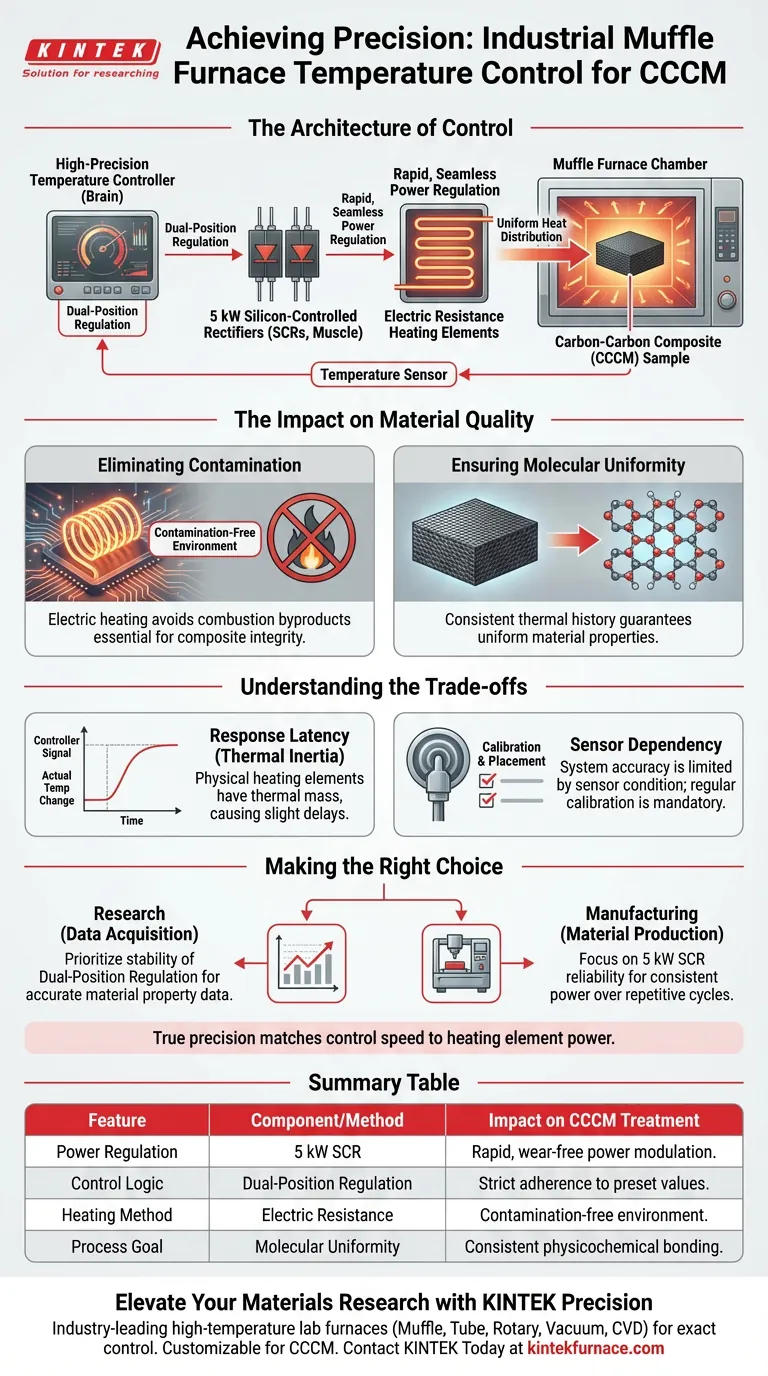
Industrial muffle furnaces achieve precise temperature control through a sophisticated automated system that couples high-precision temperature controllers with high-power silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs). Specifically designed for the heat treatment of Carbon-Carbon Composite Materials (CCCM), these systems utilize dual-position regulation and power outputs up to 5 kW to force the heating zone temperature to strictly adhere to preset values. This creates the highly stable, contamination-free thermal environment necessary for accurate material analysis and structural modification.
Core Takeaway: Precision in these furnaces is not just about measuring heat, but about how power is delivered. The integration of high-precision controllers with robust SCRs ensures that the heavy electrical load required for high temperatures is modulated with exact timing, preventing thermal drift and ensuring uniform molecular changes in sensitive composites.
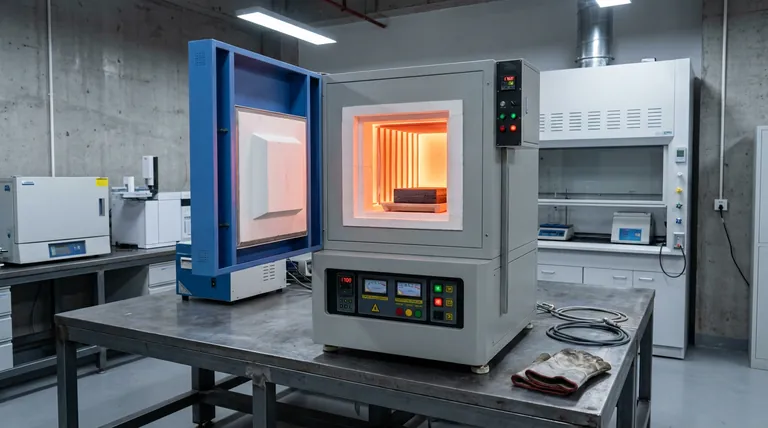

The Architecture of Control
The Role of Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs)
To handle the intense energy requirements of heat treatment, the furnace relies on high-power silicon-controlled rectifiers.
These components act as the "muscle" of the operation, managing power loads of up to 5 kW.
Unlike simple mechanical relays that might wear out or switch too slowly, SCRs allow for rapid, seamless regulation of the electrical current flowing to the heating elements.
Dual-Position Regulation Logic
The "brain" of the system is the high-precision temperature controller, which employs dual-position regulation.
This control logic constantly compares the current temperature against the programmed set value.
By strictly dictating the operation of the SCRs based on this comparison, the system ensures the heating zone does not deviate from the target profile, maintaining the rigorous stability required for CCCM processing.
The Impact on Material Quality
Eliminating Contamination via Electric Heating
Modern muffle furnaces utilize high-temperature electric heating elements rather than combustion-based methods.
This creates a contamination-free environment by eliminating combustion byproducts, which is critical for Carbon-Carbon Composite Materials.
Any foreign particulate or chemical byproduct introduced during the heating phase could compromise the integrity of the composite matrix.
Ensuring Molecular Uniformity
The ultimate goal of this precision is to facilitate structural changes at a molecular level.
Whether the goal is thermal decomposition or strengthening physicochemical bonding, the process requires uniform heat distribution.
The automated system ensures that every part of the sample experiences the exact same thermal history, guaranteeing that the resulting material properties are consistent throughout the composite.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Response Latency
While the control system is precise, the physical heating elements have thermal mass.
This means there is always a slight physical delay (latency) between the controller sending a signal and the temperature actually changing.
Operators must account for this "thermal inertia" when programming ramp rates to avoid overshooting sensitive temperature targets.
Sensor Dependency
The accuracy of the entire system is fundamentally limited by the placement and condition of the temperature sensors.
Because the controller reacts only to the data it receives, a poorly calibrated or misplaced sensor will lead to precise but inaccurate heating.
Regular calibration of the thermometer and verification of the set-value display against external standards are mandatory for valid results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your heat treatment process, align your operational strategy with your specific data requirements.
- If your primary focus is Data Acquisition (Research): Prioritize the stability of the "dual-position regulation" to ensure the temperature distribution data captured reflects the material properties, not furnace fluctuations.
- If your primary focus is Material Production (Manufacturing): Focus on the reliability of the 5 kW SCR system to maintain consistent power delivery over long, repetitive heating cycles without component failure.
True precision in heat treatment is achieved when the speed of the control logic is perfectly matched to the power of the heating elements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Component/Method | Impact on CCCM Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Power Regulation | 5 kW Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers (SCR) | Enables rapid, seamless power modulation without mechanical wear. |
| Control Logic | Dual-Position Regulation | Ensures heating zone strictly adheres to preset values with minimal deviation. |
| Heating Method | Electric Resistance Elements | Provides a contamination-free environment essential for composite integrity. |
| Process Goal | Molecular Uniformity | Guarantees consistent physicochemical bonding across the entire material matrix. |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK Precision
Precise thermal processing is the backbone of high-performance composite manufacturing. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature lab furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—engineered to deliver the exact temperature control your sensitive projects demand.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique CCCM or advanced material specifications. Don’t settle for thermal drift; achieve molecular perfection.
Contact KINTEK Today to Customize Your Furnace Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Dmytro Borovyk, D.I. Skliarenko. DETERMINATION OF THERMOPHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF CARBON-CARBON MATERIALS BY A COMPUTATIONAL-EXPERIMENTAL METHOD. DOI: 10.31472/ttpe.4.2024.4
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What steps are involved in starting a muffle furnace? Master Safe and Efficient Operation
- Why use a high-temp sintering furnace at 750°C for silver nanoparticles? Achieve purity and stability.
- What precautions should be taken when placing items into the muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Accuracy in High-Temp Operations
- What are the primary functions of muffle furnaces? Achieve Clean, Uniform Heating for Your Materials
- How do muffle furnaces help pharmaceutical companies comply with regulatory standards? Ensure Precise QC for FDA/EMA Approval
- How do box resistance furnaces facilitate the tempering process for quenched 60Si2CrV spring steel? Precision Hardening
- What role does a muffle furnace play in ZnO-doped CuO synthesis? Master Precision Nanocomposite Production
- How does a precision high-temp electric furnace affect TiO2/CQD film sintering? Enhance Your Photoanode Performance



















