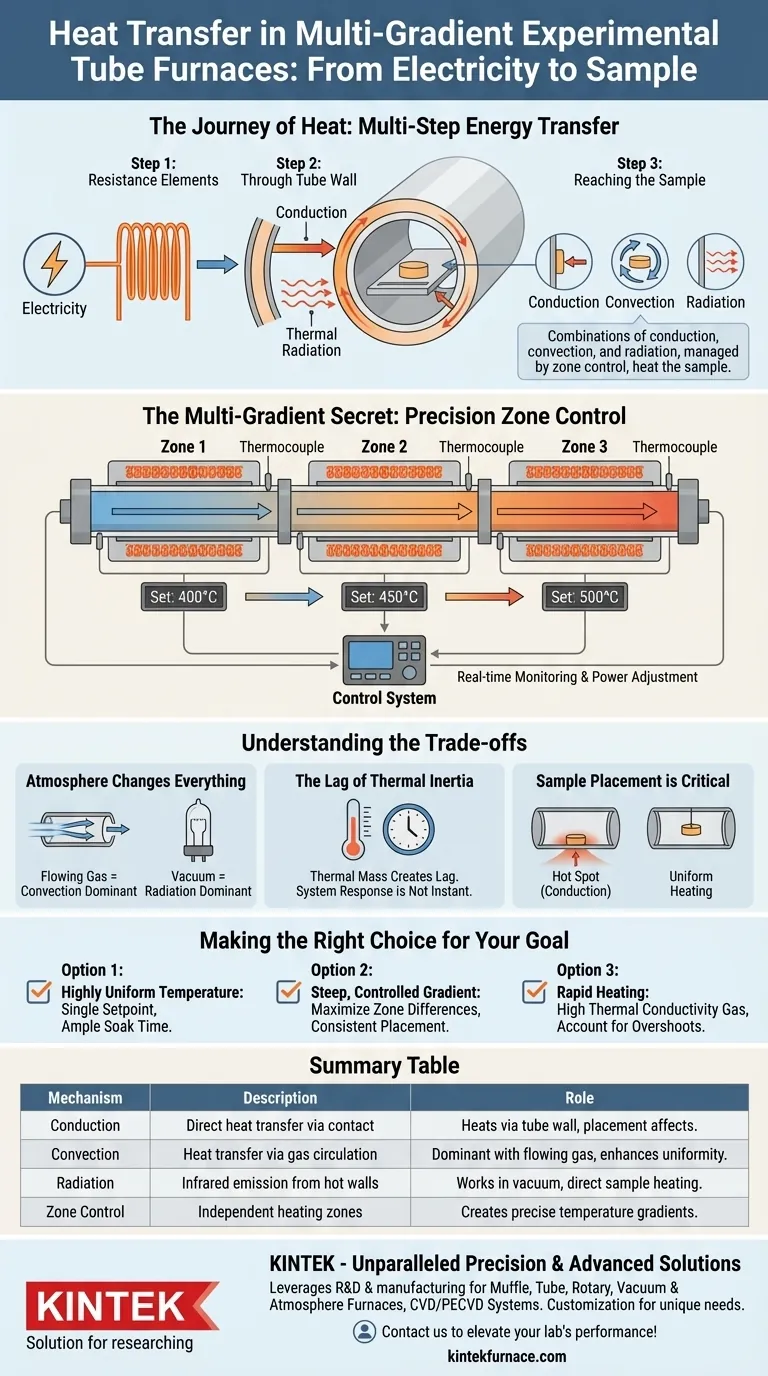
In a multi-gradient experimental tube furnace, heat is not simply applied; it is meticulously managed. The sample is heated through a combination of three fundamental mechanisms—conduction, convection, and thermal radiation—all orchestrated by a sophisticated control system that uses multiple, independent heating zones to create a precise temperature profile along the length of the tube.
A multi-gradient furnace works by converting electricity into thermal energy within distinct zones. This energy then travels through the furnace tube wall via conduction and is subsequently delivered to the sample inside through a mix of gas convection and direct radiation from the hot tube walls.
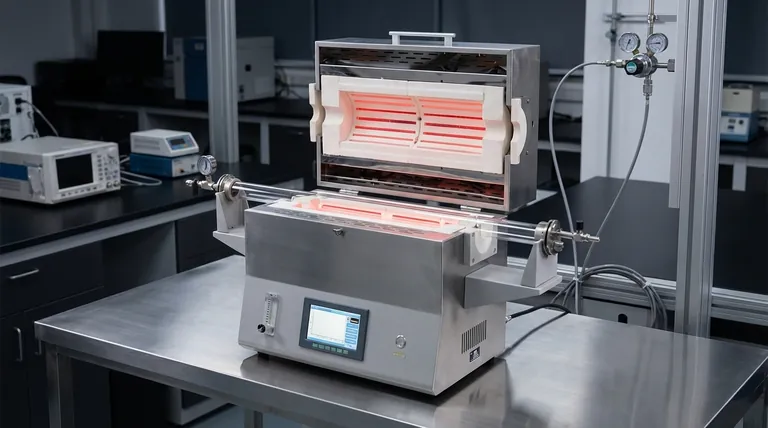

The Journey of Heat: From Electricity to Sample
Understanding the path heat takes is critical to controlling your experimental outcomes. The process is a multi-step energy transfer, managed at every stage.
Step 1: Generating Heat with Resistance Elements
The process begins with resistance heating elements. These components, which surround the furnace tube, convert electrical energy directly into thermal energy.
The amount of heat generated is precisely controlled by the power supplied to each element.
Step 2: Transfer Through the Tube Wall
This initial thermal energy is transferred to the outer wall of the furnace tube primarily through thermal conduction (direct contact) and thermal radiation from the hot elements.
The furnace tube, typically made of a ceramic or quartz material, acts as the first barrier and the primary vessel for the experiment.
Step 3: Reaching the Sample
Once the inner wall of the tube is hot, the heat must reach your sample. This happens in three ways simultaneously:
- Conduction: If the sample is in direct physical contact with the tube wall, heat transfers directly.
- Convection: The gas or atmosphere inside the tube heats up, circulates, and transfers heat to the sample. This is often the dominant mechanism in furnaces operating with a flowing gas.
- Radiation: The hot inner walls of the furnace tube emit infrared radiation, which travels through the internal atmosphere (even a vacuum) and is absorbed by the sample, heating it directly.
The "Multi-Gradient" Secret: Precision Zone Control
The defining feature of a multi-gradient furnace is its ability to create a non-uniform temperature profile. This is not achieved with a single heater but with several.
How Multiple Zones Create a Gradient
The furnace is constructed with multiple, independently controlled heating zones arranged along its length.
Each zone can be set to a different target temperature. By setting adjacent zones to different temperatures—for example, 400°C, 450°C, and 500°C—a smooth and predictable temperature gradient is established along the sample.
The Role of Sensors and Controllers
This precision is impossible without a constant feedback loop. Temperature sensors, almost always thermocouples, are placed in each zone to monitor the temperature in real time.
These sensors feed data back to the central control system. The controller constantly compares the actual temperature of each zone to its setpoint and adjusts the electrical power to the corresponding heating elements to eliminate any deviation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Mastering the furnace requires understanding its inherent physical limitations and how they impact heat transfer.
Atmosphere Changes Everything
The medium inside the tube dramatically affects heat transfer. An experiment run under a high-flow inert gas will be dominated by convection.
Conversely, an experiment run under a vacuum will nearly eliminate convection, making radiation the primary method of heating the sample. This can lead to very different heating rates and temperature uniformities.
The Lag of Thermal Inertia
Materials do not heat or cool instantly. The furnace components and the sample itself have a thermal mass that creates a lag.
The control system is designed to anticipate and manage this, but rapid changes in setpoints will always be limited by the time it takes for the system to physically respond.
Sample Placement is Critical
A sample resting on the bottom of the tube will heat differently than one suspended in the center. Contact with the wall introduces strong conduction, which can create a "hot spot" and an unintended local gradient across the sample itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use your understanding of the furnace's operation to optimize your experimental setup for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is a highly uniform temperature: Use a single temperature setpoint across all zones and allow ample soak time for the system to reach thermal equilibrium, ensuring convection and radiation have evenly heated the sample.
- If your primary focus is a steep, controlled gradient: Maximize the temperature difference between adjacent zones and ensure your sample is positioned consistently to receive predictable heat from each zone.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating: Recognize the limits of thermal inertia. Use a carrier gas with high thermal conductivity to enhance convective heat transfer, but account for potential temperature overshoots.
By understanding how heat is generated, transferred, and controlled, you can move from simply using the equipment to truly mastering it for repeatable and accurate results.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Description | Role in Multi-Gradient Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Direct heat transfer through contact | Heats sample via tube wall, affected by placement |
| Convection | Heat transfer via gas circulation | Dominant with flowing gas, enhances uniformity |
| Radiation | Infrared energy emission from hot walls | Works in vacuum, direct sample heating |
| Zone Control | Independent heating zones | Creates precise temperature gradients along tube |
Ready to achieve unparalleled precision in your high-temperature experiments? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique experimental needs are met with reliability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can elevate your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















