In short, vacuum brazing is a high-purity material joining process where a filler metal is melted between two components inside a vacuum furnace. The vacuum prevents oxidation, allowing the filler metal to flow via capillary action and form an exceptionally strong, clean, and uniform joint upon cooling without melting the base materials themselves.
The critical insight is that the vacuum is not just an incidental part of the process; it is the enabling factor. By removing atmospheric contaminants, the vacuum creates a chemically pure environment where the filler metal can perfectly wet and bond with the parent materials, resulting in a joint quality that is often impossible to achieve with other methods.

The Fundamental Principle: Joining Without Melting
Vacuum brazing operates on a simple but elegant principle: you can join two parts together without melting them. This is achieved by introducing a third material—the filler—that has a lower melting point.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The entire process hinges on the brazing filler metal. This material, often an alloy in the form of a paste, foil, or wire, is selected to have a melting point (liquidus temperature) that is lower than that of the components being joined.
When the assembly is heated, only the filler melts, leaving the parent materials in their solid state.
Capillary Action: The Driving Force
Once molten, the filler metal is drawn into the tight gap between the two components through a phenomenon called capillary action. This is the same force that pulls water up a narrow tube.
For this to work effectively, the parts must be designed with a very small, controlled clearance between them. The filler flows into this gap, completely wetting the surfaces to be joined.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
Performing this process in a vacuum furnace is what separates it from other forms of brazing. The vacuum, typically a very low-pressure environment, removes oxygen and other reactive gases.
This prevents the formation of oxides on the surface of the metal parts as they are heated. Oxides act as a barrier, preventing the filler metal from properly bonding to the parent material and creating a weak, unreliable joint.
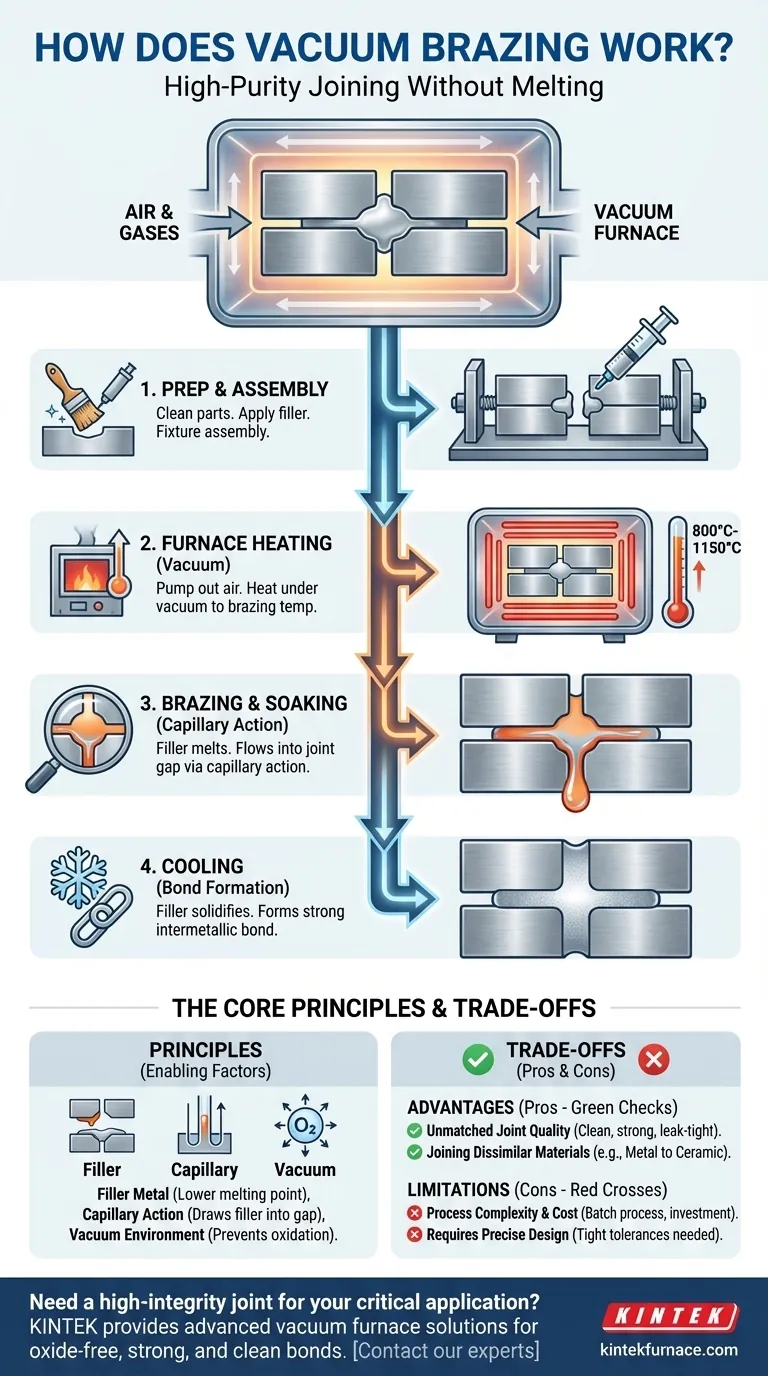
The Step-by-Step Vacuum Brazing Process
The process is a carefully controlled thermal cycle performed within a specialized vacuum furnace capable of reaching temperatures over 1200°C.
Step 1: Preparation and Assembly
The components to be joined must be meticulously cleaned to remove any oils, dirt, or other contaminants. The filler metal is then applied to the joint area, and the parts are carefully assembled and held in position with fixtures.
Step 2: The Furnace Cycle - Heating
The assembly is loaded into the vacuum furnace. The air is pumped out to create the required vacuum level, and the furnace then begins to heat the components.
The temperature is raised in a controlled manner to the specified brazing temperature, which is always above the melting point of the filler but below the melting point of the parent materials. This typically falls between 800°C and 1150°C.
Step 3: The Furnace Cycle - Brazing and Soaking
Once at temperature, the assembly is "soaked" for a short period, often around 10 minutes. During this time, the filler metal becomes fully molten and flows via capillary action to fill the joint completely.
Step 4: The Furnace Cycle - Cooling
After the soak, the assembly is slowly and uniformly cooled. As the temperature drops below the filler metal's solidification point (solidus temperature), the filler freezes, forming a strong, permanent intermetallic bond between the components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum brazing is a specialized technique with distinct advantages and limitations.
Key Advantage: Unmatched Joint Quality
The primary benefit is the creation of an extremely clean, strong, and leak-tight joint. The absence of oxides and flux contaminants results in a bond with superior structural integrity and a clean, bright finish that requires no post-process cleaning.
Key Advantage: Joining Dissimilar Materials
Because the parent materials are not melted, vacuum brazing is exceptionally effective at joining materials that cannot be welded together. This includes joining metals to ceramics (e.g., steel to ceramic) or bonding vastly different metals.
Limitation: Process Complexity and Cost
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment. The process is also inherently a batch process, which can be slower and more costly per part compared to continuous processes like automated welding, especially for high-volume production.
Limitation: Requires Precise Design
The reliance on capillary action means that the gap or "clearance" between the parts being joined is critical. It must be designed and manufactured to tight tolerances to ensure the filler metal flows properly and fills the entire joint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use vacuum brazing depends entirely on the requirements of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint integrity and cleanliness: For applications like medical implants, aerospace components, or ultra-high vacuum equipment, the oxide-free, high-purity joints created by vacuum brazing are often a necessity.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials: When you need to create a strong, reliable bond between materials like a metal and a ceramic, vacuum brazing is one of the most effective methods available.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective joining for standard applications: For general fabrication where supreme cleanliness is not critical, conventional welding or torch brazing is typically a more economical and faster choice.
Ultimately, vacuum brazing is the definitive solution when the strength, purity, and precision of the joint are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Brazing | Alternative Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Cleanliness | Oxide-free, no flux, bright finish | May require post-process cleaning |
| Material Compatibility | Excellent for dissimilar materials (e.g., metal to ceramic) | Limited by weldability |
| Process Speed & Cost | Batch process, higher cost per part | Often faster and more cost-effective for high volume |
| Joint Strength | Exceptionally strong, uniform intermetallic bond | Varies; can be weaker or have inconsistencies |
Need a high-integrity joint for your critical application?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced vacuum furnace solutions. Our expertise ensures your vacuum brazing process delivers the oxide-free, strong, and clean bonds your project demands, especially when joining challenging materials.
Let's discuss how our high-temperature furnaces and deep customization capabilities can meet your unique requirements.
Contact our experts today to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density



















