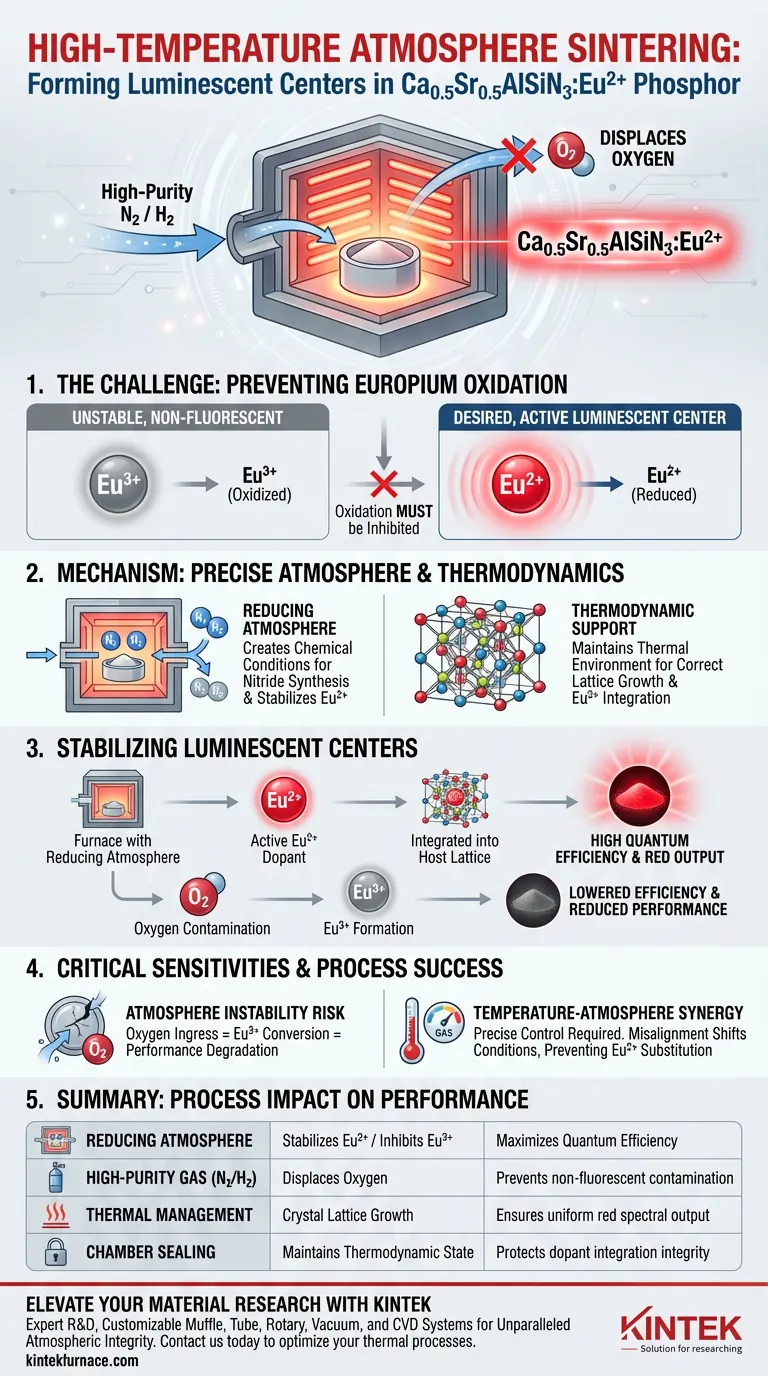
A high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace secures the formation of luminescent active centers by establishing and maintaining a strictly controlled reducing environment, typically utilizing high-purity nitrogen or a nitrogen-hydrogen mixture. This precise atmospheric control creates the specific thermodynamic conditions required to integrate Europium ions into the host lattice in their active divalent state (Eu2+).
The furnace's critical function is inhibiting the oxidation of Europium into its non-fluorescent Eu3+ form. By preventing oxidation during the heating process, the system directly dictates the phosphor's quantum efficiency and its ability to emit the desired red spectral output.

The Mechanism of Atmosphere Control
Establishing the Reducing Environment
The furnace operates by filling the sintering chamber with specific gases, most commonly high-purity nitrogen or nitrogen-hydrogen mixtures.
This gas flow displaces oxygen, creating a reducing atmosphere that is chemically necessary for the synthesis of nitride-based materials.
Thermodynamic Support for Lattice Growth
Beyond simple gas composition, the furnace maintains the thermodynamic environment required for the crystallization of the host material.
This precise thermal management allows the complex Ca0.5Sr0.5AlSiN3 lattice to grow correctly, providing a stable structure to house the luminescent ions.
Stabilizing the Luminescent Centers
Ensuring Eu2+ Integration
For the phosphor to function, Europium ions must enter the host lattice in the +2 oxidation state (Eu2+).
The furnace’s reducing atmosphere actively facilitates this valence state, ensuring that the dopant acts as an effective luminescent center.
Preventing Eu3+ Contamination
If oxygen is present or the atmosphere is not sufficiently reducing, Europium will oxidize into Eu3+.
The primary reference notes that Eu3+ is non-fluorescent in this context; therefore, the furnace's ability to inhibit this transition is the deciding factor in the material's optical performance.
Critical Process Sensitivities
The Consequence of Atmosphere Instability
Any fluctuation in the gas flow or seal integrity can introduce oxygen, immediately degrading the phosphor's performance.
Even a small percentage of Eu3+ conversion due to atmospheric compromise will significantly lower the quantum efficiency of the final product.
Temperature-Atmosphere Synergy
The effectiveness of the reducing atmosphere is tightly coupled with precise temperature control.
If the temperature profile does not align with the gas flow rates, the thermodynamic conditions may shift, preventing the proper substitution of Eu2+ into the lattice sites.
Ensuring Process Success
To maximize the quality of Ca0.5Sr0.5AlSiN3:Eu2+ phosphor production, consider the following operational priorities:
- If your primary focus is Quantum Efficiency: Prioritize the purity and flow consistency of the nitrogen/hydrogen atmosphere to strictly eliminate Eu3+ formation.
- If your primary focus is Spectral Stability: Ensure the furnace's temperature control systems are calibrated to maintain the exact thermodynamic window required for uniform lattice growth.
The success of nitride phosphor synthesis relies entirely on the furnace’s ability to protect the divalent state of the activator ion against oxidation.
Summary Table:
| Process Component | Role in Synthesis | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Reducing Atmosphere | Stabilizes Eu2+ / Inhibits Eu3+ | Maximizes Quantum Efficiency |
| High-Purity Gas (N2/H2) | Displaces Oxygen | Prevents non-fluorescent contamination |
| Thermal Management | Crystal Lattice Growth | Ensures uniform red spectral output |
| Chamber Sealing | Maintains Thermodynamic State | Protects dopant integration integrity |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a high-efficiency phosphor and a failed batch. At KINTEK, we understand that controlling the divalent state of Europium requires unparalleled atmospheric integrity.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique sintering requirements, ensuring strict reducing environments for nitride-based materials.
Ready to optimize your thermal processes? Contact us today to discover how our advanced furnace technology can enhance your laboratory's output and precision.
Visual Guide
References
- E. R. Umerov, Sougata Roy. Fabrication of MAX‐Phase Composites by Novel Combustion Synthesis and Spontaneous Metal Melt Infiltration: Structure and Tribological Behaviors. DOI: 10.1002/adem.202301792
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a fixed-bed reactor system with high-precision temperature control necessary for biochar? Achieve +/-3°C Accuracy
- What is the pressure range of an atmosphere box furnace under high-pressure conditions? Discover Custom Solutions for Your Lab
- How does the experimental box type atmosphere furnace contribute to energy conservation and environmental protection? Discover Sustainable Lab Solutions
- Why must the carbonization of coffee-based bio-adsorbents be performed in a nitrogen furnace? Expert Guide
- How do industrial vacuum or atmosphere furnaces improve Inconel 718 after WAAM? Optimize Strength and Microstructure
- What factors determine the amount of gas flow required for furnace inerting? Optimize Your Process for Safety and Efficiency
- How is the room air displaced in a furnace to operate in different atmospheres? Master Purging for Precise Material Control
- How does a controlled atmosphere annealing furnace influence the stability of retained austenite? Unlock Steel Quality



















