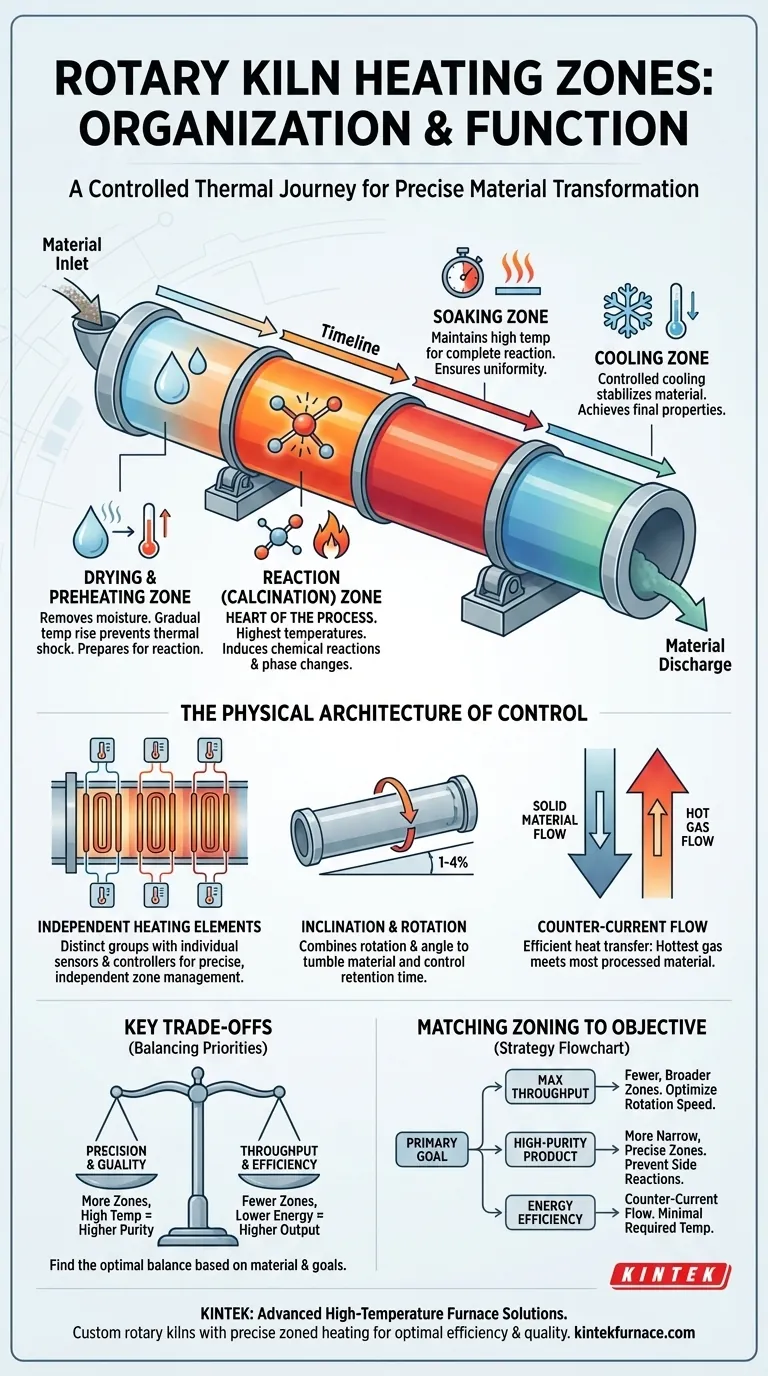
At its core, a rotary kiln is organized into a series of distinct, sequential heating zones to guide a material through a precise thermal process. These zones typically include drying, preheating, reaction (or calcination), and sometimes soaking or cooling, each maintained at a specific temperature. This division allows for independent control over each stage of the material's transformation, from removing moisture to inducing a final chemical change.
The fundamental purpose of heating zones is not simply to apply heat, but to create a controlled thermal journey. By managing the temperature and duration in each zone, you gain precise control over the chemical reactions and physical changes within the material, ensuring the quality and consistency of the final product.

The Purpose of Zoned Heating: A Material's Journey
A rotary kiln does not expose material to a single, uniform temperature. Instead, it creates a carefully managed temperature gradient that aligns with the physical and chemical changes the material must undergo as it travels from the inlet to the outlet.
The Drying & Preheating Zone
This is the first stage after the material enters the kiln. The primary function is to remove any free or bound moisture and to gradually raise the material's temperature in preparation for the intense heat of the next zone. This prevents thermal shock and ensures a stable reaction later.
The Reaction (Calcination) Zone
This is the heart of the process, where the highest temperatures are applied. Within this zone, the intended chemical reactions or phase changes occur, such as the decomposition of carbonates (calcination) or the formation of a new crystalline structure. The temperature and the material's residence time in this zone are the most critical process parameters.
The Soaking & Cooling Zone
After the main reaction, some processes require a "soaking" period where the material is held at a high temperature to ensure the reaction is complete. Following this, a controlled cooling process begins. This final stage is crucial for stabilizing the newly formed material and achieving the desired final properties.
The Physical Architecture of Control
The theoretical zones are made possible by the kiln's physical design. The ability to manage temperature independently across the length of the kiln is what makes it such a powerful processing tool.
Independent Heating Element Groups
Modern kilns are equipped with heating elements—such as alloy coils or silicon carbide rods—that are arranged in distinct groups. Each group corresponds to a thermal zone and has its own temperature controller and sensor. This allows an operator to set a unique temperature for the drying zone, a much higher one for the reaction zone, and so on.
The Role of Kiln Inclination and Rotation
The kiln itself is a slowly rotating cylinder set at a slight angle (1-4% slope). This combination of rotation and inclination is what causes the material to tumble and advance steadily through the different heating zones. The rotation speed is a key variable for controlling "retention time"—how long the material spends in each zone.
Counter-Current Flow for Efficiency
Most industrial rotary kilns use a counter-current flow system. The solid material is fed into the high end and travels down toward the discharge end. Simultaneously, hot gas from a burner at the discharge end is forced up the kiln in the opposite direction. This is highly efficient, as the hottest gases treat the most processed material, while the cooler gases preheat the incoming raw material.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Implementing a zoned heating strategy is not without its challenges. The design and operation involve balancing competing priorities to achieve an optimal outcome.
Precision vs. Throughput
Increasing the number of individually controlled zones allows for a much more precise thermal profile. However, this complexity can sometimes limit the maximum processing speed or throughput. A simpler process may benefit from fewer, broader zones to maximize output.
Energy Consumption vs. Product Quality
Maintaining very specific and high temperatures in multiple zones requires significant energy. You must balance the cost of that energy against the value added by achieving a higher-purity or more consistent final product. Over-processing or using unnecessarily high temperatures is a common source of inefficiency.
Material Properties and Retention Time
There is no universal zoning profile. The ideal temperatures, number of zones, and retention time are entirely dependent on the specific material being processed. A setup optimized for limestone calcination will be ineffective for processing minerals or synthesizing advanced materials.
Matching Kiln Zoning to Your Objective
The optimal zoning strategy is dictated by your primary goal. A well-designed thermal profile is the difference between an efficient process and a wasteful one.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput: Use fewer, broader heating zones sufficient for the core reaction, and optimize rotation speed to move material through efficiently.
- If your primary focus is high-purity product specification: Employ a greater number of narrower, independently controlled zones to create a highly precise thermal gradient that prevents unwanted side reactions.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Leverage a counter-current flow design, ensure the refractory lining is well-maintained to minimize heat loss, and set zone temperatures no higher than what is required for the reaction.
Ultimately, mastering the kiln's thermal zones is mastering control over the properties and quality of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Heating Zone | Function | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Drying & Preheating | Removes moisture, preheats material to prevent thermal shock | Gradual temperature increase, initial stage |
| Reaction (Calcination) | Induces chemical reactions or phase changes at high temperatures | Highest temperatures, critical for material transformation |
| Soaking & Cooling | Ensures reaction completion and stabilizes material properties | Controlled cooling, final stage for product quality |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's thermal processing? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom rotary kilns with precise zoned heating. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique experimental needs are met for optimal efficiency and product quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials



















