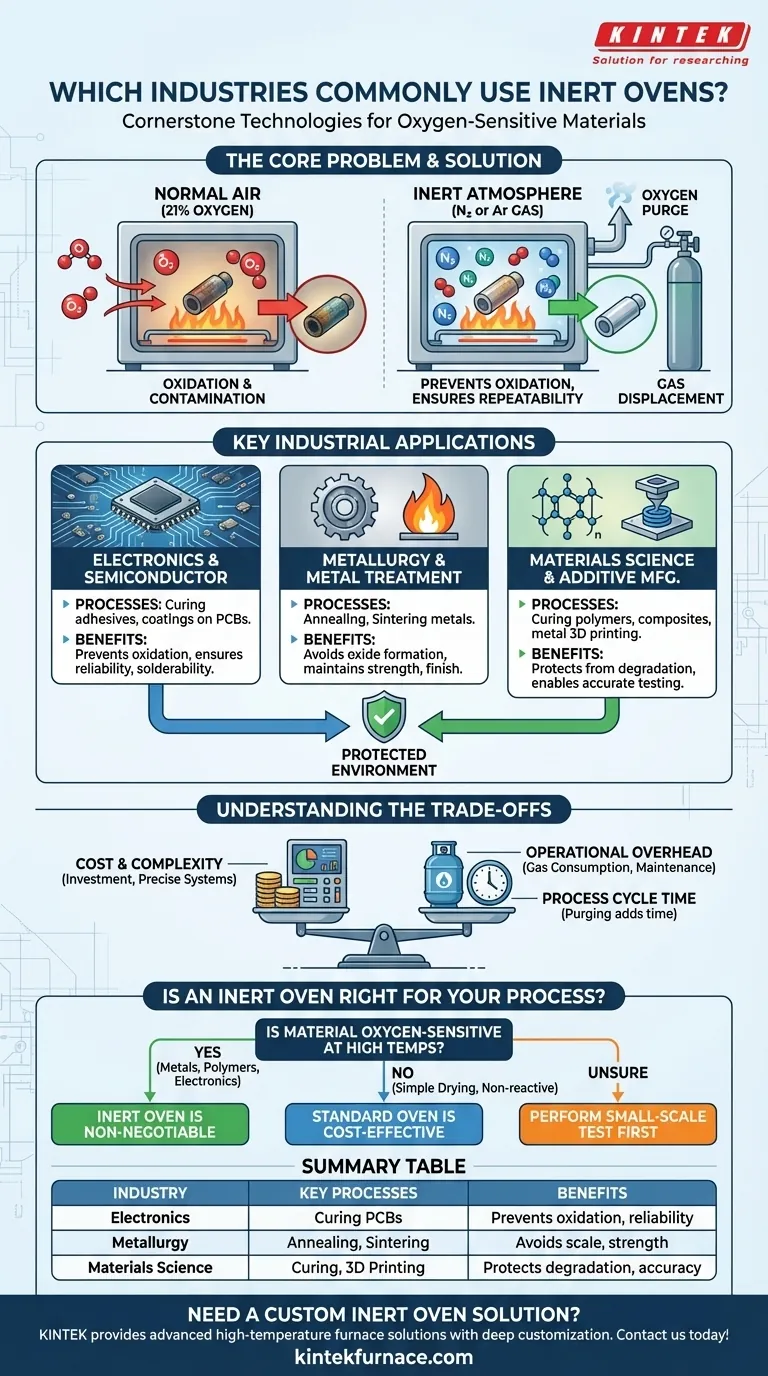
In short, inert ovens are cornerstone technologies in the electronics, metallurgy, and advanced materials science industries. Their use is mandated by processes that involve heating materials that would otherwise be damaged by oxidation or reactions with the oxygen and moisture present in normal air.
The fundamental purpose of an inert oven is to remove oxygen and moisture from the processing environment. By replacing normal air with a non-reactive gas like nitrogen or argon, these ovens create a controlled atmosphere that protects sensitive materials from degradation during critical heating processes.

The Core Problem: Why an Inert Atmosphere is Necessary
The air we breathe is approximately 21% oxygen. While essential for life, it is highly reactive, especially at the elevated temperatures found inside an industrial oven.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Many advanced materials, when heated, will readily react with oxygen. This process, known as oxidation, can fundamentally alter a material's chemical and physical properties.
This reaction can degrade performance, cause discoloration, or lead to outright failure of the component. An inert oven prevents this by creating an oxygen-free environment.
Ensuring Process Repeatability
In high-tech manufacturing, consistency is paramount. Uncontrolled reactions with ambient air introduce variables that make it impossible to guarantee repeatable results.
An inert atmosphere removes this variable, ensuring that the thermal process (like curing or annealing) is the only factor affecting the material.
How It Works: Gas Displacement
The principle is straightforward. An inert oven's chamber is sealed and then purged of ambient air.
This air is replaced with a continuous, low-pressure flow of an inert gas, most commonly nitrogen or argon. These gases are non-reactive and will not interact with the products inside the oven, even at extreme temperatures.
Key Industrial Applications and Processes
While the principle is simple, the applications are critical to modern manufacturing. The need for an inert atmosphere is dictated by the sensitivity of the material being processed.
Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
The electronics industry relies heavily on inert ovens for processes like curing adhesives, encapsulants, and coatings on printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Without an inert atmosphere, sensitive components could oxidize, leading to poor solderability, weak adhesive bonds, and premature circuit failure.
Metallurgy and Metal Treatment
In metallurgy, heat is used to change a metal's properties. Processes like annealing (to soften metal and improve ductility) and sintering (to fuse metal powders into a solid mass) are performed in inert ovens.
This prevents the formation of oxides (scale or rust) on the metal's surface, which would compromise its strength, finish, and structural integrity.
Materials Science and Additive Manufacturing
Researchers and engineers developing new polymers, composites, or ceramics use inert ovens to cure or test materials without introducing chemical changes from oxidation.
This is also critical in certain types of metal 3D printing (additive manufacturing), where metal powder is melted and fused in an inert environment to create strong, dense parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for certain applications, inert ovens are not a universal solution. Their benefits come with clear trade-offs compared to conventional industrial ovens.
Cost and Complexity
Inert ovens are significantly more complex and expensive. They require precise gas delivery systems, oxygen sensors, and superior chamber seals to maintain the inert atmosphere, all of which add to the initial investment.
Operational Overhead
There is an ongoing operational cost associated with the consumption of the inert gas (nitrogen or argon). These systems also require more sophisticated monitoring and maintenance procedures to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Process Cycle Time
The initial phase of purging the oxygen from the chamber can add time to the overall process cycle. This must be factored into production planning and throughput calculations.
Is an Inert Oven Right for Your Process?
The decision to use an inert oven is a technical one based entirely on the chemistry of your materials and the goals of your process.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive metals, polymers, or electronics: An inert oven is non-negotiable to prevent oxidation and ensure the final product meets its required specifications.
- If your primary focus is simple drying or curing of non-reactive materials (e.g., water-based coatings on steel): A standard industrial or laboratory oven is a far more cost-effective and simpler solution.
- If you are unsure about your material's reactivity at high temperatures: It is critical to perform a small-scale test in a conventional oven to observe for discoloration, brittleness, or other signs of oxidation before investing in an inert atmosphere system.
Ultimately, the decision hinges on a clear understanding of your material's chemistry and the absolute precision your process demands.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Processes | Benefits of Inert Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Curing adhesives, coatings on PCBs | Prevents oxidation, ensures component reliability |
| Metallurgy | Annealing, sintering metals | Avoids oxide formation, maintains strength and finish |
| Materials Science | Curing polymers, composites, ceramics | Protects from degradation, enables accurate testing |
Need a custom inert oven solution? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your process with reliable, tailored inert oven technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are inert atmosphere furnaces important for graphite and carbon products? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure High-Performance Results
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance



















