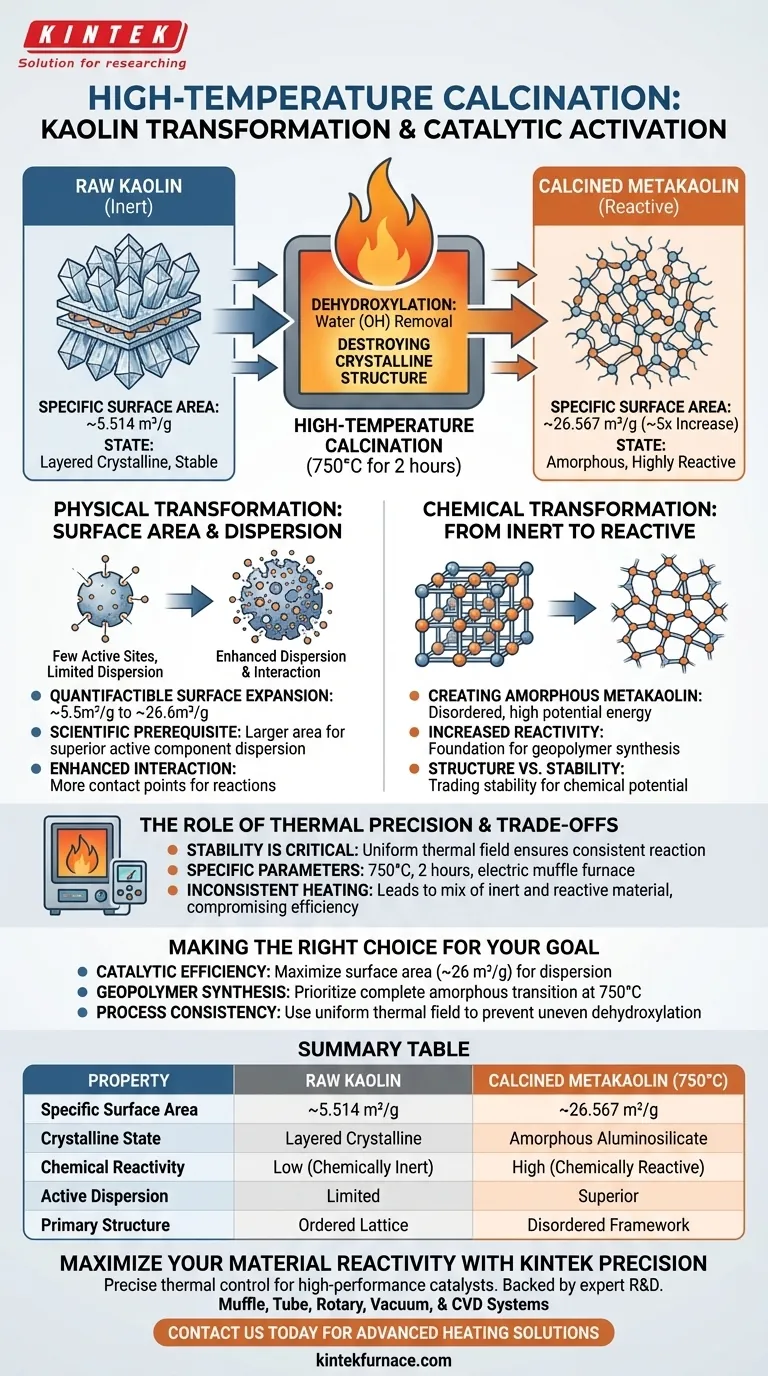
High-temperature calcination dramatically increases the specific surface area of kaolin, essentially multiplying its available reactive surface by a factor of five. By subjecting the material to a controlled thermal environment, the specific surface area expands from approximately 5.514 m²/g to 26.567 m²/g, fundamentally altering its potential for catalytic activity.
The core mechanism at work is a phase transition called dehydroxylation. This process does not simply heat the material; it destroys the original crystalline structure to create a highly reactive, amorphous framework with vastly improved dispersion capabilities.

The Physical Transformation: Surface Area and Dispersion
Quantifiable Surface Expansion
The most immediate impact of calcination is measurable via BET analysis. The process expands the specific surface area of the material from a baseline of ~5.514 m²/g to ~26.567 m²/g.
The Mechanism of Dispersion
This increase in surface area is the scientific prerequisite for catalytic efficiency. A larger surface area allows for superior dispersion of active components.
Enhanced Interaction
By expanding the physical structure, the material provides more contact points for chemical interactions. This ensures that the active components are not just present, but are accessible and effectively distributed for the reaction.
The Chemical Transformation: From Inert to Reactive
Dehydroxylation
Inside the furnace, typically at 750°C, kaolin undergoes dehydroxylation. This is the chemical removal of hydroxyl groups (water) from the crystal lattice.
Destroying the Crystalline Order
Raw kaolin possesses a layered, stable crystalline structure that is largely chemically inert. High-temperature calcination deliberately destroys this layered structure.
Creating Amorphous Metakaolin
The result of this destruction is an amorphous aluminosilicate structure known as metakaolin. Unlike its precursor, this disordered state is highly unstable and chemically reactive, serving as the necessary foundation for geopolymer synthesis.
The Role of Thermal Precision
Stability is Critical
The transformation requires a strictly controlled thermal environment. A stable thermal field is necessary to ensure the reaction is uniform throughout the material.
Specific Parameters
Standard protocols often utilize an electric muffle furnace set to 750°C for a duration of two hours. This specific time-temperature combination is tuned to maximize the conversion to the reactive amorphous state without causing sintering (which would reduce surface area).
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Control
While heat increases reactivity, the process relies on a stable thermal field. Inconsistent heating can result in a mix of unreacted kaolin (inert) and properly calcined metakaolin, compromising the efficiency of the final catalyst.
Structure vs. Stability
You are trading the physical stability of natural kaolin for the chemical reactivity of metakaolin. The amorphous structure is desirable specifically because it is "uncomfortable" and wants to react, but this also means the material must be handled and stored correctly to maintain that potential energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of your kaolin-based application, consider the following specific targets:
- If your primary focus is Catalytic Efficiency: Ensure your calcination process achieves the target specific surface area (~26 m²/g) to maximize the dispersion of active ingredients.
- If your primary focus is Geopolymer Synthesis: Prioritize the destruction of the crystalline structure at 750°C to ensure a complete transition to the amorphous, reactive state.
- If your primary focus is Process Consistency: Utilize an electric furnace that guarantees a uniform thermal field to prevent uneven dehydroxylation.
Successful calcination turns a passive filler into an active chemical engine by fundamentally re-engineering its atomic architecture.
Summary Table:
| Property | Raw Kaolin | Calcined Metakaolin (750°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Specific Surface Area | ~5.514 m²/g | ~26.567 m²/g |
| Crystalline State | Layered Crystalline | Amorphous Aluminosilicate |
| Chemical Reactivity | Low (Chemically Inert) | High (Chemically Reactive) |
| Active Dispersion | Limited | Superior |
| Primary Structure | Ordered Lattice | Disordered Framework |
Maximize Your Material Reactivity with KINTEK Precision
Precise thermal control is the difference between an inert filler and a high-performance catalyst. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-stability Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to ensure the uniform dehydroxylation and surface expansion your lab requires.
Our customizable high-temperature furnaces provide the stable thermal field necessary for consistent metakaolin production and geopolymer synthesis. Contact us today to optimize your calcination process and see how our advanced heating solutions can transform your material research.
Visual Guide
References
- Luqman Buchori, Ndaru Okvitarini. Preparation of KI/KIO3/Methoxide Kaolin Catalyst and Performance Test of Catalysis in Biodiesel Production. DOI: 10.26554/sti.2024.9.2.359-370
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do laboratory high-temperature furnaces facilitate the control of nano-scale TiC and VC precipitates? | KINTEK
- How does high-temperature substrate heating at 500 °C facilitate TiO2 formation? Enhance Film Density and Quality
- What is the purpose of a safety warning system in MDR? Ensure Reactor Integrity and Laboratory Safety
- What is the use of dental ceramic? Achieve Lifelike, Durable, and Biocompatible Restorations
- Why specific constant temperature holding times for NbC and Cr7C3? Achieve Stoichiometric Precision in Lab Synthesis
- Why is an electric heating furnace integrated with a capsule-piercing reactor? Ensure Precise Fluid Analysis
- What role does a high-pressure autoclave play in the synthesis of the (NiZnMg)MoN precursor? Achieve Structural Precision
- What is the primary role of the Thermal Oxidation (TO) process in Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy? Enhancing Hardness and Wear



















