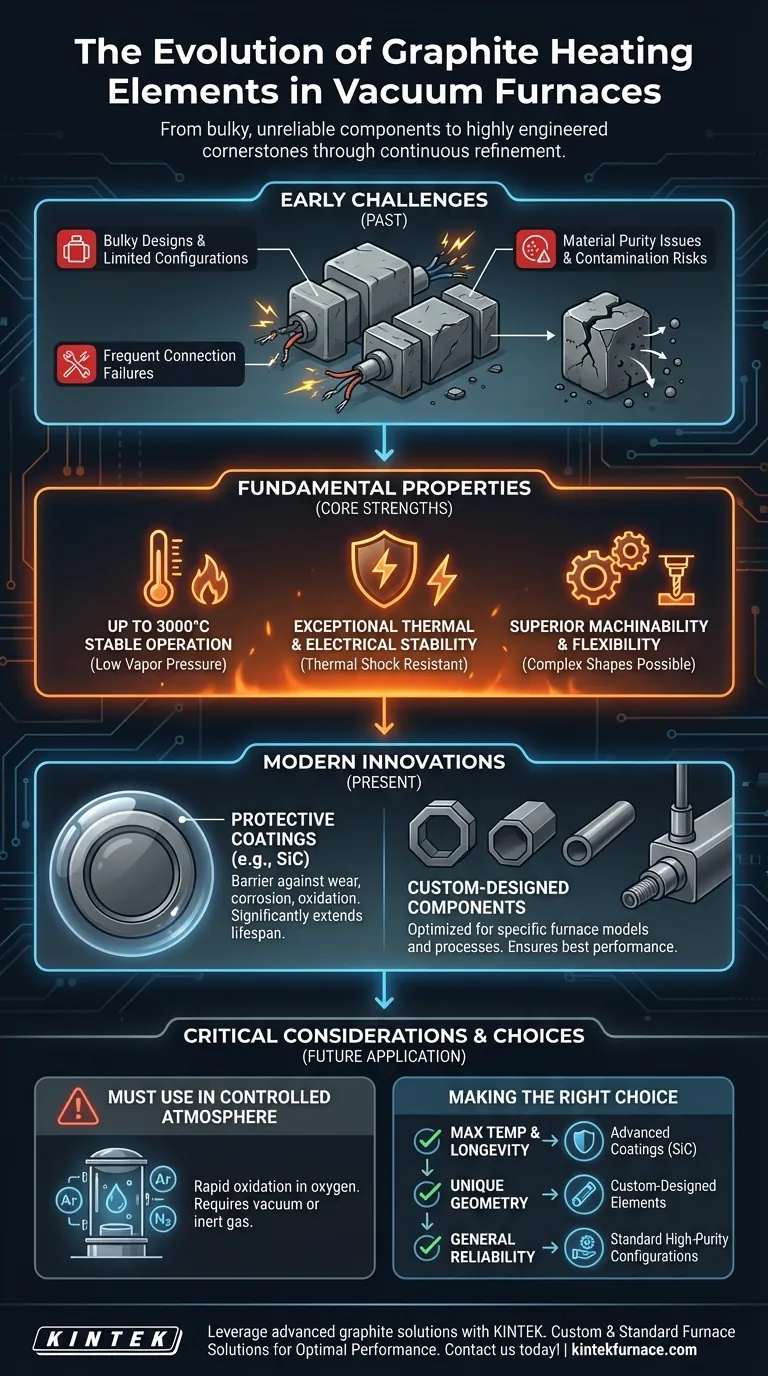
To put it simply, graphite heating elements have evolved from bulky, unreliable components into highly engineered, customizable cornerstones of modern vacuum furnaces. Early designs suffered from limited configurations, frequent electrical connection failures, and material purity issues. These challenges have been systematically overcome through advances in material science, manufacturing precision, and the development of protective surface coatings.
The evolution of graphite heating elements is not a story of a single invention, but of continuous refinement. Modern graphite's success comes from solving early design flaws while leveraging its exceptional inherent properties through advanced coatings and custom engineering.
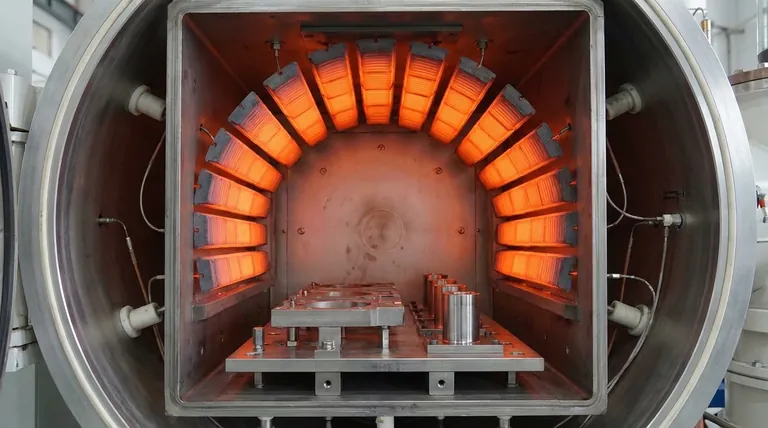
From Early Challenges to Modern Reliability
The journey of graphite in vacuum furnaces has been one of solving practical engineering problems to unlock the material's immense potential.
Overcoming Design and Connection Failures
Early graphite elements were often bulky and offered few design options. More importantly, their electrical connection points were a common point of failure, leading to costly downtime.
Modern elements are available in a wide array of configurations, including 360° circular or octagonal arrangements and flat strip or tubular forms. These designs are not only versatile for different hot zone shapes but are also engineered for simple installation and robust, reliable electrical connections.
Solving the Contamination Problem
There were initial concerns that impurities within the graphite could leach out at high temperatures, reacting unfavorably with the furnace load.
Today, highly refined manufacturing and purification processes produce an extremely pure and chemically inert material. This ensures that modern graphite elements do not contaminate the vacuum environment or the materials being processed.
The Fundamental Properties Driving Graphite's Success
Graphite's evolution was possible because its core properties make it uniquely suited for high-temperature vacuum applications.
Unmatched High-Temperature Performance
Graphite can operate stably at temperatures up to 3000°C within a vacuum or inert atmosphere, a ceiling few other materials can approach.
This is due to its extremely high melting point and a low vapor pressure, meaning it doesn't sublimate or break down easily in a vacuum environment.
Exceptional Thermal and Electrical Stability
Graphite has a low coefficient of thermal expansion and superior resistance to thermal shock. It can handle rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking or degrading.
Its good electrical conductivity and low resistivity are precisely what allow it to generate heat efficiently and uniformly when a current is applied.
Superior Machinability and Design Flexibility
Unlike many high-temperature metals, graphite is relatively easy to machine. This property allows for the creation of intricate and complex shapes, which has been critical to its evolution.
This ease of machining directly enables the custom-designed elements that are now common for specialized applications.
Key Innovations in Modern Graphite Elements
Recent advancements have moved beyond fixing old problems to actively enhancing graphite's performance and lifespan.
Protective Coatings for Extended Lifespan
Modern graphite components are often treated with advanced coatings, such as silicon carbide (SiC).
These coatings form a protective barrier that shields the graphite from wear, corrosion, and oxidation, significantly extending the service life of the heating element.
Custom-Designed Components for Optimized Processes
It is now common practice to create custom-designed graphite parts for specific furnace models and processes.
This approach optimizes properties like the element's temperature range and chemical resistance, ensuring the best possible performance and uniformity for a particular application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While modern graphite is exceptionally capable, its performance is context-dependent.
The Critical Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
Graphite's remarkable high-temperature stability is entirely dependent on its environment. When heated in the presence of oxygen, it will rapidly oxidize and degrade.
For this reason, graphite heating elements are exclusively used in vacuum furnaces or furnaces with a controlled inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen).
Material Compatibility
Although modern graphite is chemically inert for most processes, it's still crucial to consider its interaction with the specific materials being heat-treated.
In certain niche applications, direct contact between graphite and a particular metal at very high temperatures could still be a concern, which is where protective coatings provide an essential barrier.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct graphite element configuration depends entirely on your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and longevity: Seek out elements treated with advanced protective coatings like silicon carbide to prevent degradation.
- If your primary focus is a unique furnace geometry or process: Prioritize a supplier who offers custom-designed elements to ensure optimal fit and temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose reliability: Standard circular or strip configurations made from high-purity graphite are an excellent and proven choice for a wide range of applications.
By understanding this evolution, you can confidently select modern graphite heating elements that deliver precise and reliable performance for your high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Evolution Milestone | Key Advancement | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Early Designs | Limited configurations, unreliable connections | Frequent downtime, poor uniformity |
| Modern Elements | Custom shapes (circular, strip, tubular), robust connections | Enhanced reliability, easy installation |
| Material Purity | High-purity graphite, advanced purification | Chemically inert, no contamination |
| Protective Coatings | Silicon carbide (SiC) coatings | Extended lifespan, oxidation resistance |
| Temperature Range | Stable operation up to 3000°C | Superior to most alternative materials |
Ready to leverage the latest advancements in graphite heating elements for your vacuum furnace?
At KINTEK, we combine exceptional R&D with in-house manufacturing to deliver advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Whether you require standard configurations or deeply customized elements for specialized applications, our expertise in graphite technology ensures optimal performance, longevity, and temperature uniformity.
Contact us today to discuss how our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems can enhance your lab's capabilities. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- Why is graphite a preferred material for heating elements in high-temperature vacuum furnaces?
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability



















