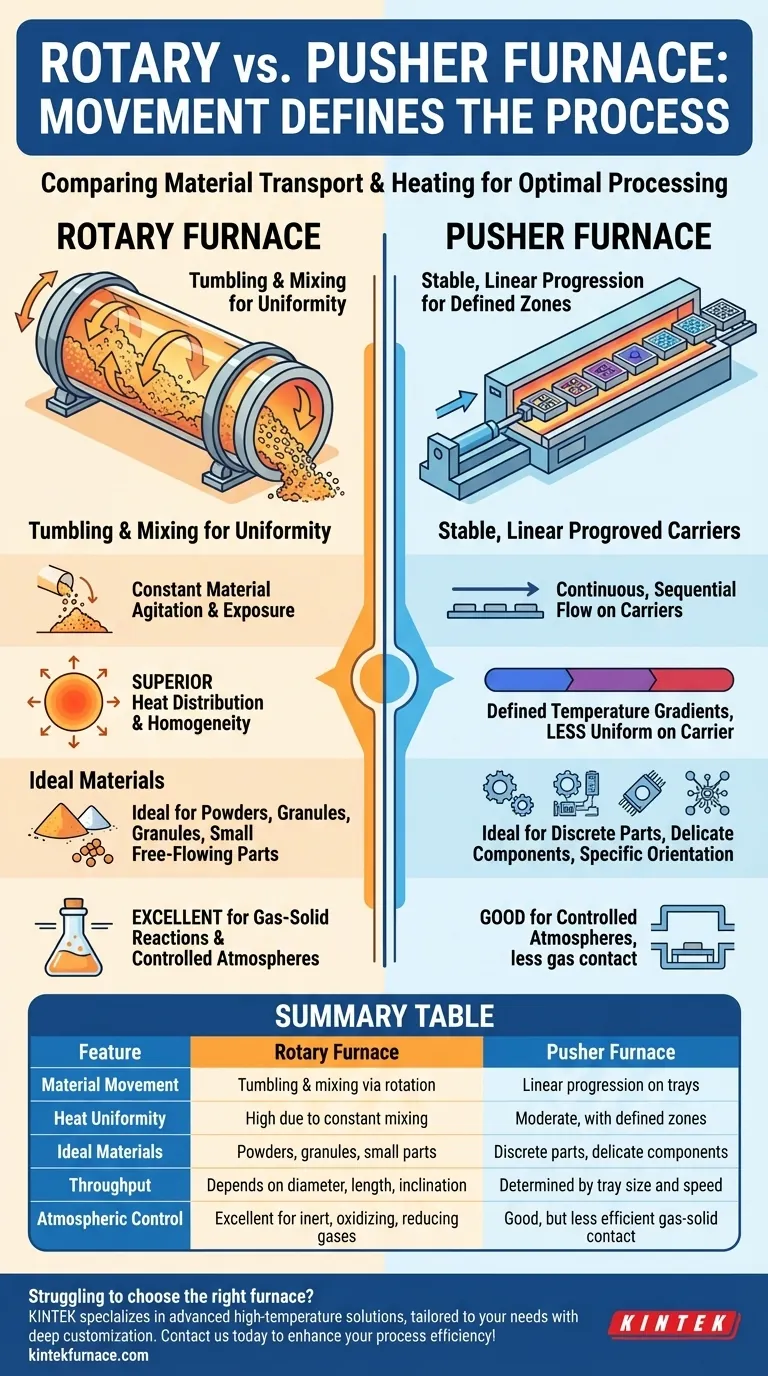
The fundamental difference between a rotary furnace and a pusher furnace lies in how material is transported and heated. A rotary furnace uses the rotation of its chamber to tumble and mix materials for highly uniform processing, while a pusher furnace moves materials in a straight line through distinct temperature zones on trays or boats.
The choice between these furnaces is not about which is superior, but which mechanism—the tumbling and mixing of a rotary furnace or the stable, linear progression of a pusher furnace—best serves the physical form of your material and your desired process outcome.

The Core Mechanical Difference: Movement Defines the Process
The method of material transport is the single most important distinction. It dictates heat transfer, material agitation, and the types of processes for which each furnace is suited.
Pusher Furnaces: Linear and Continuous Flow
A pusher furnace operates by pushing a train of trays, boats, or baskets through a long, typically horizontal chamber. A pusher mechanism at the entrance introduces new material, which advances the entire line forward.
This design creates a continuous, linear flow. Material remains stationary on its carrier, moving sequentially through pre-set temperature zones for heating, soaking, and cooling.
Rotary Furnaces: Tumbling for Uniformity
A rotary furnace, often called a rotary tube or rotary retort furnace, uses a slowly rotating cylindrical chamber. This tumbling action constantly lifts and cascades the material as it moves from the entrance to the exit.
This continuous mixing is the furnace's defining characteristic. It ensures every particle is equally exposed to the heat source and any process atmosphere.
Key Operational Implications
The mechanical differences lead to significant distinctions in performance, uniformity, and material handling capabilities.
Heat Distribution and Uniformity
A rotary furnace inherently provides superior temperature uniformity. The constant mixing eliminates hot and cold spots, which is critical for sensitive processes like calcination or catalyst roasting where precise temperature control is paramount.
A pusher furnace has defined temperature gradients along its length. While this is a desirable feature for certain multi-stage heat treatments, the material on the tray itself may experience less uniform heating compared to the tumbling action in a rotary design.
Material Handling and Agitation
Rotary furnaces are ideal for processing powders, granules, and small, free-flowing parts. The tumbling ensures that all surfaces are treated evenly.
Pusher furnaces are necessary for processing discrete parts, delicate components, or materials that must remain in a specific orientation. The material is not agitated, preventing damage or unwanted mixing.
Atmospheric Control
Both furnace types can be designed for controlled atmospheres. However, the sealed-tube design of a rotary retort furnace makes it exceptionally well-suited for maintaining inert, oxidizing, or reducing atmospheres.
The design of a rotary furnace provides excellent gas-to-solid contact, making it highly efficient for chemical reactions like reduction or oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the correct furnace requires weighing the benefits of mixing against the need for material stability.
The Advantage of Mixing
The primary advantage of a rotary furnace is its ability to produce an extremely homogenous final product. If your goal is to ensure every gram of a powder or batch of small parts is processed identically, the tumbling action is a significant benefit.
The Advantage of Stability
The primary advantage of a pusher furnace is process stability and high throughput for non-agitated parts. For heat-treating pressed-and-sintered components or parts that are loaded in specific fixtures, a pusher furnace is the only viable option.
Process Type and Throughput
Both furnaces are designed for continuous processing. A pusher furnace's throughput is determined by the size of the trays and the speed of the pusher mechanism. A rotary furnace's throughput is governed by its diameter, length, and angle of inclination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision hinges on the physical nature of your material and your ultimate processing goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal uniformity for powders or granules: A rotary furnace is the ideal choice due to its inherent mixing action.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput processing of discrete, stable parts: A pusher furnace provides the necessary stability and sequential zone control.
- If your primary focus is efficient gas-solid reactions in a controlled atmosphere: A rotary retort furnace offers superior gas contact and environmental integrity.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace begins with a clear understanding of what your material needs to achieve the desired transformation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rotary Furnace | Pusher Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Material Movement | Tumbling and mixing via rotation | Linear progression on trays |
| Heat Uniformity | High due to constant mixing | Moderate, with defined temperature zones |
| Ideal Materials | Powders, granules, small parts | Discrete parts, delicate components |
| Throughput | Depends on diameter, length, and inclination | Determined by tray size and pusher speed |
| Atmospheric Control | Excellent for inert, oxidizing, or reducing gases | Good, but less efficient gas-solid contact |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature solutions, including Rotary and Pusher Furnaces, tailored to your unique needs. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we ensure precise performance for powders, granules, or discrete parts. Contact us today to discuss how our deep customization can enhance your process efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation



















