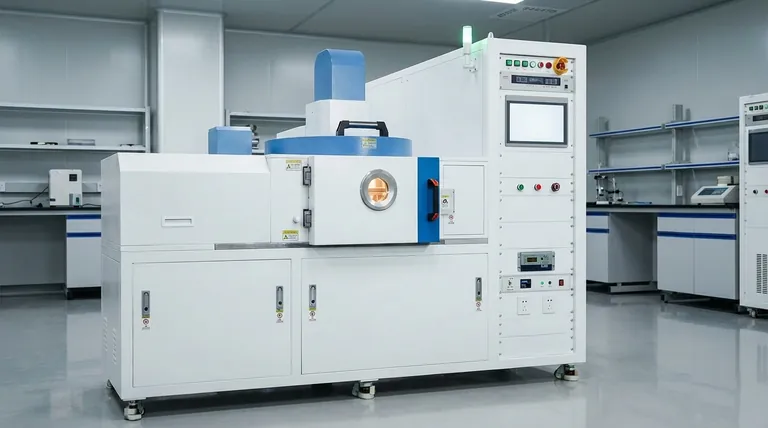
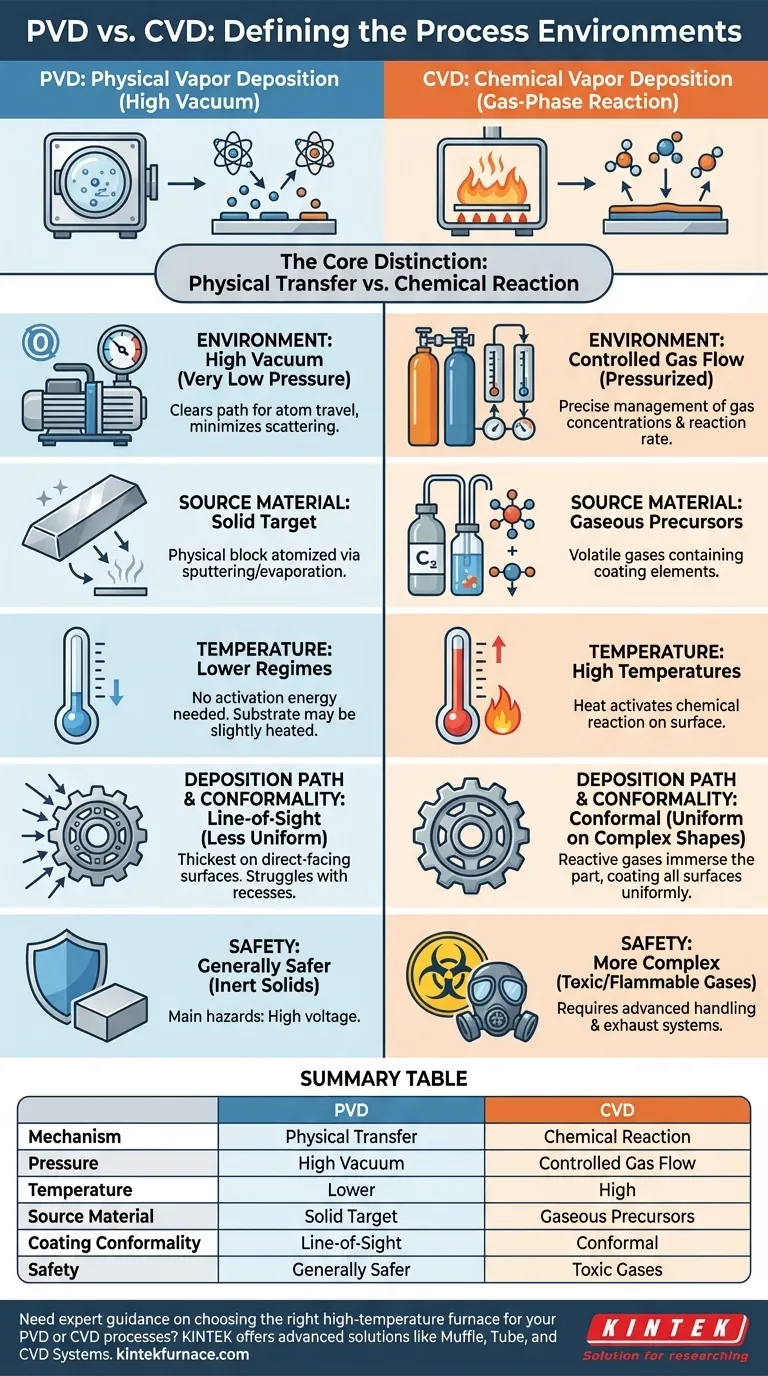
At its core, the primary difference between PVD and CVD process environments lies in their fundamental mechanisms. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) operates in a high vacuum to physically transfer a solid material onto a substrate, much like spray painting with individual atoms. In contrast, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) uses gas-phase chemical reactions at higher temperatures to "grow" a new material directly on the substrate's surface.
The choice between PVD and CVD is a choice between a physical process and a chemical one. PVD moves existing material in a vacuum, while CVD creates new material through controlled chemical reactions, a distinction that dictates the entire process environment, from temperature to safety.

The Core Distinction: Physical Transfer vs. Chemical Reaction
The environmental differences between PVD and CVD are direct consequences of their opposing deposition philosophies. One is a process of transport, the other of creation.
PVD: A High-Vacuum, Line-of-Sight Process
In PVD, the chamber is pumped down to a high vacuum. This is critical because it removes air and other particles that would otherwise collide with and scatter the atoms of the coating material.
A solid source material, or "target," is then vaporized through methods like sputtering or evaporation. These vaporized atoms travel in a straight, line-of-sight path through the vacuum and condense onto the cooler substrate, forming a thin film.
CVD: A Gas-Phase, Reactive Process
CVD does not begin with a solid target. Instead, one or more volatile gaseous precursors are introduced into the chamber under controlled pressure and flow rates.
The substrate is heated to a high temperature, which provides the energy needed to trigger a chemical reaction or decomposition of the gases on its surface. This reaction forms a solid film, effectively "growing" the coating onto the part.
A Head-to-Head Comparison of Process Environments
Understanding the core distinction makes the specific environmental differences intuitive. Each parameter is optimized for either a physical or chemical process.
Pressure: High Vacuum vs. Controlled Gas Flow
The PVD environment must be a high vacuum (very low pressure). The goal is to create a clear path for atoms to travel from the source to the substrate without interference.
The CVD environment, while controlled, is a pressurized system of flowing gases. The pressure and gas concentrations are precisely managed to control the rate and quality of the chemical reaction.
Temperature: Lower vs. Higher Regimes
PVD is generally a lower-temperature process. While the substrate may be heated to improve adhesion, the temperatures are significantly lower than in CVD because no chemical reaction needs to be activated.
CVD almost always requires high temperatures. This heat is the catalyst that provides the activation energy necessary for the precursor gases to react and form the desired solid coating on the substrate.
Source Material: Solid Target vs. Gaseous Precursors
The source material in a PVD system is a solid block or ingot of the coating material. It is a physical source that is atomized.
The source material in a CVD system consists of volatile chemical gases. These precursors contain the elements needed for the final film and are chosen based on the chemical pathway to create it.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Implications
The different environments create distinct advantages and disadvantages that make each process suitable for different goals.
Process Complexity and Control
PVD is a mechanically simpler process. Control is based on physical parameters like deposition time, power applied to the target, and substrate temperature.
CVD is inherently more complex. It requires precise control over gas chemistry, flow rates, pressure, and temperature to manage the chemical reactions, making the process more sensitive.
Coating Properties and Conformality
Because PVD is a line-of-sight process, it can struggle to evenly coat complex shapes, deep recesses, or the inside of parts. The coating is thickest on surfaces directly facing the source.
CVD excels at creating conformal coatings. Because the part is immersed in reactive gases, the coating can form uniformly over intricate geometries and non-line-of-sight surfaces.
Safety and Material Handling
PVD is generally safer, as it primarily deals with solid, inert materials in a vacuum. The main hazards are related to high-voltage equipment.
CVD often involves toxic, flammable, or corrosive precursor gases. This necessitates more complex and expensive safety protocols, gas handling systems, and exhaust treatment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right process environment depends entirely on the requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is coating simple, line-of-sight surfaces at lower temperatures: PVD is the more direct, often safer, and less complex choice for applications like decorative coatings or optics.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly uniform coating on a complex shape or require a specific material only formable via reaction: CVD is the necessary solution, despite its higher temperature and process complexity.
Ultimately, understanding whether your goal demands a physical transfer or a chemical formation is the key to selecting the correct process environment.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Physical transfer of solid material in vacuum | Chemical reaction of gases on substrate |
| Pressure | High vacuum | Controlled gas flow at higher pressure |
| Temperature | Lower temperatures | High temperatures |
| Source Material | Solid target | Gaseous precursors |
| Coating Conformality | Line-of-sight, less uniform | Conformal, uniform on complex shapes |
| Safety | Generally safer with inert solids | Involves toxic, flammable gases |
Need expert guidance on choosing the right high-temperature furnace for your PVD or CVD processes? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















