In a research context, a vacuum melting furnace serves as a cornerstone tool for creating the next generation of high-performance materials. It is primarily used for the purification of base metals and the development of precisely engineered alloys, especially those involving reactive metals like titanium and zirconium, which cannot be processed in a normal atmosphere.
The true value of a vacuum furnace isn't just its ability to melt metal, but its power to control the melting environment. By removing air and other gases, it eliminates the single biggest source of contamination, enabling the creation of materials with properties that would otherwise be impossible to achieve.
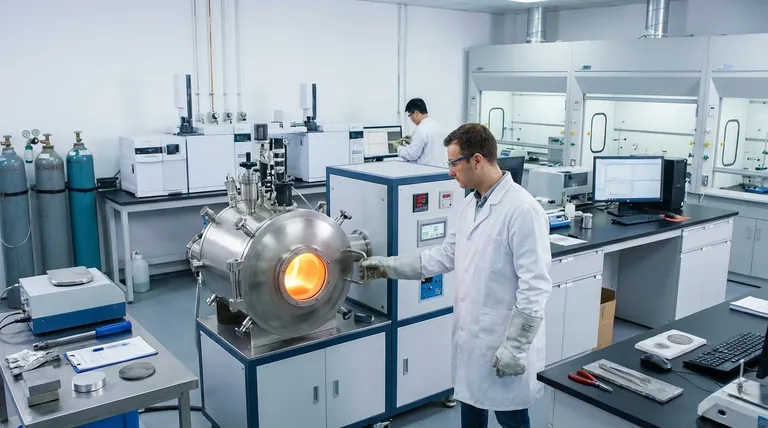

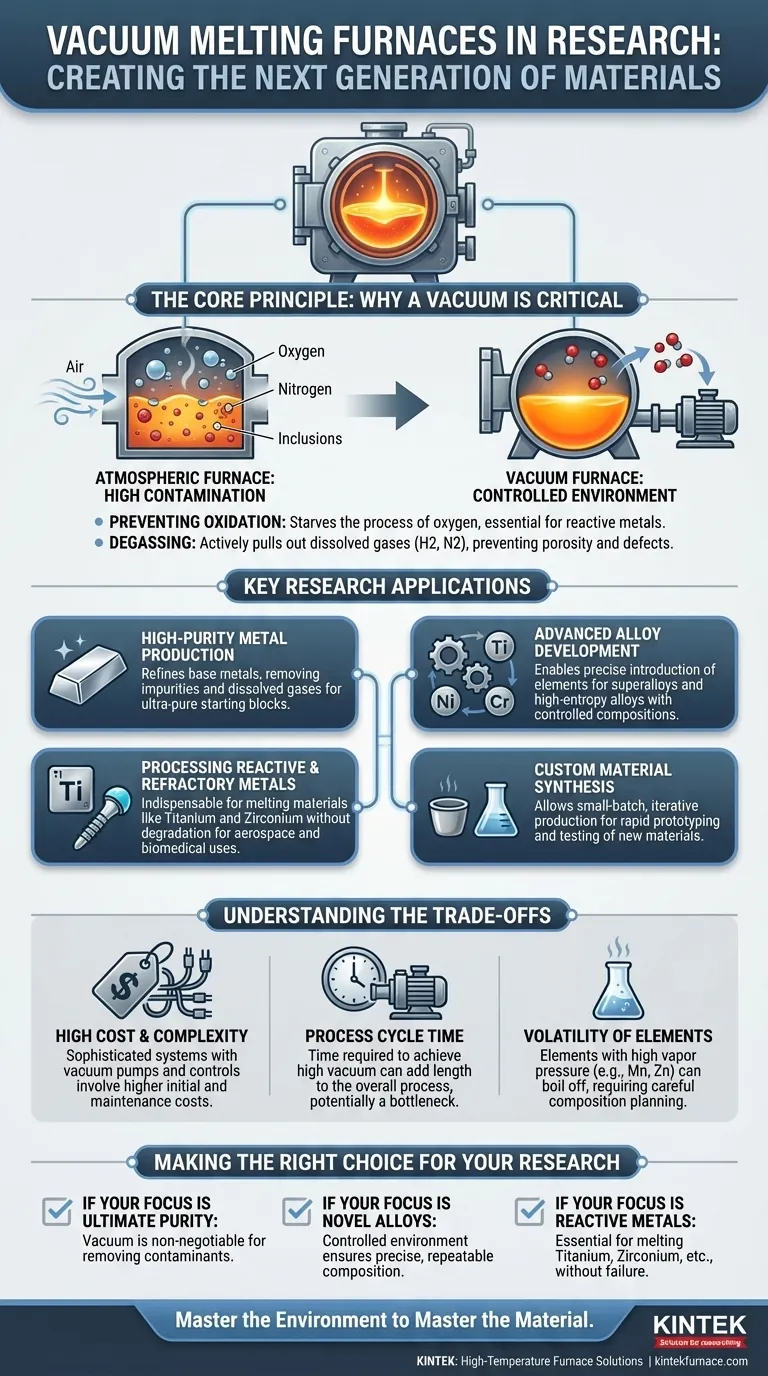
The Core Principle: Why a Vacuum is Critical
The fundamental purpose of using a vacuum is to remove the reactive gases—primarily oxygen and nitrogen—that are present in the air. At high temperatures, these gases aggressively react with molten metal, creating impurities that degrade its final properties.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
In a standard furnace, molten metal readily oxidizes, forming inclusions and altering the material's chemistry. A vacuum environment starves the process of the oxygen it needs, preserving the purity of the melt. This is essential for reactive metals like titanium, which will literally burn in the presence of air at melting temperatures.
Removing Dissolved Gases
The vacuum also has a secondary purification effect. It actively pulls dissolved gases, such as hydrogen and nitrogen, out of the molten metal itself. This process, known as degassing, is critical for improving the mechanical integrity of the final product, preventing defects like porosity and embrittlement.
Key Research Applications
The control offered by a vacuum environment unlocks several critical research applications that are central to modern materials science.
High-Purity Metal Production
Research often begins with establishing a pure, baseline material. A vacuum furnace is used to refine commercial-grade metals by melting them down, allowing impurities to either vaporize or be removed, resulting in an ultra-pure starting block for experiments.
Advanced Alloy Development
With a pure, contamination-free base, researchers can introduce precise amounts of other elements to create novel alloys. This is how materials like high-entropy alloys and aerospace superalloys are developed, where even tiny variations in composition can dramatically alter performance. The process is repeatable and highly controlled.
Processing Reactive and Refractory Metals
Materials like titanium, zirconium, and tantalum have exceptionally high melting points and are extremely reactive. A vacuum induction furnace provides both the high temperatures needed to melt them and the inert environment required to prevent their immediate degradation. This makes it indispensable for research in biomedical implants, aerospace components, and nuclear applications.
Custom Material Synthesis
Because these furnaces allow for precise control over small batches, they are perfectly suited for the iterative nature of research. Scientists can quickly produce small, custom-designed pucks or ingots of experimental materials for testing and analysis without the expense of a large-scale industrial run.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum melting technology is not without its challenges and limitations. Acknowledging them is key to its effective use.
High Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are sophisticated systems involving vacuum pumps, power supplies, and control instrumentation. Their acquisition, installation, and maintenance costs are significantly higher than those of conventional air-melt furnaces.
Process Cycle Time
Achieving a high vacuum is not instantaneous. The time required to pump down the chamber before melting can add considerable length to the overall process cycle, which can be a bottleneck in a high-throughput research environment.
Volatility of Alloying Elements
Under a deep vacuum, some elements with high vapor pressure (like manganese or zinc) can "boil off" from the molten bath. Researchers must account for this potential loss to ensure the final alloy composition matches the intended design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace should be driven by the specific requirements of the material you are creating.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity: A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable for removing atmospheric contaminants and dissolved gases from your base metal.
- If your primary focus is developing novel alloys: The controlled, repeatable environment is essential for ensuring your final composition is precise and free from unwanted variables.
- If your primary focus is working with reactive metals: A vacuum or inert gas environment is the only way to successfully melt materials like titanium, zirconium, or niobium without catastrophic failure.
Ultimately, mastering the environment is the first step toward mastering the material itself.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-Purity Metal Production | Removes impurities and dissolved gases for ultra-pure materials |
| Advanced Alloy Development | Enables precise composition control for novel alloys like superalloys |
| Processing Reactive Metals | Prevents oxidation in metals like titanium for aerospace and biomedical uses |
| Custom Material Synthesis | Allows small-batch production for iterative research and testing |
Ready to advance your materials research with precision? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions, including vacuum melting furnaces, designed for diverse laboratories. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your research outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















