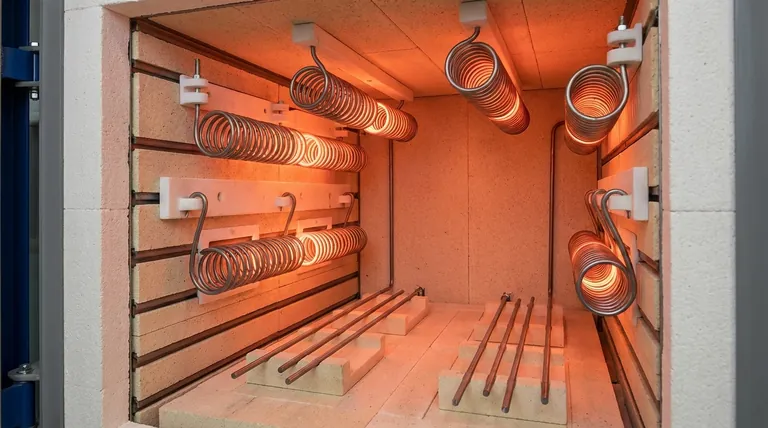
In a vacuum furnace, heating elements are not just placed; they are precisely engineered into position. They are typically mounted on the furnace's interior sidewalls, suspended from the roof, or laid on the floor using specialized hardware made from ceramic, quartz, or refractory materials. This approach is essential for providing both secure physical support and critical electrical isolation in the extreme environment of the hot zone.
The mounting method for a vacuum furnace heating element is a critical design choice, balancing the need for stable physical support at extreme temperatures with the absolute necessity of electrical isolation to prevent system failure.
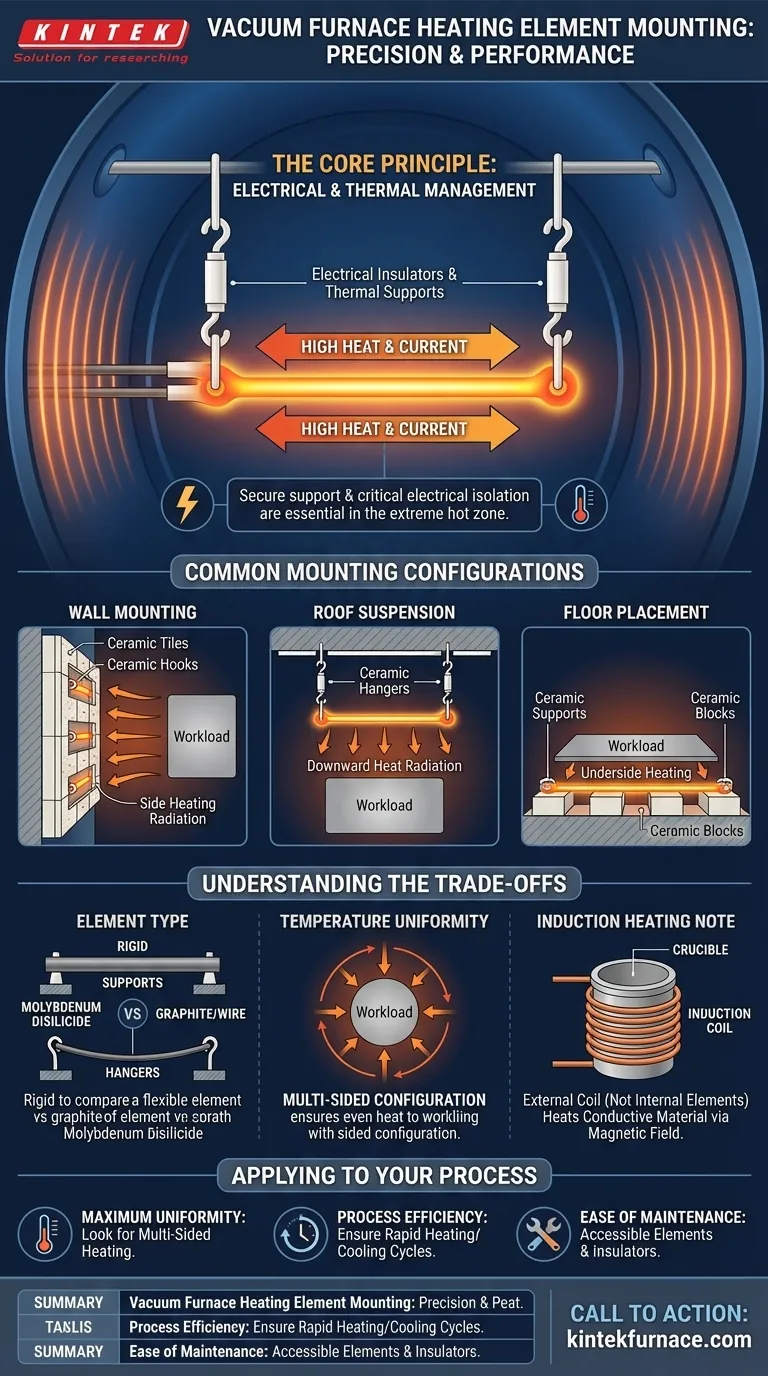
The Core Principle: Electrical and Thermal Management
The primary challenge of mounting heating elements is managing immense heat and high electrical currents within a vacuum. The mounting system is not passive; it is an active component in ensuring the furnace operates safely and effectively.
Why Electrical Isolation is Critical
Heating elements carry a significant electrical current. The mounting hardware must be a robust electrical insulator to prevent this current from short-circuiting to the furnace body.
Materials like ceramics and quartz are chosen specifically for their excellent electrical insulating properties, which they maintain even at very high temperatures.
The Role of Material Selection
The materials used for hooks, hangers, and supports must withstand the furnace's maximum operating temperature without degrading or contaminating the vacuum environment.
Refractory materials and high-purity ceramics are standard choices because they are thermally stable and have very low vapor pressure, meaning they won't "outgas" and compromise the vacuum.
Common Mounting Configurations
The placement of heating elements directly influences the temperature uniformity within the hot zone. The configuration is chosen based on the furnace's intended application and size.
Wall Mounting
This is a very common method where elements are attached to the furnace's interior sidewalls. They may be held by ceramic hooks and hangers or set into pre-formed ceramic tiles that protect both the element and the furnace insulation.
Roof Suspension
For certain heating profiles, particularly in tall or cylindrical furnaces, elements can be suspended from the furnace roof. This allows for excellent heat radiation downward and around the workload.
Floor Placement
In some designs, particularly for heating the underside of a large or flat workload, elements can be laid on the furnace floor. They are always placed on insulating ceramic supports to ensure electrical isolation and allow for thermal expansion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of mounting method is never arbitrary. It is a decision driven by physics, material science, and the specific process requirements.
Element Type Dictates Mounting
The material and shape of the heating element itself play a major role. For example, rigid molybdenum disilicide elements can be supported differently than more flexible graphite or metallic wire elements.
Impact on Temperature Uniformity
The primary goal of a vacuum furnace is uniform heating. The element arrangement—whether on two sides, four sides, or in a full cylinder—is engineered to deliver even heat to all parts of the workload. Improper placement or a failing support can create damaging hot or cold spots.
A Note on Induction Heating
It's important to distinguish resistive heating from induction heating. An induction-heated vacuum furnace does not have internal heating elements. Instead, it uses a water-cooled copper coil outside the crucible to generate a powerful magnetic field, which heats the conductive material inside.
Applying This to Your Process
Understanding how your furnace's heating elements are mounted helps you diagnose issues and appreciate the system's design.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity: Look for a furnace with a multi-sided heating element configuration that fully surrounds the workload.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: The mounting system should allow for rapid heating and cooling cycles without causing premature wear on the elements or their supports from thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is ease of maintenance: A well-designed system will have elements and their ceramic insulators that are readily accessible for inspection and replacement.
Recognizing the principles behind element mounting is key to operating your vacuum furnace reliably and achieving consistent results.
Summary Table:
| Mounting Method | Typical Location | Key Hardware Used | Primary Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wall Mounting | Interior Sidewalls | Ceramic Hooks, Hangers, Tiles | Common, good for side heating |
| Roof Suspension | Hung from Furnace Roof | Ceramic Insulators, Hangers | Excellent downward heat radiation |
| Floor Placement | On Furnace Floor | Ceramic Supports, Blocks | Ideal for heating underside of workload |
Achieve superior temperature uniformity and process reliability with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions. Our expertise in R&D and in-house manufacturing allows us to provide diverse laboratories with robust heating systems, including Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. We offer strong deep customization capabilities to design a heating element mounting configuration that precisely meets your unique thermal processing requirements, ensuring long-term performance and ease of maintenance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your vacuum furnace application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control



















