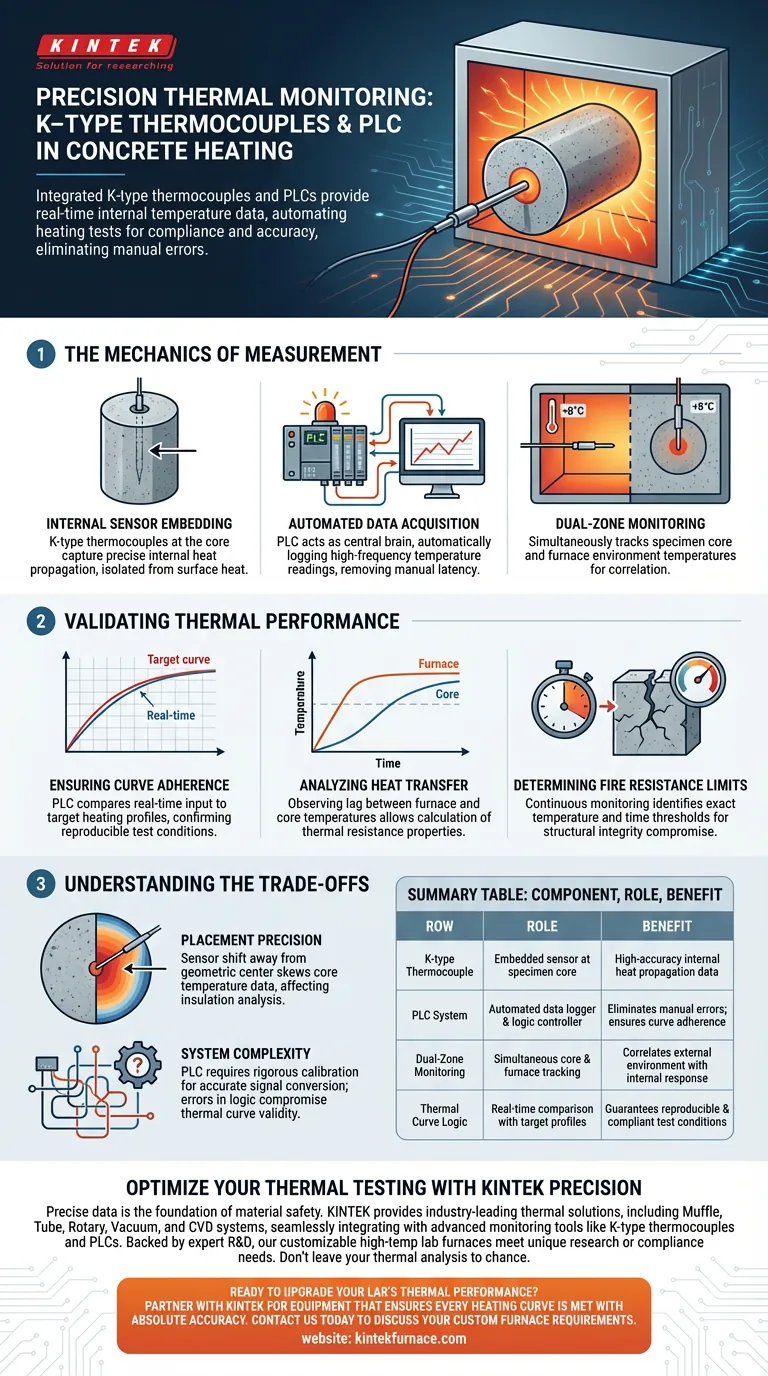
The integration of K-type thermocouples with Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) creates a unified system for precision thermal monitoring. By embedding these sensors directly into the concrete core and interfacing them with a PLC, researchers can capture real-time temperature data to verify that the heating process strictly adheres to predefined thermal curves. This automated setup allows for the simultaneous tracking of both the furnace environment and the internal specimen temperature, eliminating manual measurement errors.
The synergy between embedded sensors and automated logic control transforms static heating tests into dynamic data acquisition systems. This ensures that heat transfer is not only measured but actively verified against thermal targets to accurately evaluate the fire resistance and thermal properties of concrete.
The Mechanics of Measurement
Internal Sensor Embedding
To capture accurate internal data, K-type thermocouples are embedded directly into the center of the concrete cylinders. This placement is critical because it isolates the core temperature from the immediate surface heat. It allows for a precise reading of how heat propagates through the material's depth over time.
Automated Data Acquisition
Once embedded, these thermocouples are wired directly to a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) system. The PLC acts as the central brain of the operation, automatically logging temperature readings at high frequencies. This automation removes the latency and inconsistency associated with manual data recording.
Dual-Zone Monitoring
The system is designed to monitor two distinct data points simultaneously: the specimen core temperature and the furnace temperature distribution. By correlating these two datasets, engineers can understand exactly how the external heating environment influences the internal state of the concrete.
Validating Thermal Performance
Ensuring Curve Adherence
A primary function of the PLC integration is to ensure the experiment follows predefined thermal curves. The PLC compares real-time input from the thermocouples against the target heating profile. This confirms that the test conditions are consistent and reproducible.
Analyzing Heat Transfer
The data collected facilitates a detailed analysis of heat transfer mechanics within the concrete. By observing the lag between the furnace temperature and the core temperature, researchers can calculate the thermal resistance properties of the specimen.
Determining Fire Resistance Limits
Ultimately, this setup provides the critical data needed to establish fire resistance limits. The continuous monitoring allows researchers to identify the exact temperature and time thresholds where the concrete's structural integrity may be compromised.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Placement Precision
The reliability of the data is entirely dependent on the physical placement of the thermocouple. If the sensor shifts away from the exact geometric center during the concrete pouring or setting process, the core temperature data will be skewed. This can lead to inaccurate conclusions regarding the material's insulation properties.
System Complexity
While a PLC offers automation, it introduces complexity in setup and programming. The system requires rigorous calibration to ensure that the analog signals from the K-type thermocouples are correctly converted into digital temperature readings. Any error in the PLC's logic or signal conversion will compromise the validity of the entire thermal curve.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the value of this measurement system, align your setup with your specific analytical objectives:
- If your primary focus is Material Research: Ensure your PLC is programmed to sample at high frequencies to capture granular changes in heat transfer rates during rapid temperature spikes.
- If your primary focus is Compliance Testing: Prioritize the synchronization of furnace and core data to prove the test strictly followed the mandated thermal curves for fire resistance certification.
Precise measurement of internal temperature distribution is the only way to move from theoretical assumptions to empirical proof of concrete performance.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Temperature Measurement | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| K-type Thermocouple | Embedded sensor at specimen core | High-accuracy internal heat propagation data |
| PLC System | Automated data logger and logic controller | Eliminates manual errors; ensures curve adherence |
| Dual-Zone Monitoring | Simultaneous core and furnace tracking | Correlates external environment with internal response |
| Thermal Curve Logic | Real-time comparison with target profiles | Guarantees reproducible and compliant test conditions |
Optimize Your Thermal Testing with KINTEK Precision
Precise data is the foundation of material safety and fire resistance certification. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all designed to integrate seamlessly with advanced monitoring tools like K-type thermocouples and PLCs.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our high-temp lab furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research or industrial compliance needs. Don't leave your thermal analysis to chance—partner with KINTEK for equipment that ensures every heating curve is met with absolute accuracy.
Ready to upgrade your lab's thermal performance? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements.
Visual Guide
References
- N. Algourdin, Amir Si Larbi. High temperature performance of recycled fine concrete. DOI: 10.1007/s44242-024-00050-w
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
People Also Ask
- Why is the precise spatial arrangement of thermocouple probes necessary in magnesium combustion experiments?
- What are the physical properties of MoSi2 heating elements? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- In which industries are silicon carbide heating elements commonly used? Essential for High-Temp, Precision Applications
- What is the maximum temperature of a heating element? Balancing Material Limits, Atmosphere & Design
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the technical considerations for selecting high-density graphite substrates? Optimize Your Thermal Experiments
- How does an electric heating system ensure stable ignition during coal gasification? Achieving Reliable Process Control
- What are the three essential components needed to produce graphite heating elements? The Key to Reliable High-Temp Performance



















