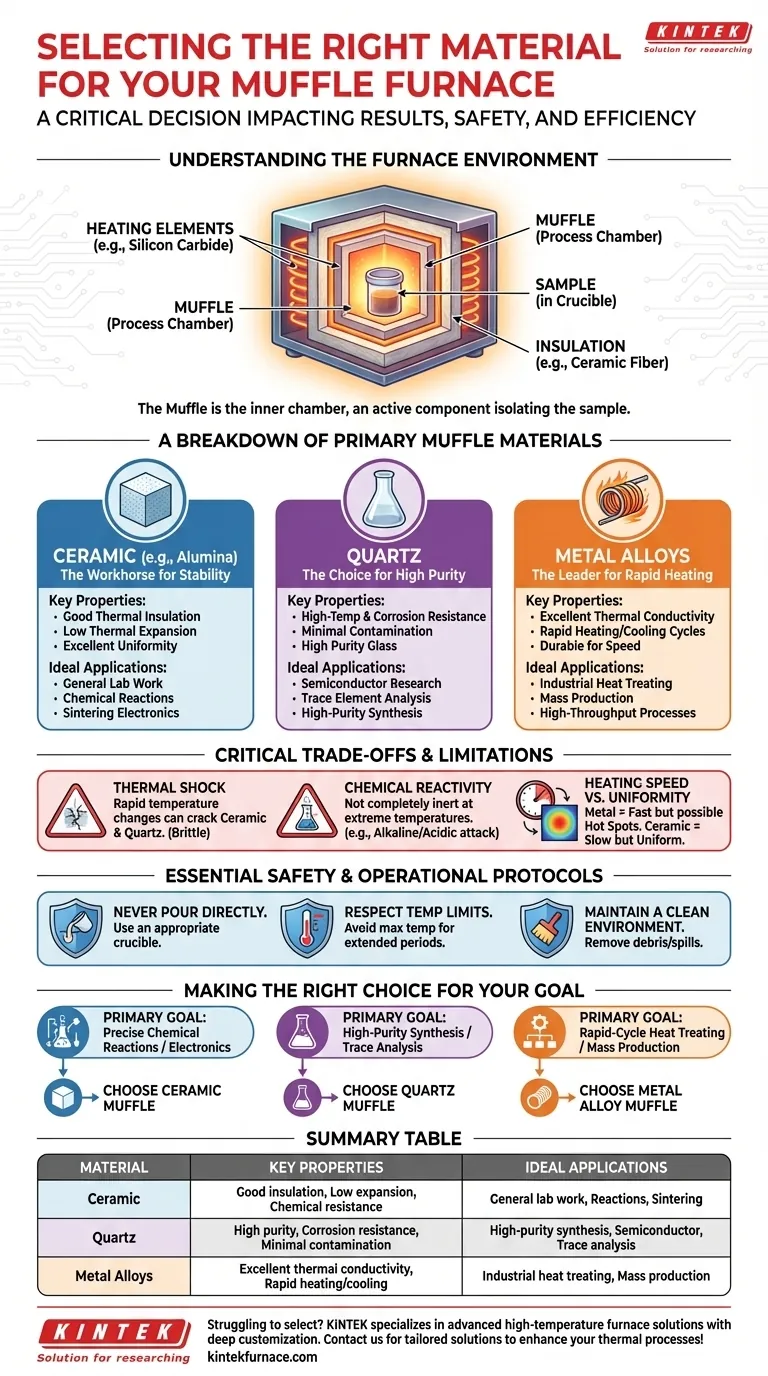
The right material selection for a muffle furnace is not a simple choice but a critical decision that directly impacts your results. The selection hinges on three primary factors: the maximum temperature of your process, the chemical reactivity of your samples, and your need for heating speed versus thermal stability. The most common materials for the furnace's inner chamber, or "muffle," are ceramic, quartz, and specialized metal alloys, each with a distinct purpose.
The core takeaway is that the furnace muffle is not a passive container; it is an active component in your thermal process. Your choice is a strategic trade-off between the chemical inertness and stability of ceramics and the rapid thermal conductivity of metals, dictated entirely by the goals of your experiment or production run.
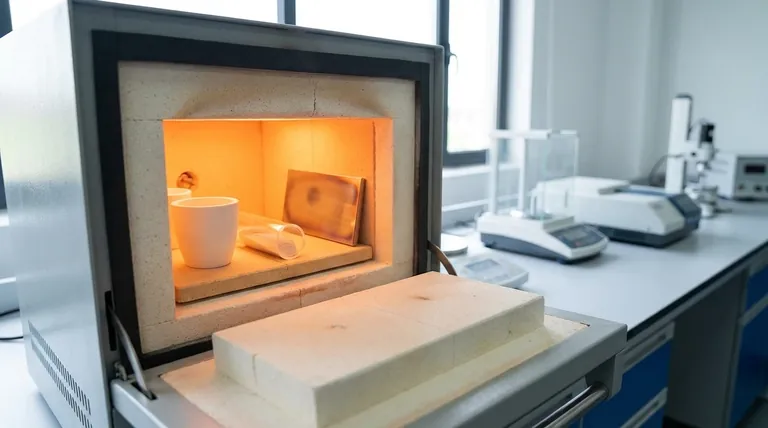

Understanding the Furnace Environment
A muffle furnace creates a controlled, high-temperature environment by isolating the sample from the heating elements. Understanding its key parts clarifies why material selection is so crucial.
The Muffle: Your Process Chamber
The muffle is the inner chamber that holds your sample. It is constructed from a refractory material designed to withstand extreme heat and protect the sample from direct contact with the heating elements, preventing contamination.
Heating Elements and Insulation
Elements like silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide surround the muffle, radiating heat inward. High-grade insulation, such as ceramic fiber, surrounds the entire assembly to minimize heat loss and ensure temperature stability. Your choice of muffle material must work in concert with this system.
A Breakdown of Primary Muffle Materials
Each material offers a unique combination of properties. Your application will determine which one is the appropriate choice.
Ceramic: The Workhorse for Stability
Ceramic muffles, often made of materials like alumina, are the most common choice for general-purpose laboratory work. They offer an excellent balance of properties.
Their key advantages are good thermal insulation and a low coefficient of thermal expansion. This makes them highly resistant to heat and stable during slow temperature changes, ensuring uniform heating for sensitive processes like chemical reactions or sintering electronic components.
Quartz: The Choice for High Purity
Quartz is a type of high-purity glass with exceptional high-temperature and corrosion resistance. It is the ideal material when sample purity is the absolute top priority.
It is transparent to certain wavelengths of radiation and is exceptionally clean, introducing minimal contamination into the process. This makes it a top choice for semiconductor research and trace element analysis where even minute impurities can compromise results.
Metal Alloys: The Leader for Rapid Heating
Muffles made from high-temperature metal alloys are designed for industrial applications and processes that require speed. Their defining characteristic is excellent thermal conductivity.
This allows for very rapid heating and cooling cycles, making them perfect for high-throughput heat treating and mass production environments where cycle time is a critical economic factor.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Limitations
No material is perfect. Acknowledging the trade-offs is essential for preventing failed experiments and equipment damage.
Thermal Shock: The Enemy of Ceramic and Quartz
Both ceramic and quartz are brittle. Rapid changes in temperature—heating or cooling too quickly—can create internal stresses that cause them to crack. This is the single most common failure mode for these materials.
Chemical Reactivity at Temperature
While generally inert, no material is completely non-reactive at extreme temperatures. Highly alkaline or acidic substances can slowly etch ceramic or quartz surfaces over time, especially at the furnace's maximum operating temperature.
Heating Speed vs. Uniformity
There is a direct trade-off here. Metal muffles heat very quickly but can sometimes create temperature gradients or "hot spots." Ceramic muffles heat much more slowly but provide superior temperature uniformity once they reach a thermal equilibrium, which is critical for sensitive processes.
Essential Safety and Operational Protocols
The material you choose is only as good as your operating procedure. Following these rules is non-negotiable for safety and equipment longevity.
Never Pour Materials Directly
It is strictly forbidden to pour any liquid, powder, or molten metal directly into the furnace chamber. Always use an appropriate crucible or container made of a compatible material to hold your sample.
Respect the Temperature Limits
Never operate the furnace above its maximum rated temperature. Furthermore, avoid running the furnace at its absolute maximum temperature for extended periods, as this drastically shortens the life of both the heating elements and the muffle.
Maintain a Clean Environment
Keep the furnace chamber clean of debris and spills. Contaminants can become fused to the muffle surface at high temperatures, causing damage and compromising future experiments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use this guide to make a definitive decision based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is precise chemical reactions or processing electronics: A ceramic or alumina muffle provides the best combination of chemical resistance and thermal uniformity.
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis or trace analysis: A quartz muffle is the superior choice to minimize the risk of sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is rapid-cycle heat treating or mass production: A metal alloy muffle offers the fastest heating rates and durability required for industrial throughput.
By matching the material to your specific process requirements, you ensure not only the success of your work but also the safety and longevity of your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Properties | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic | Good thermal insulation, low thermal expansion, chemical resistance | General lab work, chemical reactions, sintering electronics |
| Quartz | High purity, corrosion resistance, minimal contamination | High-purity synthesis, semiconductor research, trace analysis |
| Metal Alloys | Excellent thermal conductivity, rapid heating/cooling | Industrial heat treating, mass production, high-throughput processes |
Struggling to select the right muffle furnace material for your lab's unique needs? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely match your experimental requirements—ensuring optimal performance, safety, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















