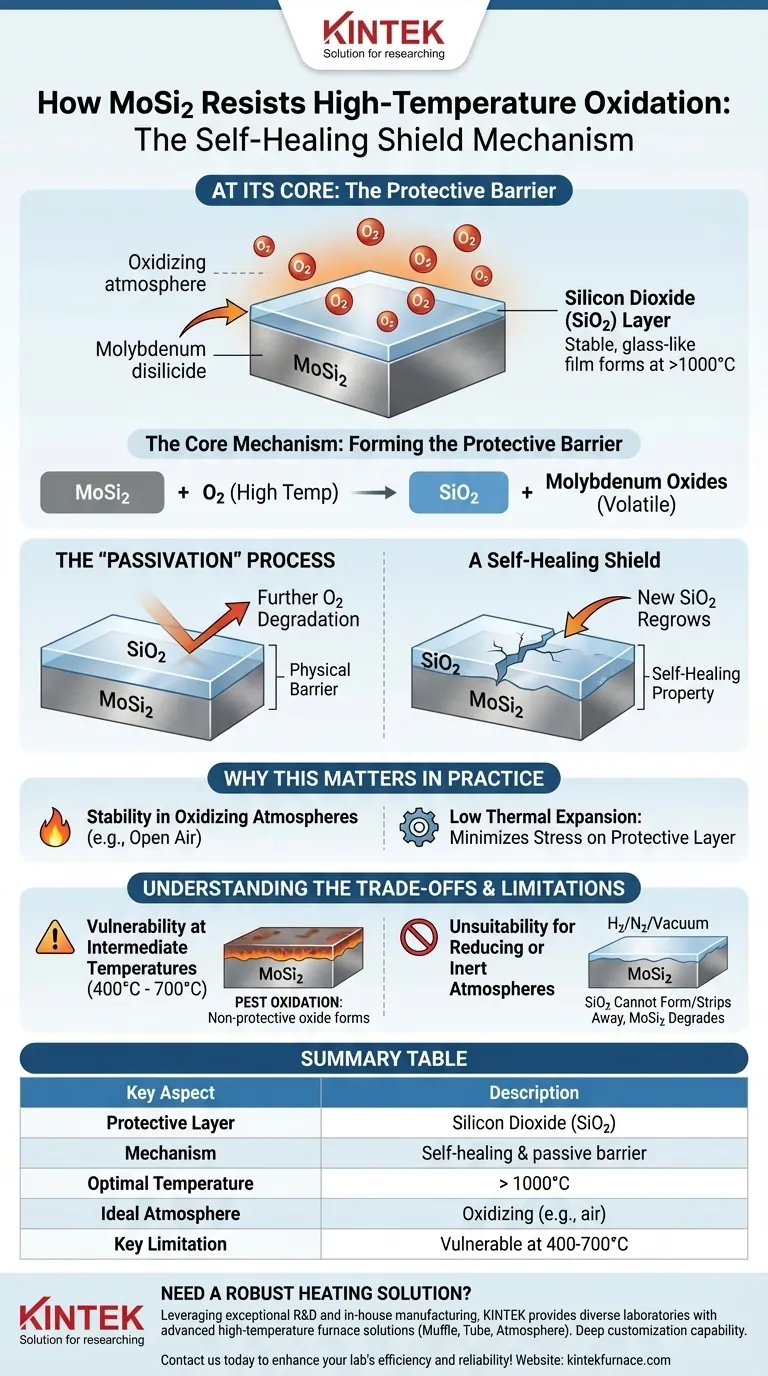
At its core, molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) resists oxidation at high temperatures by forming a thin, protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO2) on its surface. When heated in an oxidizing atmosphere, the silicon in the MoSi2 reacts with oxygen to create a durable, glass-like film that acts as a physical barrier, preventing further oxygen from reaching and degrading the underlying material.
The true value of MoSi2 is not just its inherent composition, but its ability to create its own self-healing, protective shield. This dynamic process is what grants it exceptional stability, but it also dictates the specific operating conditions required to maintain that protection.
The Core Mechanism: Forming the Protective Barrier
The resistance of MoSi2 is an active, not a passive, quality. It depends on a chemical reaction that occurs at the surface of the material when it is put into service.
The Role of Silicon Dioxide (SiO2)
When MoSi2 is exposed to high temperatures (typically above 1000°C) in the presence of oxygen, a chemical reaction takes place. The silicon within the molybdenum disilicide oxidizes, forming a stable and non-porous layer of silicon dioxide (SiO2), also known as silica.
The "Passivation" Process
This newly formed SiO2 layer effectively "passivates" the surface. This means it creates a barrier that is chemically inert and impermeable to oxygen.
Once this thin, glassy film is fully formed, it prevents oxygen from reaching the fresh MoSi2 beneath it. This halts the oxidation process, protecting the integrity of the component.
A Self-Healing Shield
A critical feature of this mechanism is its self-healing property. If the protective silica layer is scratched or damaged during operation, the newly exposed MoSi2 will immediately react with the surrounding oxygen to "regrow" the SiO2 film in that spot, effectively repairing the shield.
Why This Matters in Practice
Understanding this mechanism is key to using MoSi2 components effectively and ensuring their longevity in demanding applications like industrial furnace heating elements.
Stability in Oxidizing Atmospheres
The formation of the SiO2 layer is the primary reason MoSi2 elements are exceptionally well-suited for long-term use in oxidizing atmospheres, such as open air. The material works with the oxygen to protect itself.
Low Thermal Expansion
MoSi2 also possesses a small thermal expansion coefficient. This means it expands and contracts very little during heating and cooling cycles. This property is crucial, as it minimizes the mechanical stress on the protective SiO2 layer, reducing the risk of it cracking and flaking off.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, this protective mechanism is not universal and comes with specific operational requirements and limitations. Its effectiveness is directly tied to temperature and atmosphere.
Vulnerability at Intermediate Temperatures
The formation of the stable, glassy SiO2 layer only occurs efficiently at very high temperatures. At intermediate temperatures (e.g., 400°C to 700°C), MoSi2 can suffer from a catastrophic form of oxidation often called "pest" oxidation, where a different, non-protective oxide forms. Prolonged operation in this temperature range must be avoided.
Unsuitability for Reducing Atmospheres
The entire protective mechanism relies on the presence of oxygen. In reducing or inert atmospheres (like hydrogen, nitrogen, or a vacuum), the SiO2 layer cannot form or can be stripped away. Without this protective oxide film, the MoSi2 material is left vulnerable to degradation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To leverage MoSi2 effectively, your operational strategy must align with the material's protective mechanism.
- If your primary focus is maximum life in an air furnace: Ensure your process allows the elements to quickly heat through the intermediate temperature range and operate consistently at high temperatures to form and maintain a robust silica layer.
- If your process involves frequent thermal cycling: The low thermal expansion is an advantage, but be mindful to minimize the time spent in the 400-700°C range to prevent pest oxidation.
- If you are operating in a reducing or vacuum environment: MoSi2 is fundamentally unsuitable for this application, as its protective mechanism requires oxygen to function.
Understanding this dynamic interplay between material, temperature, and atmosphere is the key to successfully leveraging MoSi2's unique high-temperature capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Protective Layer | Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) |
| Mechanism | Self-healing, passive barrier |
| Optimal Temperature | > 1000°C |
| Ideal Atmosphere | Oxidizing (e.g., air) |
| Key Limitation | Vulnerable at 400-700°C ("pest" oxidation) |
Need a robust heating solution for your high-temperature processes?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering



















