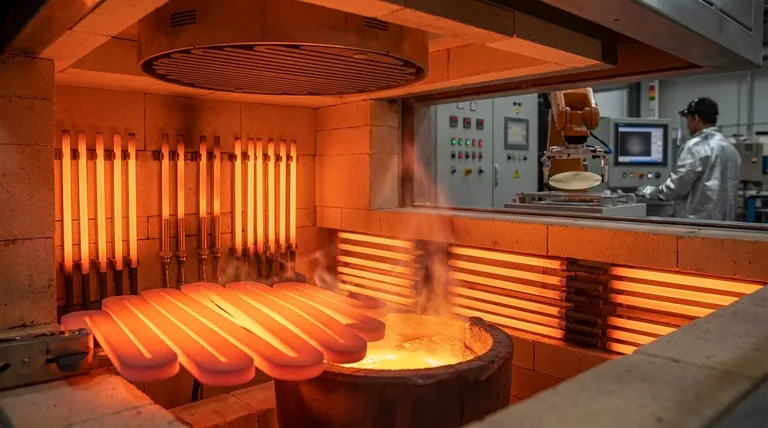
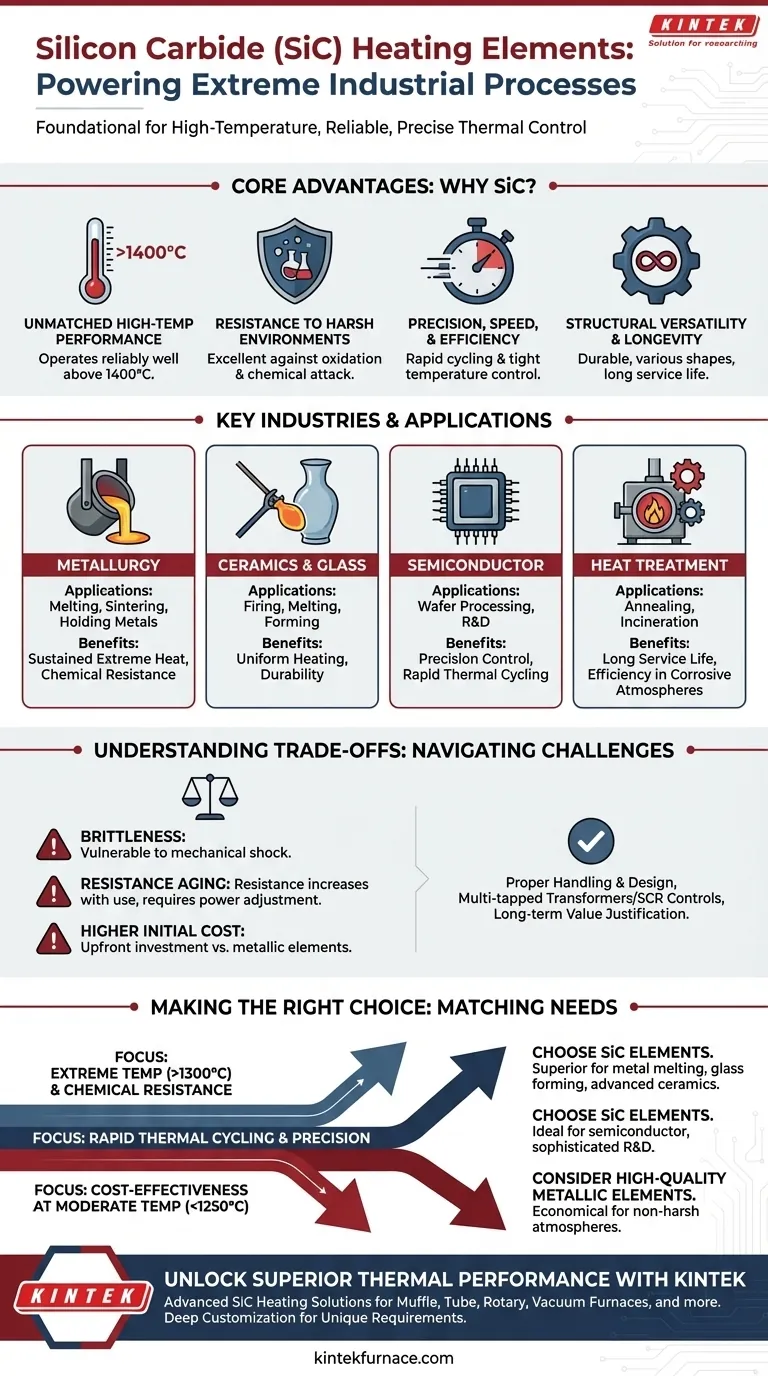
In short, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are foundational components in industries that demand extreme temperatures and reliable, precise thermal control. Their use is widespread in demanding fields such as metallurgy, ceramics and glass manufacturing, semiconductor production, and industrial heat treatment. SiC elements are chosen for their ability to perform where conventional metallic elements would fail.
The core reason silicon carbide is so prevalent is its unique combination of properties: it can operate at exceptionally high temperatures, offers a long service life even in harsh chemical atmospheres, and provides the rapid, precise control necessary for sensitive industrial processes.

Why These Industries Rely on Silicon Carbide
The decision to use SiC heating elements is not arbitrary; it is driven by specific engineering requirements that only a material like silicon carbide can meet. Different industries leverage distinct advantages of this advanced ceramic.
Unmatched High-Temperature Performance
Silicon carbide elements can operate reliably at furnace temperatures well above 1400°C (2550°F), far exceeding the limits of most metallic heating elements.
This capability is essential for metallurgy, where processes like melting, sintering, and holding molten metals require sustained, extreme heat. It is equally critical in glass manufacturing for melting and forming applications.
Resistance to Harsh Environments
SiC elements exhibit excellent resistance to oxidation and chemical attack, even at high temperatures. This makes them ideal for use in furnaces with reactive atmospheres.
This property is vital for heat treatment of metals and in incineration processes, where corrosive byproducts are common. It ensures a long and predictable service life, reducing costly downtime.
Precision, Speed, and Efficiency
The elements heat and cool quickly, allowing for rapid process cycling and tight temperature control. An electric current passes through the element, generating radiant heat that can be precisely modulated by adjusting the voltage.
This responsiveness is critical in semiconductor manufacturing and laboratory R&D, where thermal profiles must be followed exactly. Their energy efficiency also lowers operational costs in energy-intensive applications.
Structural Versatility and Longevity
SiC elements are manufactured in various shapes, including rods, spirals, and U-shapes, and can be installed either vertically or horizontally. This allows for flexible furnace design.
Their inherent durability and long operational lifespan make them an economical choice over the long term, despite a potentially higher initial investment. This reliability is a key factor for any high-throughput industrial operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, SiC elements are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to successful implementation and avoiding common pitfalls.
Brittleness and Mechanical Shock
Like most ceramics, silicon carbide is brittle. The elements can fracture if subjected to significant mechanical shock, such as being dropped or improperly secured against vibration.
Careful handling during installation and maintenance is non-negotiable. Furnace designs must also account for thermal expansion to avoid placing mechanical stress on the elements as they heat up.
Resistance Aging
A fundamental characteristic of SiC is that its electrical resistance gradually increases with use over time. This phenomenon is known as aging.
To compensate for this, the power supply system must be capable of delivering progressively higher voltage to maintain the required power output (heat). This often necessitates the use of multi-tapped transformers or sophisticated SCR controls.
Higher Initial Cost
The upfront cost of SiC elements and their required power control systems is typically higher than that of standard metallic elements like Kanthal (FeCrAl).
This initial investment is justified by longer service life, higher temperature capability, and improved process control, but it must be factored into the economic analysis of the furnace system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating element technology requires aligning its capabilities with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures (>1300°C) and chemical resistance: SiC elements are the superior choice for processes like metal melting, glass forming, or advanced ceramics firing.
- If your primary focus is rapid thermal cycling and precision: The fast response time and controllability of SiC make it ideal for semiconductor processing and sophisticated R&D furnaces.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness at moderate temperatures (<1250°C): High-quality metallic elements may provide a more economical solution for applications without harsh atmospheres or extreme thermal demands.
Ultimately, understanding these core characteristics ensures you select a heating solution that delivers both performance and long-term value.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Key Benefits of SiC Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Melting, sintering, holding metals | High-temperature operation (>1400°C), chemical resistance |
| Ceramics & Glass | Firing, melting, forming | Uniform heating, durability in harsh environments |
| Semiconductor | Wafer processing, R&D | Precision control, rapid thermal cycling |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, incineration | Long service life, efficiency in corrosive atmospheres |
Unlock superior thermal performance with KINTEK's advanced silicon carbide heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your industrial processes with reliable, precise heating elements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















