In inductive heating evaporation, the setup uses a ceramic crucible encircled by an external induction coil, which is in turn protected by a refractory brick housing. This configuration is designed specifically to leverage electromagnetic induction, which generates heat directly within the conductive material being evaporated.
The fundamental difference lies in the heating principle: inductive systems use a magnetic field to heat the target material directly, while other methods like resistive heating heat a crucible indirectly, which then transfers its heat to the material. This distinction dictates every choice in material and configuration.
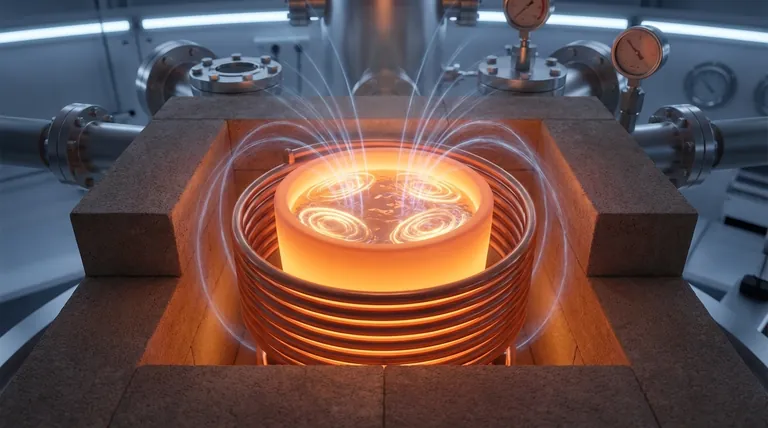
The Inductive Heating Configuration: A Direct Approach
The entire assembly for inductive heating is engineered to allow a magnetic field to pass through the crucible and interact directly with the material inside, such as molten magnesium.
The Ceramic Crucible
The crucible must be made of a material like ceramic because it is an electrical insulator and is transparent to magnetic fields. This allows the energy from the induction coil to pass through the crucible walls without heating them, concentrating the effect on the conductive metal inside.
The External Induction Coil
An induction coil is positioned around the crucible's exterior. When an alternating current flows through this coil, it generates a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field in the space where the crucible sits.
The Principle of Eddy Currents
This magnetic field penetrates the ceramic crucible and induces circular electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the molten magnesium. The inherent electrical resistance of the magnesium causes this current flow to generate intense heat, melting and evaporating the material from the inside out.
The Refractory Brick Housing
A housing made of refractory bricks is placed around the entire setup. It serves two critical functions: providing thermal insulation to maintain high temperatures efficiently and offering physical protection for the external coil from the intense heat.
How This Differs from Resistive Heating: An Indirect Method
To fully appreciate the inductive setup, it's useful to contrast it with the more conventional resistive heating method. The goal is the same—evaporation—but the mechanism is entirely different.
The Heating Element and Crucible
In resistive heating, a resistance wire is wound directly around the exterior of a crucible, which is often made of alumina. This wire is the source of heat, similar to the element in an electric stove.
The Mechanism of Indirect Heating
The process is indirect: electricity heats the wire, the hot wire heats the crucible through conduction and radiation, and finally, the hot crucible transfers its heat to the material inside. This is a much slower, multi-step energy transfer.
The Need for Different Insulation
Instead of dense refractory bricks, resistive systems often use lighter insulation like alumina fiber cotton. Its primary role is to simply trap the radiant heat being emitted by the hot crucible and wire assembly.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Efficiency
The choice between these configurations is not arbitrary; it centers on a critical trade-off between efficiency and complexity.
Why Inductive Heating is More Efficient
Inductive heating is fundamentally more efficient because it generates heat precisely where it is needed—within the target material itself. Far less energy is wasted heating the crucible and surrounding components first, leading to faster heat-up times and lower energy consumption.
The Inefficiency of Resistive Heating
Resistive heating loses significant energy to the environment. The system must first bring the heating wire and the entire mass of the crucible up to temperature before the target material begins to heat effectively. This creates thermal lag and wastes energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding these core principles allows you to select the technology that best aligns with your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and rapid heating: Inductive heating is the superior choice, as its direct heating mechanism minimizes wasted energy and reduces process time.
- If your primary focus is equipment simplicity and potentially lower initial cost: Resistive heating offers a more straightforward design, though it comes at the cost of lower thermal efficiency and slower performance.
Ultimately, selecting the right configuration depends on understanding that how you generate the heat is just as important as how much heat you generate.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Inductive Heating | Resistive Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Principle | Direct (via magnetic field) | Indirect (via conduction/radiation) |
| Crucible Material | Ceramic (magnetic field transparent) | Often Alumina |
| Heat Generation | Inside the target material | In external wire, then crucible |
| Primary Insulation | Refractory Brick Housing | Alumina Fiber Cotton |
| Efficiency | High (minimal energy waste) | Lower (thermal lag, energy loss) |
| Heating Speed | Fast | Slower |
Optimize Your Evaporation Process with KINTEK
Understanding the nuances of heating technology is crucial for achieving peak performance in your lab. Whether your priority is maximum energy efficiency with rapid inductive heating or the simpler setup of a resistive system, the right equipment is key.
KINTEK's expert R&D and manufacturing team delivers precisely that. We offer a range of high-performance lab furnaces, including customizable Vacuum and CVD systems, designed to meet your unique thermal processing needs.
Let us help you select the perfect system to enhance your process efficiency and results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and receive a personalized solution!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- How does induction heating ensure precision in manufacturing processes? Achieve Superior Thermal Control & Repeatability
- What are some specific applications of vacuum hot press furnaces? Unlock Advanced Material Fabrication
- How does the use of vacuum in hot-pressing affect the material processing? Achieve Denser, Purer, and Stronger Materials
- What role does Vacuum Hot Press technology play in the automotive industry? Boost EV Batteries, Safety, and Efficiency
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density



















