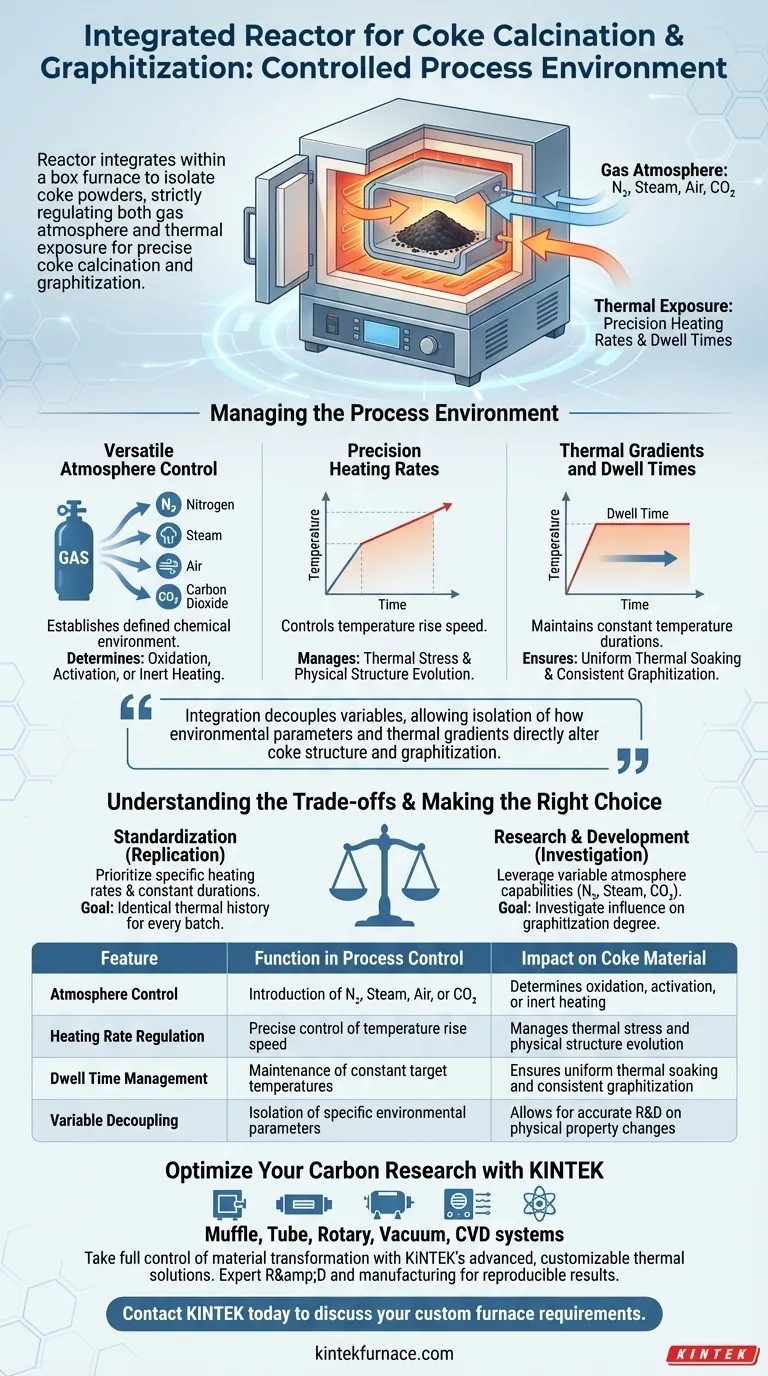
A reactor integrated within a box furnace maintains a controlled process environment by isolating coke powders within a specialized chamber that strictly regulates both the gas atmosphere and thermal exposure. This configuration enables the precise introduction of specific gases—such as nitrogen, steam, air, or carbon dioxide—while simultaneously enforcing exact heating rates and constant temperature durations to ensure a standardized thermal treatment.
This integration is essential for decoupling variables, allowing researchers to isolate how specific environmental parameters and thermal gradients directly alter the physical structure and degree of graphitization in coke.

Managing the Process Environment
Versatile Atmosphere Control
The core function of the integrated reactor is to establish a defined chemical environment distinct from the ambient air.
The system allows for the introduction of various agents, including nitrogen, steam, air, or carbon dioxide. This capability is critical for determining whether the coke undergoes oxidation, activation, or inert heating during the process.
Precision Heating Rates
Unlike standard firing, this setup provides control over specific heating rates.
By regulating how quickly the temperature rises, the system controls the thermal stress and energy input applied to the coke powders. This is a key factor in determining how the material's physical structure evolves.
Thermal Gradients and Dwell Times
To achieve consistent graphitization, the system manages temperature gradients and maintains constant temperature durations.
These "dwell times" allow the material to soak at a target temperature, ensuring that the thermal effects permeate the powder uniformly. This uniformity is required to produce standardized data regarding the material's transformation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Complexity of Standardization
While this setup offers precision, it relies heavily on the rigid control of multiple interacting variables.
Because the system is designed to investigate how slight changes in environmental parameters influence graphitization, any deviation in gas flow or thermal gradient can alter the physical structure of the coke. Achieving the "standardized thermal treatment" promised by the system requires rigorous monitoring to ensure reproducibility between batches.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of an integrated reactor system, align your process parameters with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Standardization: Prioritize the replication of specific heating rates and constant temperature durations to ensure every batch of coke powder receives an identical thermal history.
- If your primary focus is Research & Development: Leverage the variable atmosphere capabilities (switching between nitrogen, steam, or CO2) to investigate how different environmental parameters specifically influence the degree of graphitization.
By precisely manipulating these thermal and atmospheric variables, you gain the ability to engineer the physical structure of coke with high predictability.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Process Control | Impact on Coke Material |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Introduction of N2, Steam, Air, or CO2 | Determines oxidation, activation, or inert heating |
| Heating Rate Regulation | Precise control of temperature rise speed | Manages thermal stress and physical structure evolution |
| Dwell Time Management | Maintenance of constant target temperatures | Ensures uniform thermal soaking and consistent graphitization |
| Variable Decoupling | Isolation of specific environmental parameters | Allows for accurate R&D on physical property changes |
Optimize Your Carbon Research with KINTEK
Take full control of your material transformation with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific research needs. Whether you are standardizing coke calcination or exploring complex graphitization parameters, our integrated furnace systems provide the atmosphere precision and thermal uniformity required for reproducible results.
Ready to elevate your lab's thermal processing? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace requirements with our specialists.
Visual Guide
References
- P. Nanthagopal R. Sachithananthan. Analytical Review on Impact of Catalytic Coke Formation on Reactor Surfaces During the Thermal Cracking Process. DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.17985550
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of gases are used in inert ovens to create a controlled environment? Discover Nitrogen vs. Argon for Optimal Results
- What is the difference between a vacuum furnace and an atmospheric furnace? Choosing the Right Thermal Process
- What are the benefits of using a dosing furnace with a nitrogen degassing system? Pure, Defect-Free Aluminum Casting
- Which industries commonly use inert ovens? Essential for Electronics, Metallurgy, and Materials Science
- What are some examples of inert gases used in inert atmospheres? Optimize Your Process with Nitrogen or Argon
- What is the function of an industrial resistance furnace in melting Al-Fe-Ni-Sc-Zr alloys? Achieve Alloy Homogeneity
- What distinguishes an endothermic atmosphere from an exothermic atmosphere? Key Differences for Heat Treatment
- Why must a high-precision furnace be used for stress relief of Inconel 625 parts? Ensure 3D Print Dimensional Accuracy



















