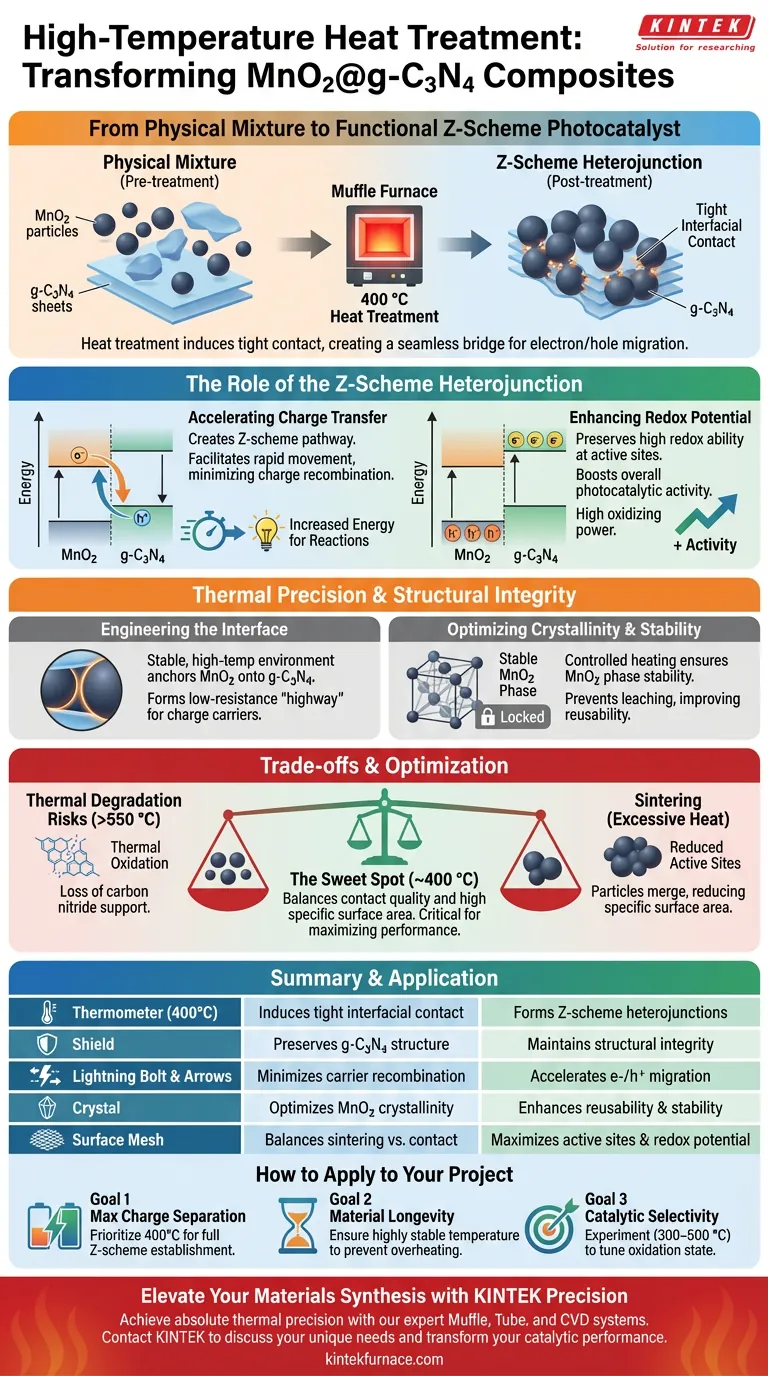
High-temperature heat treatment is the transformative step that converts a physical mixture of components into a functional photocatalytic system. By subjecting the $MnO_2@g-C_3N_4$ composite to approximately 400 °C in a muffle furnace, you induce the tight interfacial contact necessary to construct a Z-scheme heterojunction. This specific architecture is responsible for accelerating the transfer of photogenerated charges, which directly leads to superior catalytic performance.
The core value of muffle furnace treatment lies in interfacial engineering; it creates a seamless bridge between the $MnO_2$ particles and the $g-C_3N_4$ support, enabling the efficient separation and migration of electrons and holes.

The Role of the Z-Scheme Heterojunction
Accelerating Charge Transfer
The primary benefit of the 400 °C heat treatment is the creation of a Z-scheme pathway for electrons.
This configuration allows photogenerated electrons and holes to migrate between the two semiconductors more effectively than they would in isolation.
By facilitating this rapid movement, the system minimizes charge recombination, ensuring that more energy is available to drive the desired chemical reactions.
Enhancing Redox Potential
The Z-scheme doesn't just move charges; it preserves high redox ability at the active sites.
Through this heterojunction, electrons with high reducing power and holes with high oxidizing power are maintained in their respective bands.
This synergy significantly boosts the overall photocatalytic activity of the $MnO_2@g-C_3N_4$ composite compared to its individual precursors.
Thermal Precision and Structural Integrity
Engineering the Interface
A muffle furnace provides the stable, high-temperature environment required to anchor $MnO_2$ particles onto the $g-C_3N_4$ nanosheets.
At 400 °C, the materials undergo enough thermal excitation to form tight interfacial contact without destroying the underlying polymer structure of the $g-C_3N_4$.
This contact acts as a low-resistance "highway" for charge carriers, which is the foundational requirement for any high-performance supported catalyst.
Optimizing Crystallinity and Stability
The controlled heating process also influences the crystallinity of the metallic oxide phase.
Similar to how precise temperatures control oxygen vacancies in other oxides, the muffle furnace ensures the $MnO_2$ phase is stable and securely attached.
This thermal "locking" prevents the active catalyst from leaching or aggregating during liquid-phase reactions, improving the material's reusability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Degradation Risks
While heat is necessary for heterojunction formation, $g-C_3N_4$ is sensitive to extreme temperatures and can begin to decompose if pushed too far.
Exceeding the optimal temperature range (typically above 550 °C in air) can lead to the thermal oxidation and loss of the carbon nitride support.
Surface Area vs. Contact Quality
There is a delicate balance between achieving tight contact and maintaining a high specific surface area.
Excessive heat can cause particles to undergo sintering, where small particles merge into larger ones, reducing the number of available active sites.
Finding the "sweet spot"—such as the 400 °C benchmark—is critical to maximizing the interface without sacrificing the surface-to-volume ratio.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve the best results with your composite material, consider your primary objective when setting your furnace parameters:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Charge Separation: Prioritize the 400 °C threshold to ensure the Z-scheme heterojunction is fully established through tight interfacial bonding.
- If your primary focus is Material Longevity: Ensure the muffle furnace maintains a highly stable temperature to prevent the localized overheating that leads to support degradation.
- If your primary focus is Catalytic Selectivity: Experiment with slight temperature variations (300–500 °C) to tune the oxidation state and oxygen vacancy concentration of the $MnO_2$ phase.
By precisely controlling the thermal environment of the muffle furnace, you transition from a simple material blend to a highly engineered, high-efficiency catalytic engine.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Influence on MnO2@g-C3N4 Composite | Benefit to Catalysis |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (400°C) | Induces tight interfacial contact | Forms Z-scheme heterojunctions |
| Thermal Stability | Preserves g-C3N4 polymer structure | Maintains structural integrity/support |
| Charge Dynamics | Minimizes carrier recombination | Accelerates electron/hole migration |
| Phase Control | Optimizes MnO2 crystallinity | Enhances material reusability & stability |
| Surface Engineering | Balances sintering vs. contact | Maximizes active sites and redox potential |
Elevate Your Materials Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect Z-scheme heterojunction requires the absolute thermal precision found in KINTEK laboratory solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for advanced interfacial engineering.
Whether you are optimizing $MnO_2$ composites or developing next-generation photocatalysts, our customizable high-temperature furnaces ensure the stability and accuracy your research demands. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique needs and see how our expert equipment can transform your catalytic performance.
Visual Guide
References
- Guanglu Lu, Zijian Zhang. Z-Type Heterojunction MnO2@g-C3N4 Photocatalyst-Activated Peroxymonosulfate for the Removal of Tetracycline Hydrochloride in Water. DOI: 10.3390/toxics12010070
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What material properties can be achieved using a box furnace? Unlock Enhanced Hardness, Strength, and More
- How does a laboratory high-temperature box furnace ensure the material performance of NN-10ST based ceramics?
- What is the role of a laboratory drying oven or hot plate in slurry processing? Optimize Composite Material Quality
- Why is temperature control important in a muffle furnace? Ensure Accurate, Repeatable Results
- Why is the use of a Muffle Furnace critical during the calcination stage of TiO2/g-C3N4? Master Composite Synthesis
- What is a muffle furnace and how does it differ from conventional furnaces? Discover the Key to Contamination-Free Heating
- How should alkaline substances be handled in a muffle furnace? Protect Your Equipment from Corrosion
- What is a batch furnace? Maximize Flexibility and Precision for Your Heat Treatment



















