At its core, a laboratory furnace is the primary tool used in material synthesis to provide the controlled thermal energy required to transform raw materials into new substances with specific, desirable properties. By enabling fundamental processes like annealing, sintering, melting, and calcination, furnaces allow researchers to precisely manipulate the atomic and crystalline structure of everything from advanced ceramics and metal alloys to novel nanomaterials.
The true function of a furnace in material synthesis is not simply to heat things up. It is to create a highly controlled environment—defined by temperature, atmosphere, and pressure—that dictates how atoms arrange themselves, thereby determining the final properties and performance of the newly created material.
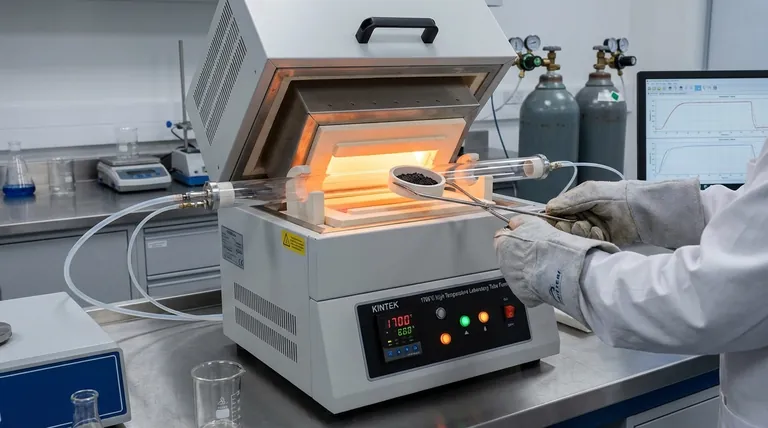

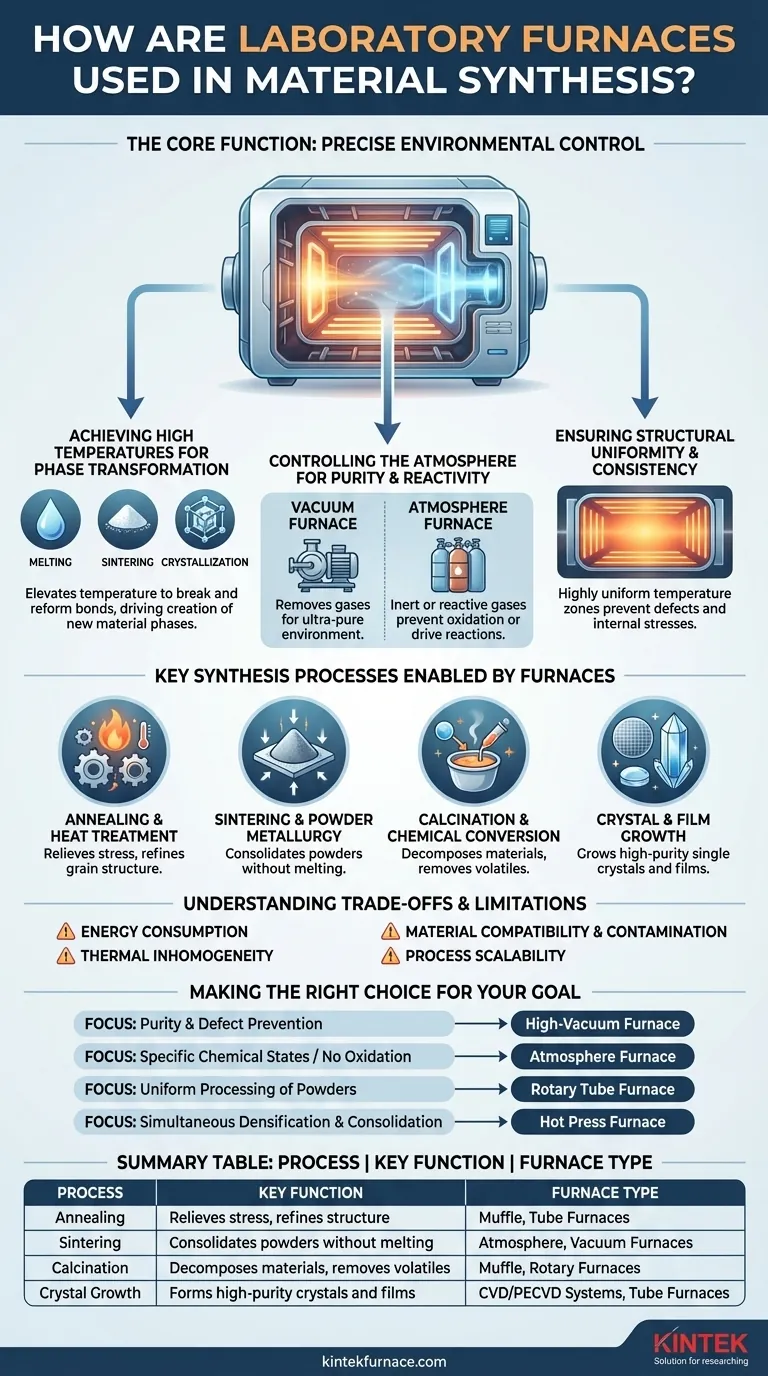
The Core Function: Precise Environmental Control
The furnace's value comes from its ability to impose a specific, stable, and uniform environment on a set of precursor materials. This control allows for the deliberate creation of materials that would not form under normal conditions.
Achieving High Temperatures for Phase Transformation
Heat is the primary catalyst for change. By elevating temperature, furnaces provide the energy needed to break and reform chemical bonds, driving the creation of new material phases.
This energy enables foundational processes like melting raw components into a homogenous liquid, sintering powders into a solid mass, or facilitating crystallization into an ordered structure.
Controlling the Atmosphere for Purity and Reactivity
Many synthesis processes fail if exposed to ambient air. The furnace chamber allows for total control over the gaseous environment.
A vacuum furnace removes atmospheric gases to create an ultra-pure environment, which is critical for preventing contamination when synthesizing reactive materials like superconductors or certain nanomaterials.
An atmosphere furnace can be filled with an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent unwanted oxidation. It can also be filled with reactive gases (like hydrogen or oxygen) to actively drive specific chemical reactions and create desired oxides or reduce existing ones.
Ensuring Structural Uniformity and Consistency
Non-uniform heating creates thermal gradients, which lead to defects, internal stresses, and inconsistent material properties.
Modern laboratory furnaces are designed to provide highly uniform temperature zones. This consistency is crucial for processes like annealing silicon wafers or growing large, single crystals, where a single defect can render the final product useless.
Key Synthesis Processes Enabled by Furnaces
Different synthesis goals require different furnace-enabled processes. Each process leverages temperature and atmosphere in a unique way to achieve a specific structural or chemical outcome.
Annealing and Heat Treatment
Annealing involves heating a material to a specific temperature and then cooling it slowly. This process is used to relieve internal stresses, increase softness, and refine the grain structure, which improves ductility and reduces brittleness in metals and ceramics.
Sintering and Powder Metallurgy
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder using heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. It is essential for producing high-strength ceramic components and precision metal parts used in various industries.
Calcination and Chemical Conversion
Calcination is a thermal treatment process applied to ores and other solid materials to bring about a thermal decomposition or phase transition. In material synthesis, it's used to produce active catalysts, durable pigments, and to remove volatile components from a mixture.
Crystal and Film Growth
In the semiconductor and optoelectronics industries, furnaces are indispensable for growing high-purity single crystals and depositing thin films. Processes like epitaxial growth and doping of silicon wafers occur in specialized furnaces to manufacture integrated circuits, LEDs, and solar cells.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a furnace is a complex instrument with inherent challenges that must be managed to ensure successful synthesis.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining high temperatures, especially over long periods, is extremely energy-intensive. The operational cost of a furnace is a significant consideration in both research and industrial settings.
Thermal Inhomogeneity
Achieving perfect temperature uniformity is a constant engineering challenge. Even small cool spots or hot spots within the furnace chamber can lead to defects, incomplete reactions, or non-uniform properties in the final material.
Material Compatibility and Contamination
The materials used to construct the furnace itself (heating elements, insulation, chamber walls) can become a source of contamination at very high temperatures. Choosing the right furnace materials is critical for maintaining the purity of the synthesized product.
Process Scalability
A synthesis protocol that works perfectly in a small, highly controlled laboratory furnace may not translate directly to a larger, industrial-scale furnace. Scaling up often introduces new challenges related to heat distribution and process control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific synthesis objective dictates the type of furnace and control system you need. The choice is a balance between the required process environment, material compatibility, and budget.
- If your primary focus is material purity and defect prevention: A high-vacuum furnace is non-negotiable to eliminate atmospheric contamination.
- If your primary focus is creating specific chemical states or preventing oxidation: An atmosphere furnace with precise gas mixing and flow control is your essential tool.
- If your primary focus is processing powders or granular materials uniformly: A rotary tube furnace provides continuous mixing and exposure to heat and gases.
- If your primary focus is densifying and consolidating powders simultaneously: A hot press furnace, which combines high temperature with mechanical pressure, is required.
Ultimately, mastering material synthesis is an exercise in mastering the controlled environment of the furnace.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Function | Furnace Type |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Relieves stress, refines structure | Muffle, Tube Furnaces |
| Sintering | Consolidates powders without melting | Atmosphere, Vacuum Furnaces |
| Calcination | Decomposes materials, removes volatiles | Muffle, Rotary Furnaces |
| Crystal Growth | Forms high-purity crystals and films | CVD/PECVD Systems, Tube Furnaces |
Ready to elevate your material synthesis with precision? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring purity, uniformity, and scalability for advanced ceramics, metal alloys, and nanomaterials. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















