In short, a box furnace is used to achieve specific material properties by enabling precise thermal processing. These properties include improved hardness, strength, corrosion resistance, and ductility, as well as enhanced density and electrical conductivity, by fundamentally altering a material's internal microstructure.
A box furnace achieves these outcomes not by direct action, but by creating a highly controlled environment. It is the precise management of temperature and atmosphere that facilitates metallurgical processes like annealing or sintering, which are what truly change the material's final characteristics.
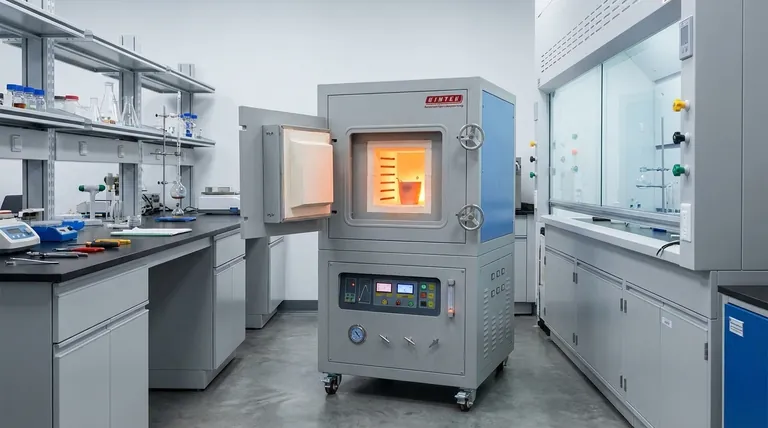

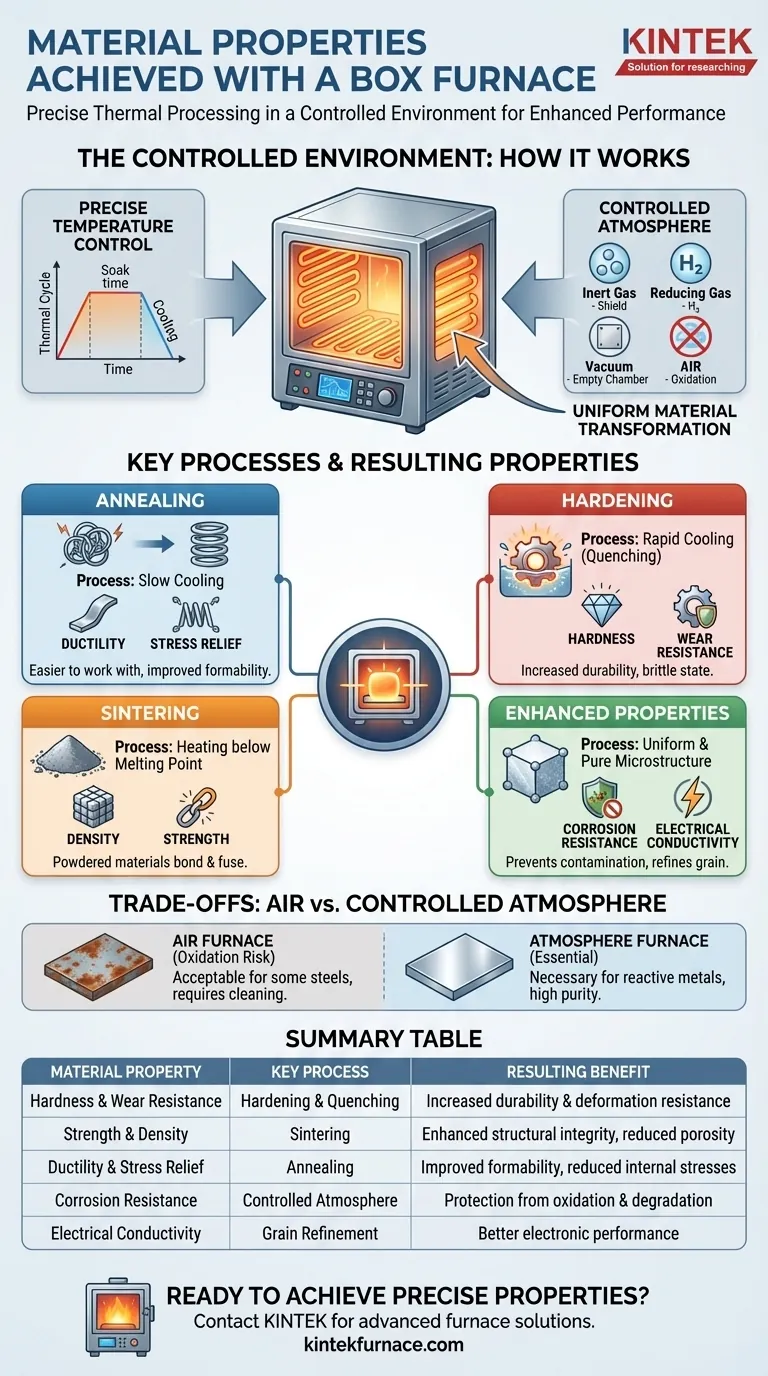
How a Box Furnace Alters Material Properties
A box furnace acts as a controlled environment where heat and atmosphere are the primary tools for material transformation. The final properties of a component are a direct result of how these two variables are managed.
The Principle of a Controlled Atmosphere
The most critical feature of an advanced box furnace is its ability to control the gaseous environment. Heating metals in open air causes oxidation (scaling), which can compromise surface finish and structural integrity.
Atmosphere control prevents this. Using inert gases like nitrogen or argon displaces oxygen, protecting the material. Using reducing gases like hydrogen can actively remove surface oxides. A vacuum environment removes all reactive gases entirely.
The Role of Precise Temperature Control
Modern box furnaces use programmable controllers and uniform heating zones. This precision is not just about reaching a target temperature, but about controlling the entire thermal cycle—the rate of heating, the time spent at temperature (soak time), and the rate of cooling.
This control ensures that the entire part undergoes the intended transformation uniformly, leading to consistent and predictable material properties.
Key Processes and Their Resulting Properties
Different thermal processes performed within the furnace yield different results. The process you choose depends entirely on your desired outcome for the material.
Annealing for Stress Relief and Ductility
Annealing involves heating a material and then cooling it slowly. This process relieves internal stresses, refines the grain structure, and increases ductility (the ability to deform without fracturing), making the material softer and easier to work with.
Hardening for Strength and Wear Resistance
Heat treatments for hardening typically involve heating a metal to a specific temperature and then cooling it rapidly (a process called quenching). This locks the material's crystalline structure in a very hard, brittle state, dramatically increasing its hardness and wear resistance.
Sintering for Density and Strength
Sintering is a process used for powdered materials (metals or ceramics). The furnace heats the compacted powder to a temperature below its melting point, causing the particles to bond and fuse together. This significantly increases the material's density and strength.
Enhancing Other Key Properties
By creating a uniform, stress-free, and pure microstructure, controlled heat treatments can also enhance other properties. Preventing contamination improves corrosion resistance, and a refined grain structure can improve electrical conductivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Atmosphere vs. Air
The most significant decision is whether a simple air furnace is sufficient or if a controlled atmosphere is required. This choice has major implications for cost, complexity, and final material quality.
The Risk of Oxidation in Air
For many common steels and non-critical applications, heating in a standard furnace with an air atmosphere is acceptable. However, this will always produce an oxide layer on the surface that may need to be cleaned off later.
The Necessity of Atmosphere Control
For reactive metals (like titanium), high-purity applications, or processes where surface finish is critical (like brazing), an atmosphere furnace is non-negotiable. The controlled environment is essential to prevent unwanted chemical reactions that would degrade the material's properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right process, you must first define your end goal. The furnace is the tool, but the process is what delivers the result.
- If your primary focus is hardening basic steels: A simple box furnace with controlled heating and quenching capabilities may be sufficient.
- If your primary focus is achieving high ductility or preventing surface oxidation: You require an atmosphere furnace capable of using inert or reducing gases during an annealing cycle.
- If your primary focus is increasing the density and strength of powdered materials: A sintering process in a vacuum or controlled atmosphere furnace is the correct approach.
- If your primary focus is removing internal stresses for structural uniformity: A precisely controlled annealing cycle is the essential process for your material.
Ultimately, selecting the right box furnace and process is about defining your desired end-state and understanding the controlled environment needed to achieve it.
Summary Table:
| Material Property | Key Process | Resulting Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness & Wear Resistance | Hardening & Quenching | Increased durability and resistance to deformation |
| Strength & Density | Sintering | Enhanced structural integrity and reduced porosity |
| Ductility & Stress Relief | Annealing | Improved formability and reduced internal stresses |
| Corrosion Resistance | Controlled Atmosphere | Protection from oxidation and chemical degradation |
| Electrical Conductivity | Grain Refinement | Better performance in electronic applications |
Ready to achieve precise material properties in your lab? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your material processing outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is calcination essential for NaFePO4 phase formation? Engineering High-Performance Sodium Iron Phosphate
- Why is immediate water-quenching required after thermal simulation? Preserve (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 Alloy Microstructure
- Why is a laboratory high-temperature box furnace essential for KNN ceramic powders? Mastering Solid-State Synthesis
- What is the significance of the thermal environment in calcination? Achieve Pure Ceramic Phases with KINTEK
- How is a muffle furnace utilized for AlN crystal post-processing? Optimize Surface Purity via Staged Oxidation



















