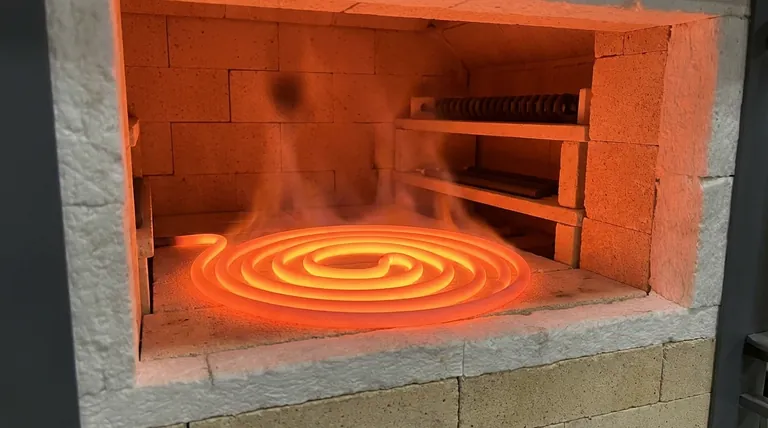
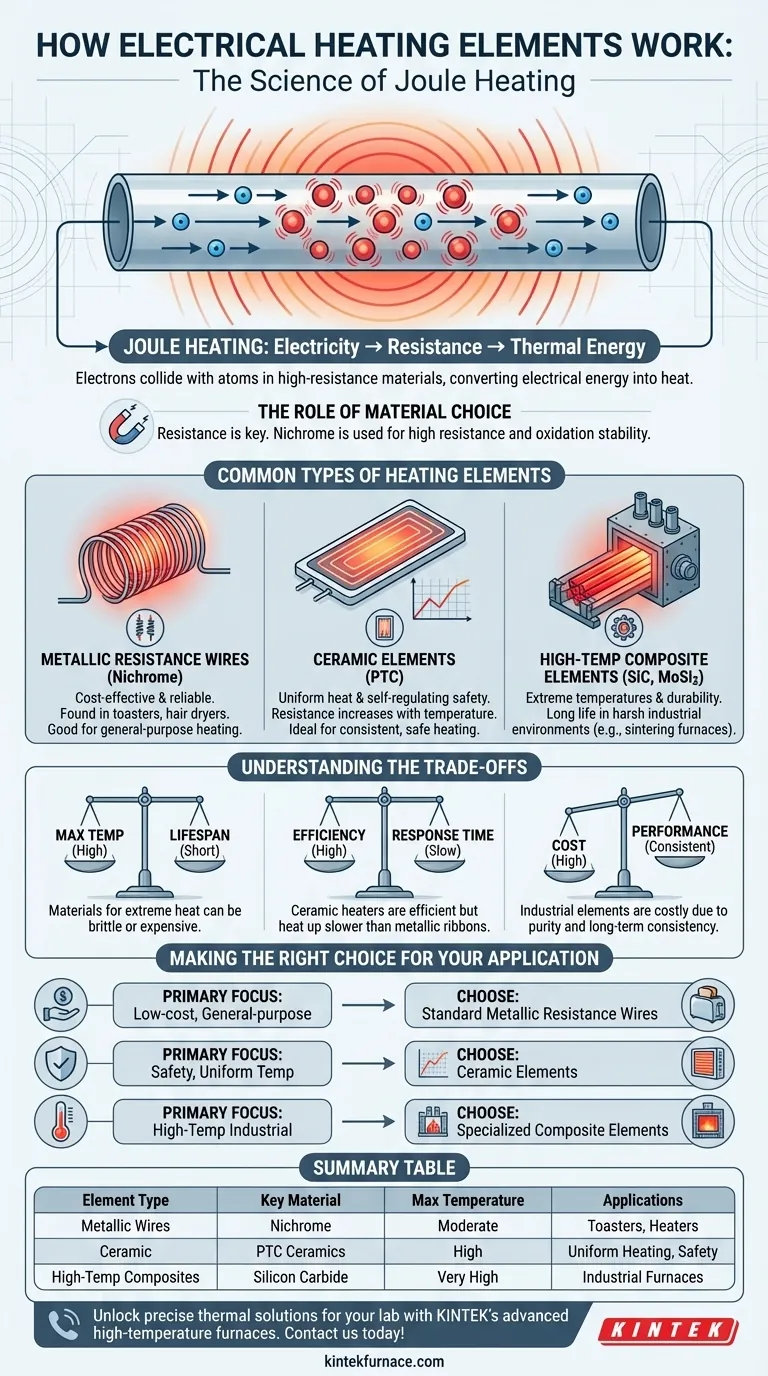
At its core, an electrical heating element works by converting electrical energy into thermal energy through a process called Joule heating. When an electric current is passed through a material with high electrical resistance, the opposition to the current's flow generates a significant amount of heat. This intentionally generated heat is then radiated or conducted to perform its intended function, from toasting bread to firing industrial ceramics.
The effectiveness of a heating element is not about its ability to simply get hot, but about its material composition. The entire design hinges on choosing a material with the ideal electrical resistance to convert electricity into a precise, controllable, and durable source of heat.

The Fundamental Principle: Joule Heating
The physics behind every electrical heater is straightforward yet powerful. Understanding this principle is the key to understanding why different elements are used for different tasks.
What is Electrical Resistance?
Think of electrical resistance as a form of friction for electricity. As electrons flow through a conductor, they collide with the atoms of the material. In a low-resistance material like copper, these collisions are minimal.
In a high-resistance material, however, the electrons collide frequently and forcefully with the atoms. These collisions transfer kinetic energy, causing the atoms to vibrate more intensely, which we perceive as heat.
The Role of Material Choice
This is where the engineering comes in. The choice of material is the single most important factor. Materials like nichrome (an alloy of nickel and chromium) are used because they have high resistance and, crucially, do not oxidize or break down at high temperatures.
Other advanced materials are chosen for their specific properties, such as the ability to withstand extreme temperatures or provide uniform heat distribution.
From Current to Heat
The amount of heat generated is directly proportional to the resistance of the element and the square of the current passing through it. This relationship means that a small increase in current can produce a large increase in heat output.
This principle allows for the precise temperature control that is critical in both household appliances and sensitive industrial systems.
Common Types of Heating Elements
Not all heating elements are created equal. The material choice dictates the element's performance, lifespan, and ideal application.
Metallic Resistance Wires
These are the most common type of heating element, often made of nichrome. They are formed into coils or ribbons and are found in appliances like toasters, hair dryers, and electric space heaters. They are cost-effective and reliable for general-purpose heating.
Ceramic Elements
Ceramic heaters use advanced ceramic materials, such as Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) ceramics. An electric current passes through the ceramic, which resists the flow and generates heat.
Their key advantage is uniform heat distribution and inherent safety. As PTC ceramics heat up, their resistance increases, causing them to self-regulate and prevent overheating. This makes them ideal for applications requiring consistent, reliable heat.
High-Temperature Composite Elements
For demanding industrial applications like sintering furnaces, specialized elements are required. Materials like silicon carbide and molybdenum disilicide can operate at extremely high temperatures for extended periods.
These elements are designed for maximum durability and long service life in harsh environments where precise temperature profiles are non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for selecting the right component for a given task.
Maximum Temperature vs. Lifespan
Materials that can withstand extreme heat, like molybdenum disilicide, are often more brittle or expensive than common metallic alloys. Pushing a standard nichrome element beyond its design temperature will cause it to rapidly degrade and fail.
Efficiency vs. Response Time
Ceramic heaters are known for their high efficiency and even heating, but they may have a slower response time (the time it takes to heat up) compared to a thin metallic ribbon element. The mass and thermal conductivity of the material dictate how quickly it can transfer its heat.
Cost vs. Performance
High-performance elements used in industrial furnaces are significantly more expensive than the simple resistance wires in a toaster. The cost reflects the purity of the materials, the complex manufacturing process, and the element's ability to provide consistent performance over thousands of hours.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the operational goal. By understanding the core properties of each type, you can select the element that provides the best performance for your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, general-purpose heating: Standard metallic resistance wires (nichrome) offer the best value for common household appliances.
- If your primary focus is safety and uniform temperature: Ceramic elements provide excellent heat distribution and self-regulating properties that prevent overheating.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature industrial processing: Specialized composite elements like silicon carbide are required for their durability and precise control in extreme environments.
Ultimately, understanding these material-driven principles empowers you to move from simply using heat to intelligently engineering and controlling it.
Summary Table:
| Element Type | Key Material | Max Temperature | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Wires | Nichrome | Moderate | Toasters, Heaters |
| Ceramic | PTC Ceramics | High | Uniform Heating, Safety |
| High-Temp Composites | Silicon Carbide | Very High | Industrial Furnaces |
Unlock precise thermal solutions for your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions



















