The integration of digital control systems significantly elevates industrial furnace performance by replacing manual oversight with automated precision. By combining Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) regulators with robust safety mechanisms, operators achieve exact adherence to heat treatment curves while simultaneously mitigating electrical risks through compliance with standards like NR-10 and NR-12.
Modern digital integration transforms electric furnaces from simple heating elements into precision tools. It ensures repeatable quality through automated thermal management while protecting both the asset and the operator via active safety monitoring.
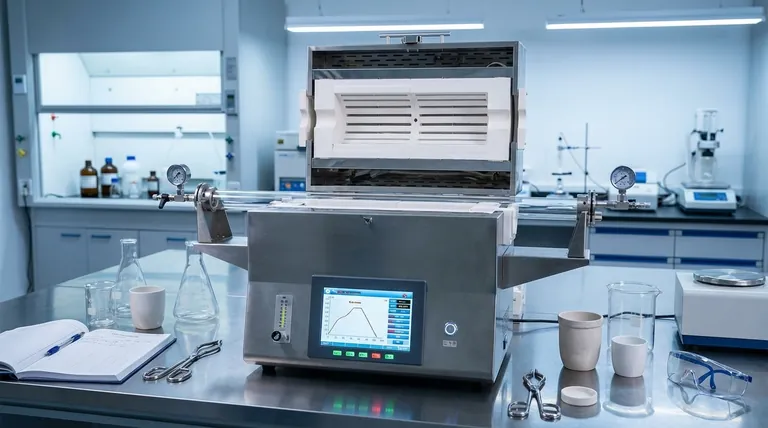

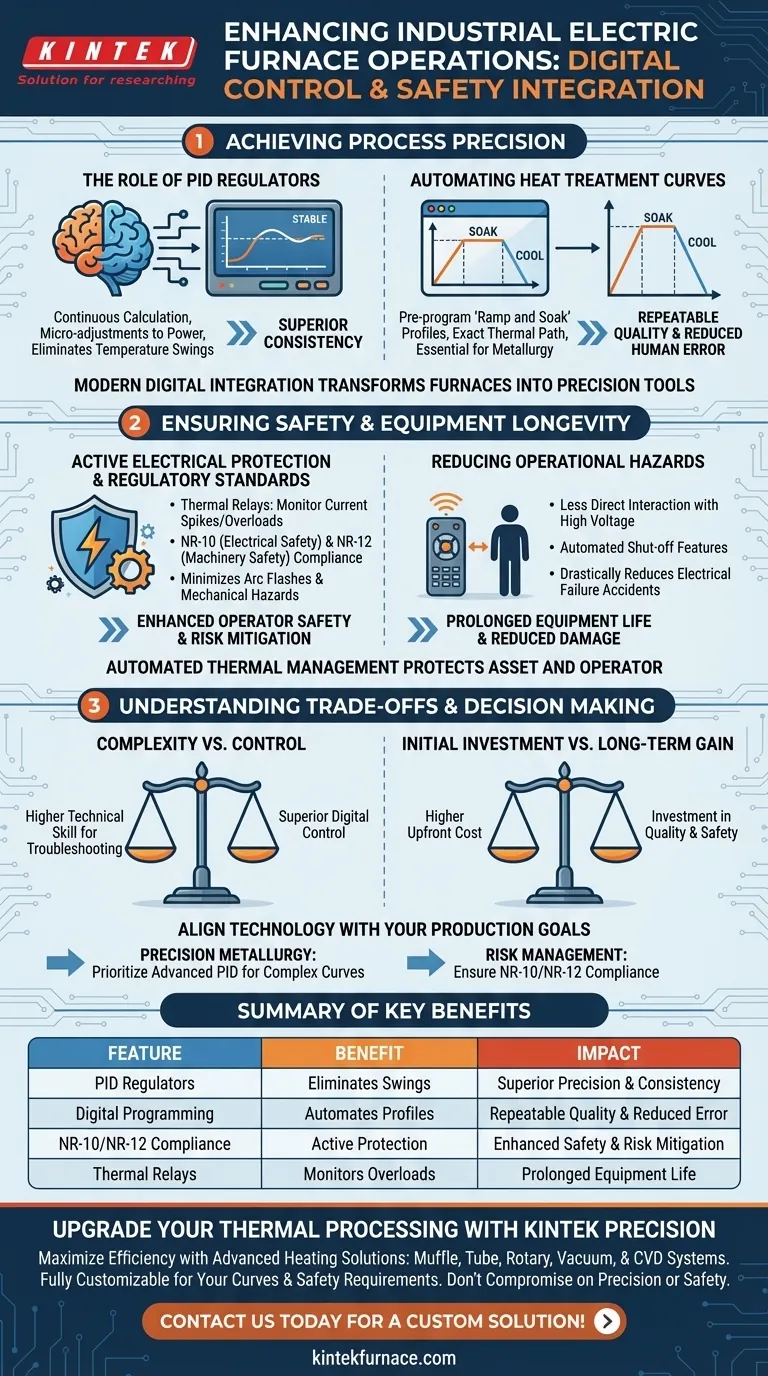
Achieving Process Precision
The Role of PID Regulators
PID regulators serve as the "brain" of the modern furnace. They continuously calculate the error between the desired temperature and the actual temperature, making micro-adjustments to power input. This eliminates the temperature swings common with basic on/off controls.
Automating Heat Treatment Curves
Many industrial processes require specific heating rates, hold times, and cooling periods. Digital controllers allow you to pre-program these complex "ramp and soak" profiles. This ensures the material follows the exact thermal path required to achieve specific metallurgical properties.
Eliminating Human Error
Manual temperature management is prone to inconsistency. Digital automation ensures that once a cycle is programmed, it runs identically every time. This repeatability is essential for maintaining uniform product quality across different batches.
Ensuring Safety and Equipment Longevity
Active Electrical Protection
Thermal relays and integrated protection devices act as an automatic shield for your hardware. They monitor the system for current spikes and thermal overloads. If an anomaly is detected, the system cuts power immediately, preventing damage to expensive heating elements and circuitry.
Meeting Regulatory Standards
Compliance with industrial safety norms is a critical function of these integrated systems. The primary reference highlights adherence to standards like NR-10 (electrical safety) and NR-12 (machinery safety). These integrations ensure the equipment minimizes the risk of arc flashes, shocks, and mechanical hazards.
Reducing Operational Hazards
By automating the control process, operators interact less frequently with high-voltage components during operation. This distance, combined with automated shut-off features, drastically reduces the likelihood of workplace accidents related to electrical failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity in Troubleshooting
While digital systems offer superior control, they introduce a layer of technical complexity. Troubleshooting a misconfigured PID controller or a digital relay fault often requires a higher technical skill set than repairing simple analog components.
Initial Investment vs. Long-term Gain
Integrated digital panels typically command a higher upfront cost than basic manual controls. This expenditure is an investment in quality and safety, but it may strain budgets for operations that only require rough, low-precision heating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
To maximize the value of your electric furnace, you must align the technology with your production goals.
- If your primary focus is Precision Metallurgy: Prioritize advanced PID controllers that support complex, multi-stage heat treatment curves to guarantee material properties.
- If your primary focus is Risk Management: Ensure the integration specifically cites compliance with standards like NR-10/NR-12 and features redundant thermal overload protection.
Ultimately, digital integration is not just a feature upgrade; it is a fundamental requirement for establishing a safe, repeatable, and compliant industrial heating process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| PID Regulators | Eliminates temperature swings with micro-adjustments | Superior precision and consistency |
| Digital Programming | Automates "ramp and soak" thermal profiles | Repeatable quality and reduced human error |
| NR-10/NR-12 Compliance | Ensures active electrical and machinery protection | Enhanced operator safety and risk mitigation |
| Thermal Relays | Monitors for current spikes and overloads | Prolonged equipment life and reduced damage |
Upgrade Your Thermal Processing with KINTEK Precision
Maximize your laboratory and industrial efficiency with KINTEK’s advanced heating solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific heat treatment curves and safety requirements.
Don't compromise on precision or safety. Let our experts help you integrate the latest digital control technologies into your workflow to ensure repeatable results and total regulatory compliance.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature operations? Contact us today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Gustavo Ribeiro Zanini, LUIS CARLOS GERON. PROJETO DE UM FORNO ELÉTRICO INDUSTRIAL PARA TRATAMENTO TÉRMICO TUBOS DE AÇO SA-178 GR A. DOI: 10.52138/citec.v17i01.437
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory oven play in the evaluation of the physical properties of teak activated carbon? Accuracy Tips
- What is the purpose of using a PID controller to drive a heating furnace? Master Thermal Kinetics Precision
- What is the function of high-purity graphite molds during SPS of Cu2Se? Essential Tips for Superior Sintering
- What is the technical value of using precise digital PID temperature controllers? Enhancing Ceramic Property Analysis
- Why is an alumina crucible necessary when synthesizing U0.92Mn3Si2C inside a quartz tube? Ensure Vessel Integrity
- What are the primary functions of a self-preheating heat exchanger? Maximize Thermal Efficiency in Double-P Tubes
- What is the function of a ceramic crucible with a lid during g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Polycondensation Results
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for MAX phase sintering? Ensure Purity in High-Temperature Synthesis



















