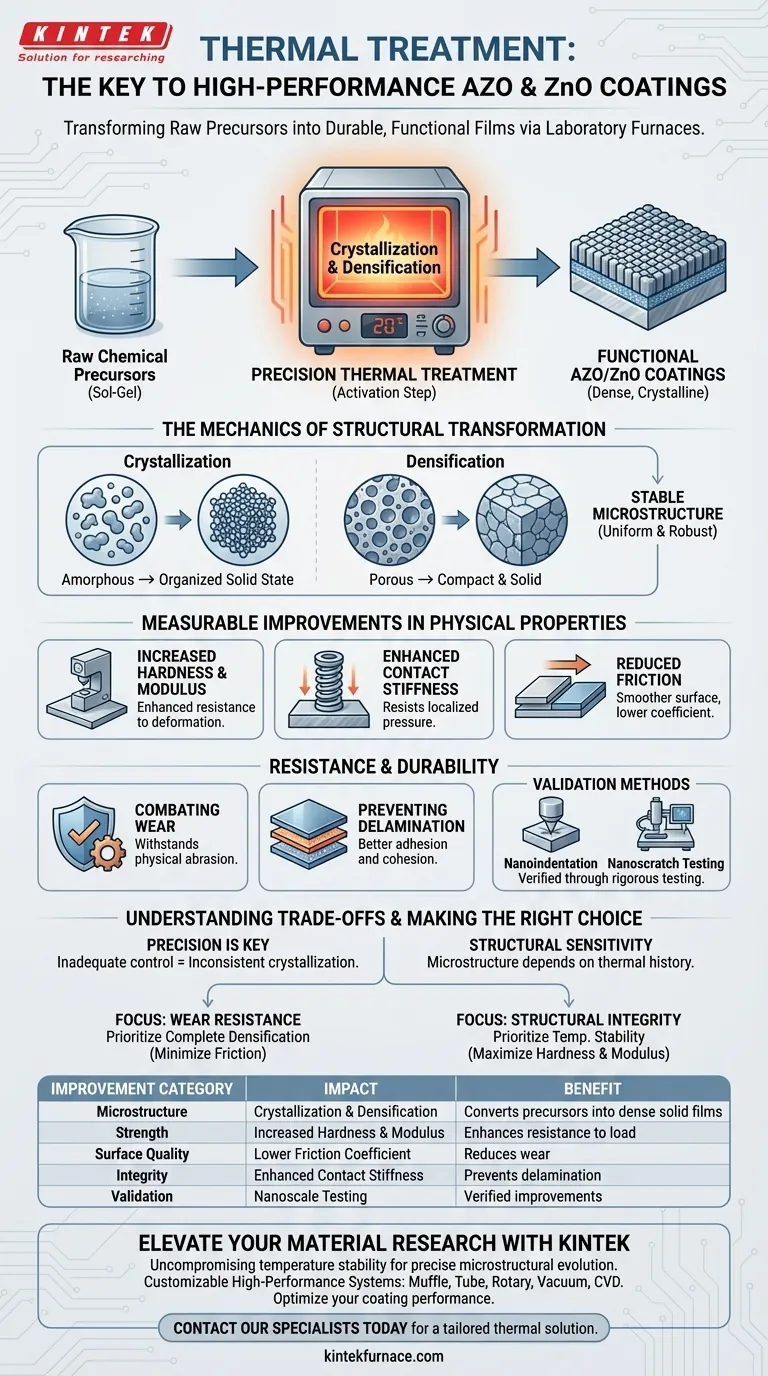
Thermal treatment is the critical activation step that transforms raw chemical precursors into functional, durable coatings. For AZO and ZnO films, laboratory furnaces facilitate the necessary crystallization and densification of sol-gel precursors. This precise thermal control evolves the material's microstructure, directly resulting in superior mechanical resilience and stability.
The thermal process converts sol-gel precursors into dense, crystalline thin films, significantly boosting their hardness and elastic modulus. This structural evolution is essential for minimizing friction and preventing wear or delamination during practical use.

The Mechanics of Structural Transformation
Crystallization of Precursors
The primary function of the laboratory furnace in this context is to promote crystallization. The heat treatment drives the phase transition of the sol-gel precursors, turning them into an organized solid state.
Densification of the Film
Alongside crystallization, the thermal energy creates densification. This process removes porosity from the film, ensuring the material is compact and solid rather than loose or porous.
Achieving Microstructural Stability
The furnace allows for the formation of a stable microscopic structure. By maintaining precise temperature control, the treatment ensures the internal lattice of the coating is uniform and robust.
Measurable Improvements in Physical Properties
Increased Hardness and Modulus
The structural changes induced by heat lead to a measurable increase in hardness. Furthermore, the elastic modulus—the material's resistance to being deformed elastically—is significantly enhanced.
Enhanced Contact Stiffness
The treatment improves the contact stiffness of the coatings. This property is vital for applications where the surface must resist localized pressure without yielding.
Reduction of Friction
A fully treated, dense surface exhibits a lower friction coefficient. This smoothness is a direct result of the stable microstructure achieved during the heating process.
Resistance and Durability
Combating Wear
The combination of increased hardness and reduced friction creates a surface that is highly resistant to wear. The coating can withstand physical abrasion much better than untreated precursors.
Preventing Delamination
Thermal treatment significantly enhances resistance to delamination. The densification process ensures better adhesion and internal cohesion, preventing the coating from peeling away from the substrate.
Validation Methods
These mechanical improvements are not theoretical. They have been verified through rigorous testing methods, specifically nanoindentation and nanoscratch testing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Precision
While thermal treatment is beneficial, the primary reference emphasizes the need for "precise temperature control." Inadequate control can lead to inconsistent crystallization, which would fail to yield the desired mechanical properties.
Structural Sensitivity
The microstructure is sensitive to the thermal history of the sample. If the furnace does not maintain the specific conditions required for the sol-gel precursors, the resulting film may lack the required densification or stability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the performance of AZO and ZnO coatings, align your thermal treatment strategy with your specific mechanical requirements.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance: Ensure the thermal profile allows for complete densification to minimize the friction coefficient.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Prioritize precise temperature stability to maximize the hardness and elastic modulus, preventing deformation under load.
Precise thermal treatment is the bridge between a raw chemical precursor and a high-performance, mechanically stable coating.
Summary Table:
| Improvement Category | Impact of Thermal Treatment | Benefit for AZO/ZnO Coatings |
|---|---|---|
| Microstructure | Crystallization & Densification | Converts precursors into dense, organized solid films |
| Strength | Increased Hardness & Modulus | Enhances resistance to elastic deformation and load |
| Surface Quality | Lower Friction Coefficient | Smoother surface reduces wear and physical abrasion |
| Integrity | Enhanced Contact Stiffness | Prevents delamination and ensures better substrate adhesion |
| Validation | Nanoscale Testing | Verified improvements via nanoindentation and nanoscratch tests |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precise microstructural evolution requires uncompromising temperature stability. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of AZO and ZnO coating processes.
Whether you are scaling up production or refining laboratory sol-gel densification, our high-temp furnaces provide the thermal control necessary to maximize hardness and prevent delamination.
Ready to optimize your coating performance? Contact our specialists today for a tailored thermal solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Seyyedeh Sedigheh Azad, Iraj Mohammadpoor‐Baltork. Stability enhancement of perovskite solar cells using multifunctional inorganic materials with UV protective, self cleaning, and high wear resistance properties. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-57133-8
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What happens during the sintering process? Transform Powder into Dense, High-Strength Components
- Why is a vacuum desiccator essential for studying geopolymer porosity? Achieve Precise Material Characterization
- What are the key advantages of using electric furnaces across industries? Boost Efficiency and Precision in Your Processes
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory oven during sugarcane bagasse ash preparation? Optimize Material Pretreatment
- What is the importance of using a vacuum drying oven for MoS2/rGO battery electrodes? Maximize Battery Performance
- What are the core technical advantages of using SPS for Titanium Diboride ceramics? Achieve High Density & Fine Grains
- How does the "Flux Melting" process in MOF glass preparation utilize heating equipment? Low-Temp MOF Vitrification
- Why are precision hydrothermal reactors necessary for nut shell modification? Unlock Biomass Energy Potential



















