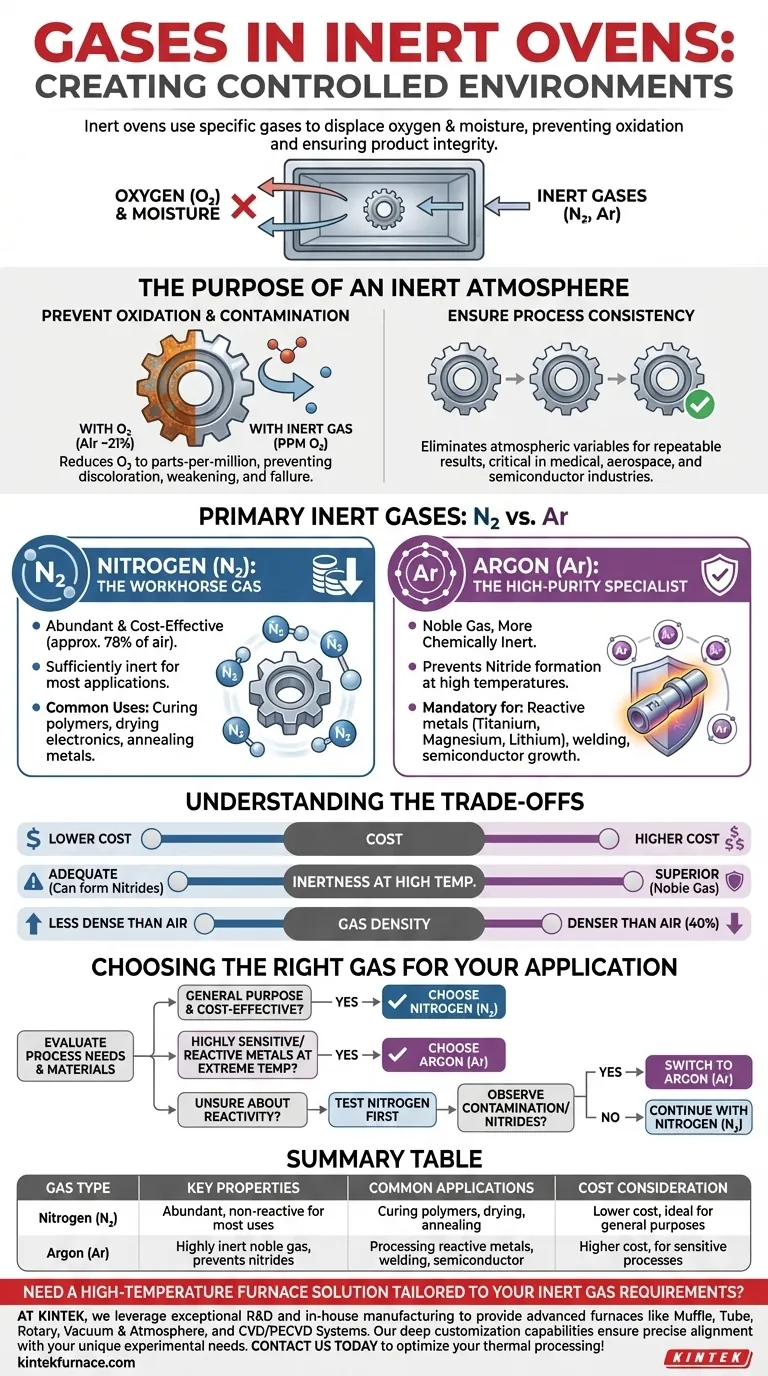
In an inert oven, the controlled atmosphere is created using specific inert gases, most commonly nitrogen (N₂) and argon (Ar). These gases are introduced into the sealed chamber to displace oxygen and moisture, which can cause undesirable reactions like oxidation at elevated temperatures. This process protects the material being processed and ensures the integrity of the final product.
The choice of an inert gas is not arbitrary; it's a calculated decision based on the required level of inertness for your specific process, the reactivity of your materials, and a direct trade-off between operational cost and performance.
The Purpose of an Inert Atmosphere
The fundamental goal of using an inert gas is to remove reactive elements from the oven's environment, primarily oxygen. This controlled atmosphere is critical for high-reliability thermal processing.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Oxygen is highly reactive, especially when heated. For many materials, its presence leads to oxidation, which can manifest as discoloration, tarnishing, weakened structural integrity, or a complete failure of the part's intended function.
By purging the chamber with a gas like nitrogen or argon, you physically push the oxygen out, reducing its concentration from ~21% (in normal air) to mere parts-per-million (PPM). This prevents these destructive reactions from occurring.
Ensuring Process Consistency
An inert atmosphere eliminates a major variable from your process: atmospheric reactivity. This ensures that the results you achieve today will be identical to the results you achieve tomorrow.
This repeatability is non-negotiable in industries like medical device manufacturing, aerospace engineering, and semiconductor fabrication, where even minor deviations can lead to catastrophic failures.
A Closer Look at the Primary Inert Gases
While both nitrogen and argon are effective, they have distinct properties that make them suitable for different applications.
Nitrogen (N₂): The Workhorse Gas
Nitrogen is the most widely used inert gas for industrial ovens. It constitutes approximately 78% of the air we breathe, making it abundant and highly cost-effective to produce and acquire.
For the vast majority of applications—such as curing polymers, drying electronics, or annealing common metals—nitrogen provides a sufficiently inert environment to prevent oxidation without incurring high operational costs.
Argon (Ar): The High-Purity Specialist
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is more chemically inert than nitrogen. While nitrogen is non-reactive in most situations, it can react with certain elements at very high temperatures to form nitrides.
This makes argon the mandatory choice when working with highly reactive metals like titanium, magnesium, or lithium. It is also preferred for advanced processes like welding or semiconductor crystal growth where absolute non-reactivity is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Nitrogen vs. Argon
Choosing between these two gases requires balancing three key factors.
Cost
This is the most significant differentiator. Nitrogen is substantially cheaper than argon. For processes where nitrogen is sufficient, using argon results in unnecessarily high operational expenses.
Inertness at High Temperatures
Argon is always more inert than nitrogen. If your process involves temperatures high enough to cause nitrogen to react with your specific material (forming nitrides), you must use argon. For most other applications, the inertness of nitrogen is perfectly adequate.
Gas Density
Argon is about 40% denser than air, while nitrogen is slightly less dense than air. This means argon can be more effective at displacing air from the bottom up in a chamber. However, a properly designed oven with good circulation can achieve a low-PPM oxygen environment with either gas.
Choosing the Right Gas for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your materials and process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general-purpose curing or annealing: Nitrogen (N₂) is the most practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is processing highly sensitive or reactive metals at extreme temperatures: Argon (Ar) is essential to guarantee absolute inertness and prevent unwanted chemical reactions.
- If you are unsure about your material's reactivity: Start by evaluating nitrogen, but be prepared to test with or switch to argon if you observe any signs of contamination or nitride formation.
Ultimately, selecting the correct inert gas is a crucial step in guaranteeing the quality, reliability, and repeatability of your thermal processing.

Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Key Properties | Common Applications | Cost Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Abundant, cost-effective, non-reactive for most uses | Curing polymers, drying electronics, annealing metals | Lower cost, ideal for general purposes |
| Argon (Ar) | Highly inert noble gas, prevents nitride formation | Processing reactive metals (e.g., titanium), welding, semiconductor growth | Higher cost, used for sensitive processes |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your inert gas requirements? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing process reliability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage



















