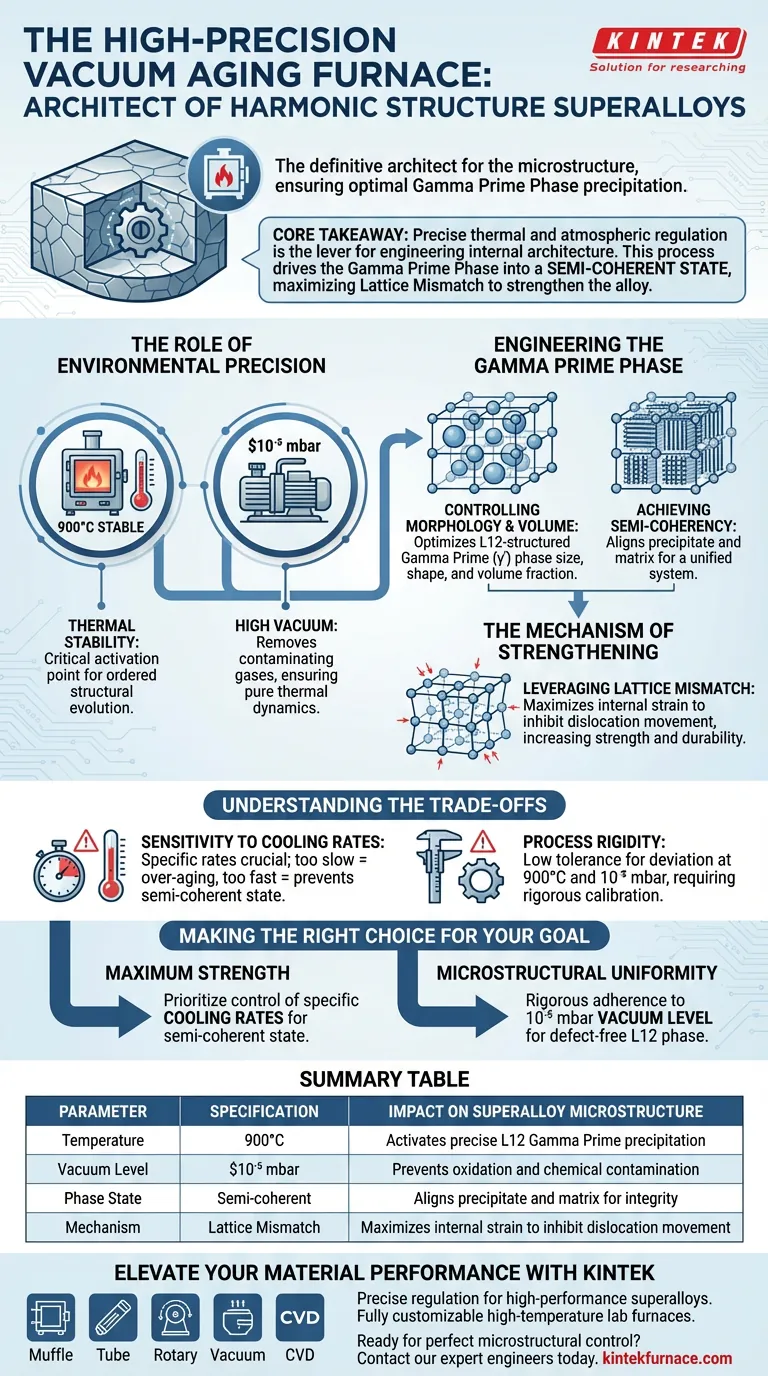
A high-precision vacuum aging furnace acts as the definitive architect for the microstructure of harmonic structure superalloys. By maintaining a strict 900°C temperature under a high vacuum of $10^{-5}$ mbar, the equipment ensures the L12-structured gamma prime phase precipitates with the exact size, shape, and volume fraction required for optimal performance.
Core Takeaway Precise thermal and atmospheric regulation is not merely about preventing oxidation; it is the lever for engineering the material's internal architecture. This process drives the gamma prime phase into a semi-coherent state with the matrix, maximizing lattice mismatch to significantly strengthen the alloy.

The Role of Environmental Precision
Thermal Stability at 900°C
The furnace provides a stable high-temperature environment specifically at 900°C.
This temperature is not arbitrary; it is the critical activation point required to initiate the precipitation process. Maintaining this exact temperature ensures that the reaction kinetics proceed at a rate that allows for ordered structural evolution rather than chaotic growth.
The Necessity of High Vacuum
Operating at a vacuum level of $10^{-5}$ mbar is essential for maintaining the purity of the phase transformation.
This high-vacuum environment removes gases that could react with the alloy surface or diffuse into the matrix. By eliminating these variables, the furnace ensures that the precipitation is driven strictly by thermal dynamics, not by chemical contamination.
Engineering the Gamma Prime Phase
Controlling Morphology and Volume
The primary function of this aging process is to dictate the physical characteristics of the L12-structured gamma prime ($\gamma'$) phase.
Without this precision, the precipitates could become too large or irregularly shaped. The furnace ensures the gamma prime phase precipitates from the gamma matrix in a highly ordered manner, optimizing its volume fraction for mechanical support.
Achieving Semi-Coherency
The ultimate goal of controlling the precipitation is to reach a semi-coherent state.
In this state, the crystal structures of the precipitate and the matrix are aligned but distinct. This alignment is critical because it allows the material to behave as a unified system rather than a composite of disjointed parts.
The Mechanism of Strengthening
Leveraging Lattice Mismatch
The enhancement of the superalloy is directly linked to increased lattice mismatch.
By ensuring the gamma prime phase precipitates in an ordered, semi-coherent state, the furnace maximizes the strain at the interface between the precipitate and the matrix. This internal strain (mismatch) inhibits dislocation movement, which is the fundamental mechanism that increases the material's strength and durability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Cooling Rates
While the furnace provides stability, the process relies heavily on specific cooling rates.
If the cooling rate deviates even slightly after the aging process, the "ordered manner" of precipitation can be disrupted. A rate that is too slow may lead to over-aging (coarsening of particles), while a rate that is too fast may prevent the semi-coherent state from fully developing.
Process Rigidity
The specificity of the 900°C and $10^{-5}$ mbar parameters implies a low tolerance for deviation.
This is not a flexible process; it requires equipment capable of maintaining these exact conditions without fluctuation. The trade-off for high performance is the requirement for rigorous equipment calibration and maintenance to prevent batch variability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the potential of harmonic structure superalloys, you must align your processing parameters with your specific mechanical requirements.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Strength: Prioritize the control of specific cooling rates to preserve the semi-coherent state and maximize lattice mismatch.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Uniformity: rigorous adherence to the $10^{-5}$ mbar vacuum level is essential to ensure the ordered precipitation of the L12 phase without defects.
Precision in the aging environment is the single most critical factor in translating raw alloy potential into realized material performance.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification | Impact on Superalloy Microstructure |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 900°C | Activates precise L12-structured gamma prime precipitation |
| Vacuum Level | $10^{-5}$ mbar | Prevents oxidation and chemical contamination of phases |
| Phase State | Semi-coherent | Aligns precipitate and matrix for unified structural integrity |
| Mechanism | Lattice Mismatch | Maximizes internal strain to inhibit dislocation movement |
Elevate Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Precise thermal regulation is the difference between a standard alloy and a high-performance superalloy. KINTEK provides the industry-leading R&D and manufacturing expertise needed to master these complex transformations. Whether you require Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our high-temperature lab furnaces are fully customizable to meet your exact $10^{-5}$ mbar and 900°C+ requirements.
Ready to achieve perfect microstructural control? Contact our expert engineers today to discuss your unique project needs and discover how our precision systems bring your materials to life.
Visual Guide
References
- Mónica Campos, J. M. Torralba. Enhancement of γ/γ’ Microstructured Cobalt Superalloys Produced from Atomized Powder by Creating a Harmonic Structure. DOI: 10.3390/met14010070
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does Reinforcement Learning (RL) optimize energy consumption? Boost Furnace Efficiency by Up to 30%
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing
- How does temperature control precision of industrial melting furnaces affect intermetallic phase selection?
- What applications does a vacuum melting furnace have in research? Unlock High-Purity Material Development
- What role does an industrial-grade vacuum furnace play in the brazing process of MnCoNiCuGe5 high-entropy alloys?
- How are vacuum coating furnaces applied in the semiconductor and electronic components industry? Essential for High-Purity Electronics
- Why is a vacuum oven required for drying NMC811 precursors? Essential Steps for High-Nickel Cathode Purity
- Why does magnesium distillation use a two-stage pump? A strategic division of labor for efficiency.



















