High-density graphite substrates are the industry standard for these experiments due to their chemical inertness. They provide a stable, non-reactive foundation that withstands extreme temperatures without influencing the molten calcium silicate slag or aluminum droplets. This ensures that the chemical data collected reflects only the interaction between the metal and the slag, rather than an interaction with the container itself.
The core technical value of high-density graphite lies in its ability to isolate the reaction at the metal-slag interface, preventing substrate interference that would otherwise compromise wetting behavior analysis and introduce contamination.
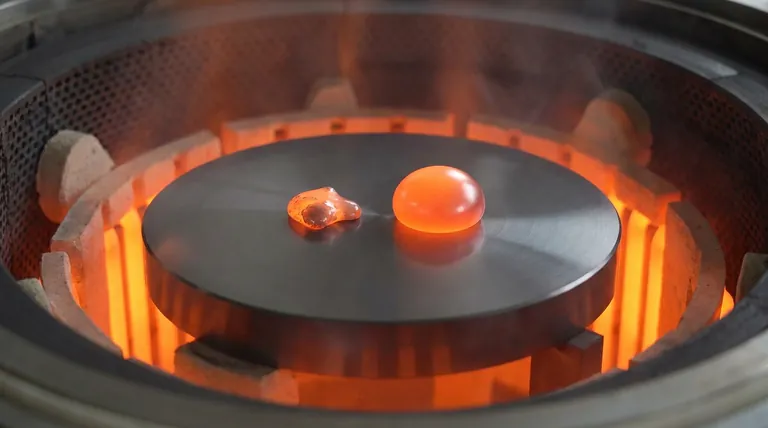
Chemical Stability and Reaction Isolation
Preventing Substrate Contamination
The most critical requirement for a carrier substrate is neutrality. High-density graphite is chemically stable, meaning it acts as a strictly passive support system.
It prevents the substrate material from leaching into or reacting with the molten samples. This guarantees that the final composition of the slag and aluminum remains pure and unaltered by the carrier.
Confining the Reaction Interface
In thermal reduction experiments, the specific focus is the interaction between the aluminum reductant and the oxide slag.
High-density graphite ensures that chemical reactions are confined strictly to this metal-slag interface. By eliminating side reactions between the sample and the base, researchers can accurately isolate the reduction mechanics.
Physical Interaction and Wetting Mechanics
Non-Wetting Properties
Accurate analysis of wetting behavior requires the sample to maintain its natural shape without adhering to the surface.
High-density graphite exhibits excellent non-wetting properties at high temperatures. This repels the molten slag and metal, preventing them from spreading uncontrollably or infiltrating the substrate surface.
Preserving Geometric Integrity
Because the graphite resists wetting, the molten aluminum and slag droplets retain their intended droplet formation.
This physical stability is essential for optical measurements of contact angles. If the substrate were to wet, the geometry of the droplet would distort, rendering wetting behavior analysis invalid.
Understanding the Material Requirements
The Necessity of High Density
Not all graphite is suitable for these applications; the specification of high density is deliberate.
Lower-density variants may possess surface porosity that could lead to physical infiltration of the molten liquid. To ensure the "excellent non-wetting properties" cited, the material must be sufficiently dense to present a sealed, impermeable surface to the melt.
Thermal Resilience
The substrate must endure the specific thermal profile of calcium silicate reduction without degrading.
While graphite is generally heat resistant, the high-density designation ensures structural integrity is maintained even at the extreme temperatures required to melt silicate slags and aluminum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing your experimental apparatus, prioritize the grade of graphite based on your specific analytical needs:
- If your primary focus is chemical purity: Select the highest density grade available to ensure zero reactivity and prevent carbon contamination in the aluminum or slag phases.
- If your primary focus is wetting behavior analysis: Ensure the surface finish is polished and the density is sufficient to guarantee hydrophobic-like behavior with molten metals, preserving droplet geometry.
The success of your thermal reduction study depends on viewing the substrate not just as a holder, but as a critical control variable in your experiment.
Summary Table:
| Technical Requirement | High-Density Graphite Property | Experimental Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Neutrality | High inertness and stability | Prevents sample contamination and ensures data purity |
| Interface Control | Reaction isolation | Confines reactions strictly to the metal-slag interface |
| Wetting Behavior | Non-wetting characteristics | Preserves droplet geometry for accurate contact angle analysis |
| Surface Integrity | High density/low porosity | Prevents physical infiltration of molten slag or aluminum |
| Thermal Stability | Structural resilience | Maintains integrity at extreme reduction temperatures |
Elevate Your Research with Precision Lab Furnaces
Ensure the success of your thermal reduction studies with the right equipment and substrates. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable for your unique experimental needs. Whether you are analyzing metal-slag interfaces or performing complex chemical vapor depositions, our high-temperature lab furnaces provide the stability and control required for accurate results.
Ready to optimize your lab setup? Contact KINTEK today to discuss our customizable furnace solutions and high-density material support.
References
- Harald Philipson, Kristian Etienne Einarsrud. Investigation of Liquid–Liquid Reaction Phenomena of Aluminum in Calcium Silicate Slag. DOI: 10.3390/ma17071466
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How convenient are MoSi2 heating elements to install and maintain? Maximize Uptime with Easy Hot-Swappable Elements
- What is a heating element and its key components? Discover How It Powers Efficient Heat Generation
- Why is high temperature stability important for graphite heating elements? Ensure Reliable Performance in Extreme Heat
- How do electrical heating elements work? Master Heat Generation for Your Lab
- What are the technical advantages of micro-tubular ceramic heaters? Speed Up Your Rapid Thermal Cycling Tests
- What are some common types of silicon carbide heating elements? Explore Shapes, Coatings, and High-Temp Performance
- What are the advantages of using molybdenum-disilicide heating elements for aluminum alloy processing? (Rapid Heating Guide)
- Are ceramic heaters safe to use? Discover Why They're a Top Choice for Home Safety












