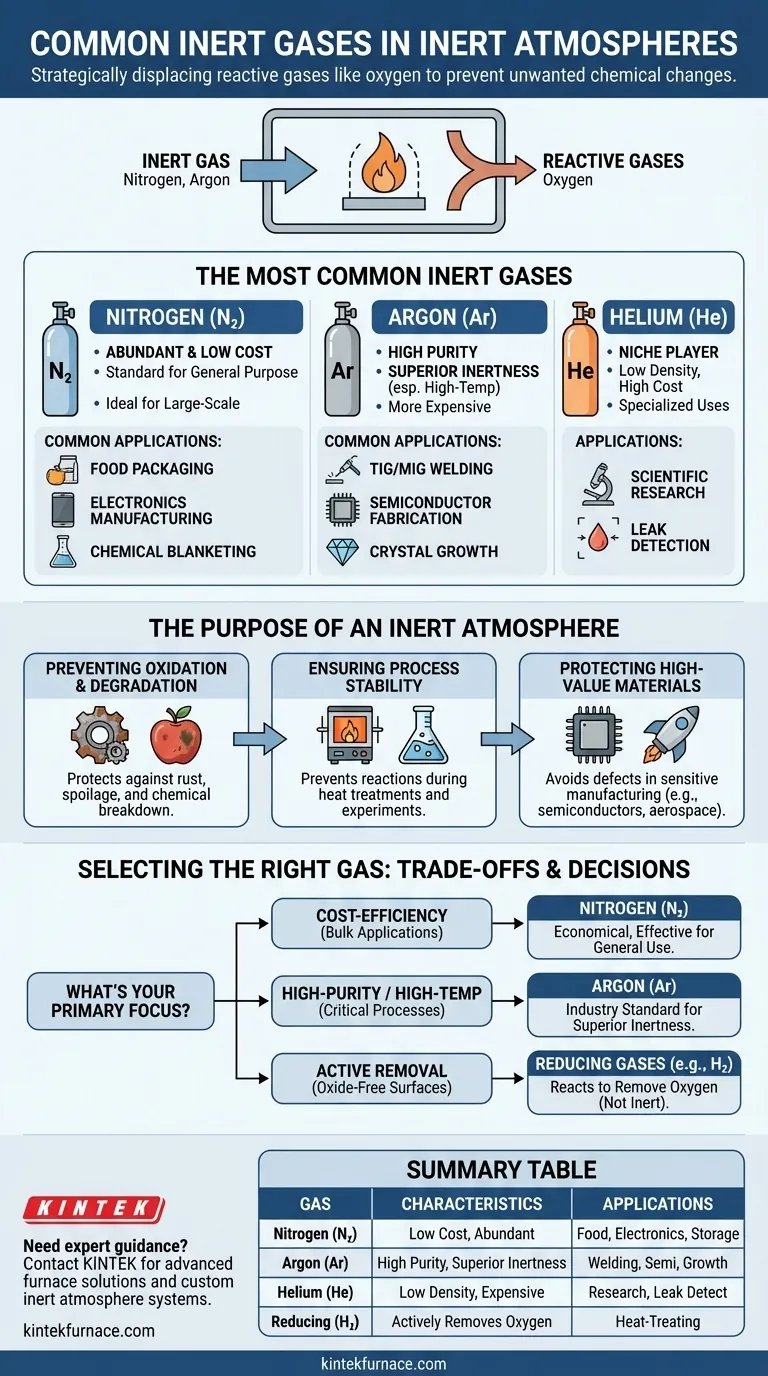
In practice, the most common inert gases used to create a non-reactive atmosphere are nitrogen and argon. Nitrogen is the go-to choice for its low cost and wide availability, making it ideal for large-scale applications. Argon, while more expensive, is used for high-purity or high-temperature processes where even the slight reactivity of nitrogen is unacceptable.
The goal of an inert atmosphere is not simply to fill a space, but to strategically displace reactive gases like oxygen to prevent unwanted chemical changes. The choice of gas is a technical decision balancing cost against the required level of chemical inactivity for a specific process.

The Purpose of an Inert Atmosphere
An inert atmosphere is a controlled environment designed to prevent unwanted chemical reactions. Its primary function is to protect a substance or process from the ambient air, which is highly reactive.
Preventing Oxidation and Degradation
The most common adversary is oxygen, which causes oxidation—the process responsible for metal rust, food spoilage, and the degradation of sensitive chemicals. By displacing oxygen with an inert gas, the shelf life and integrity of a product can be dramatically extended.
Ensuring Process Stability
In many industrial and scientific processes, reactive gases can interfere with results or damage equipment. High-temperature heat treatments, for example, require an inert atmosphere to prevent the metal from oxidizing. Similarly, sensitive electrochemical experiments rely on it to ensure results are accurate and repeatable.
Protecting High-Value Materials
Industries like semiconductor manufacturing and aerospace welding handle materials that are extremely sensitive to contamination. An inert gas like argon creates a pristine environment, preventing defects that could lead to catastrophic failure.
A Closer Look at Common Inert Gases
While several gases are technically inert, only a few are practical for widespread use. The choice is determined by cost, purity, density, and specific process requirements.
Nitrogen (N₂): The Workhorse
Nitrogen constitutes approximately 79% of the air we breathe, making it abundant and highly cost-effective to produce in pure form. It is the standard choice for general-purpose inerting, including food packaging, electronics manufacturing, and blanketing chemical storage tanks.
Argon (Ar): The High-Purity Specialist
Argon is significantly more inert than nitrogen, especially at high temperatures where nitrogen can sometimes react with certain metals to form nitrides. This superior inertness makes it essential for high-specification applications like TIG and MIG welding, crystal growth, and semiconductor fabrication.
Helium (He): The Niche Player
Helium is also extremely inert, but its low density and high cost limit its use to specialized applications. Its unique properties, such as high thermal conductivity and the ability to find microscopic leaks, make it valuable in specific scientific research and advanced manufacturing processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an inert gas is not a one-size-fits-all decision. It requires a clear understanding of the compromises between performance and cost.
Cost vs. Required Purity
The most significant trade-off is between nitrogen and argon. For many applications, nitrogen provides sufficient protection at a fraction of the cost. However, for processes where even minute contamination is unacceptable, the higher cost of argon is a necessary investment to guarantee quality and prevent failure.
True Inertness vs. Reducing Atmospheres
Some processes use gases like hydrogen (H₂) or endothermic gas mixtures. These are not truly inert; they are reducing gases. Instead of just displacing oxygen, they actively react with it to remove it from the atmosphere. This is a different protective mechanism used in specific heat-treating applications to achieve a bright, oxide-free surface on metals.
Practical Implementation Challenges
Creating and maintaining a pure inert atmosphere is a technical challenge. Methods range from simply purging a container with gas to using complex vacuum systems to first remove all air before backfilling. Leaks or improper purging can compromise the entire process, making a high-purity gas useless.
Selecting the Right Gas for Your Application
Your choice should be directly linked to the technical demands of your project and your tolerance for potential reactions.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for bulk applications: Nitrogen is almost always the most economical and effective choice for tasks like food packaging or general-purpose purging.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing or high-temperature metallurgy: Argon is the industry standard, as its superior inertness prevents unwanted side reactions that can occur with nitrogen.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation via active removal: A reducing gas like hydrogen or an endothermic mixture may be more effective than a truly inert gas.
Ultimately, selecting the correct inert gas is a critical engineering decision that directly protects the integrity of your material and the success of your process.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Low cost, abundant, widely available | Food packaging, electronics manufacturing, chemical storage blanketing |
| Argon (Ar) | High purity, superior inertness at high temperatures | TIG/MIG welding, semiconductor fabrication, crystal growth |
| Helium (He) | Low density, high thermal conductivity, expensive | Specialized scientific research, leak detection |
| Reducing Gases (e.g., H₂) | Actively removes oxygen, not inert | Specific heat-treating for oxide-free metal surfaces |
Need expert guidance on selecting the perfect inert gas for your high-temperature processes? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, helping you prevent oxidation, ensure process stability, and protect high-value materials. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















