In industrial settings, drop tube furnaces are specialized tools for high-temperature material processing where controlled atmospheres and uniform heating are paramount. They are critical in manufacturing advanced materials like ceramics, battery components, and specialized alloys, enabling processes that are difficult or impossible to achieve in other furnace types.
The key to understanding the industrial role of a drop tube furnace is its vertical orientation. This design isn't arbitrary; it leverages gravity and fluid dynamics to enable highly specific processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), pyrolysis, and the synthesis of high-purity powders.
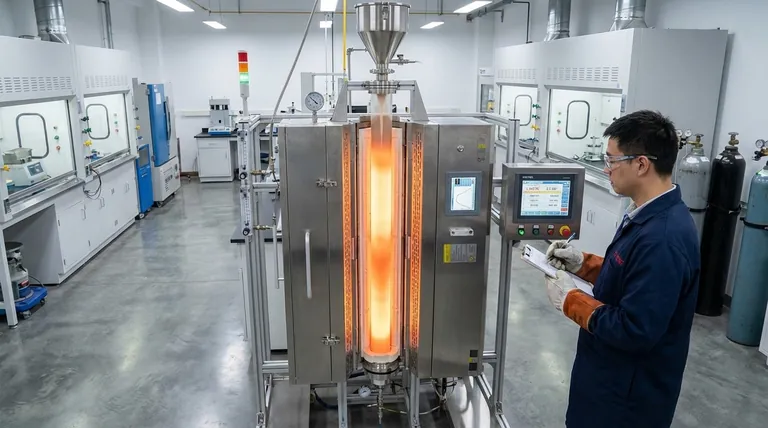

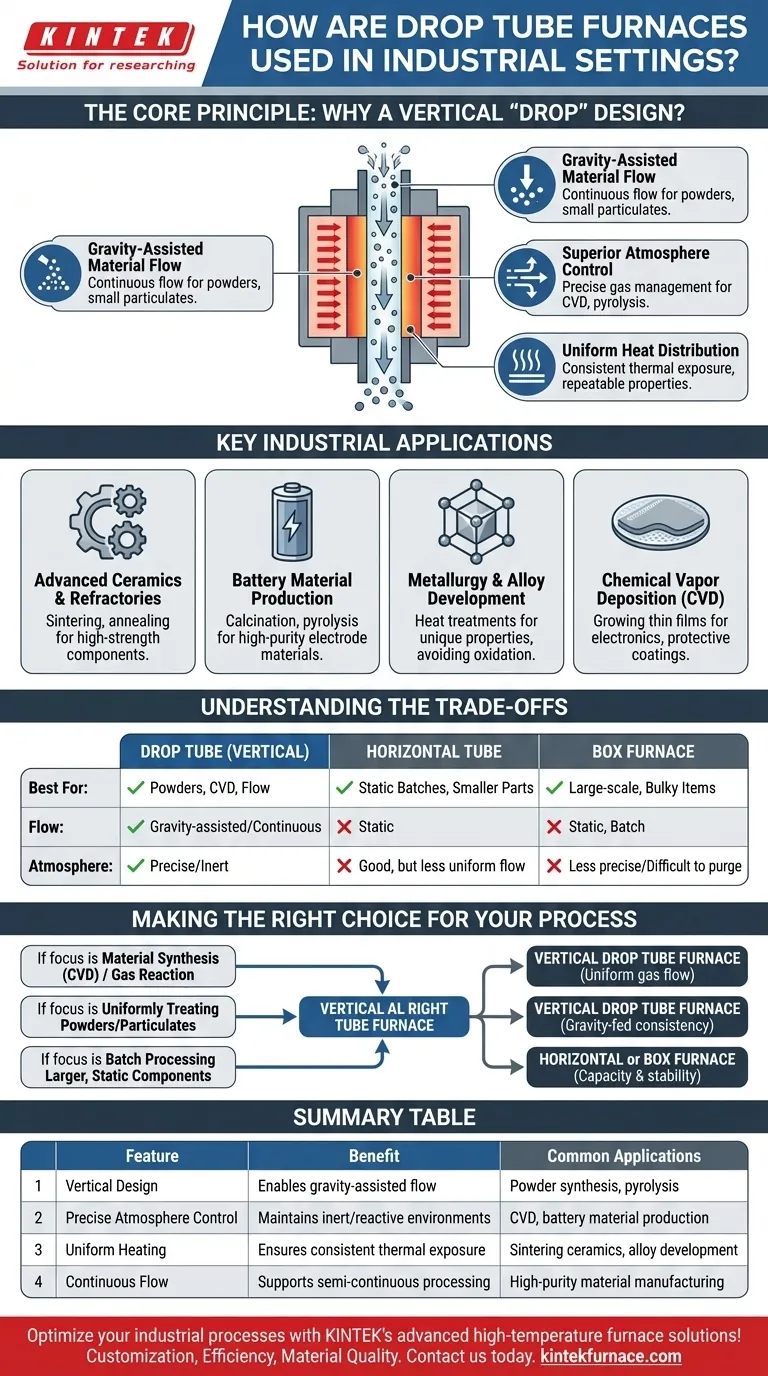
The Core Principle: Why a Vertical "Drop" Design?
A drop tube furnace is a specific type of vertical tube furnace. Its design directly facilitates certain industrial processes by using gravity as a key part of the operation.
Gravity-Assisted Material Flow
The primary advantage is the ability to drop or flow material through the heated zone. This is ideal for powders, small particulates, or even liquid droplets that need uniform, brief exposure to high temperatures.
This continuous or semi-continuous flow contrasts with static batch processes, enabling unique reactions and treatments.
Superior Atmosphere Control
The vertical tube is exceptionally well-suited for processes requiring precise gas management. Gases can be introduced from the top or bottom, creating a specific flow path.
This is crucial for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where precursor gases must flow uniformly over a substrate, or for pyrolysis, where material thermally decomposes in an inert atmosphere.
Uniform Heat Distribution
With heating elements surrounding the central tube, these furnaces create an extremely uniform temperature zone along the vertical axis.
This ensures that every particle falling through the furnace experiences nearly identical thermal conditions, leading to highly consistent and repeatable material properties.
Key Industrial Applications
The unique design of drop tube furnaces makes them indispensable in several high-tech manufacturing sectors.
Advanced Ceramics and Refractories
These furnaces are used for sintering and annealing ceramic powders into dense, high-strength components. The controlled, high-temperature environment is essential for achieving the desired microstructure.
Battery Material Production
The production of cathode and anode materials for lithium-ion batteries often involves calcination or pyrolysis of precursor chemicals. A drop tube furnace provides the strict atmospheric control needed to produce high-purity, high-performance electrode materials.
Metallurgy and Alloy Development
Specific heat treatments are used to create advanced alloys with unique properties. The precise temperature and atmosphere control allows manufacturers to anneal metals or create specific crystalline structures without unwanted oxidation.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
In the semiconductor and advanced materials industries, CVD is a cornerstone process. Drop tube furnaces are used to grow thin films on substrates, creating components for electronics or durable, protective coatings on industrial parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single tool is perfect for every job. The value of a drop tube furnace becomes clear when compared to other thermal processing equipment.
vs. Horizontal Tube Furnaces
Horizontal furnaces are excellent for processing static samples in batches, such as treating a tray of components or growing crystals along a flat plane. They are generally simpler to load and unload for solid, stable parts.
However, they are less effective for processes that rely on gravity or require the uniform flow of powders and gases that a vertical tube enables.
vs. Box Furnaces
Box furnaces are the workhorses for large-scale heat treatment of bulky items, like large steel parts or high-volume batches of electronic components. Their primary advantage is capacity.
Their drawback is less precise atmospheric control. It is difficult to purge oxygen and maintain a pure inert gas environment in a large chamber, making them unsuitable for the highly sensitive materials processed in a tube furnace.
Limitations in Scale
While industrial, drop tube furnaces are typically used for producing higher-value, lower-volume materials. The diameter of the process tube itself presents a physical limitation on throughput compared to massive industrial kilns used for bulk materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace is critical for achieving your manufacturing goals. Your decision should be guided by the specific material transformation you need to perform.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis via gas reaction (like CVD): The vertical orientation of a drop tube furnace provides the ideal, uniform gas flow dynamics required for high-quality film deposition.
- If your primary focus is uniformly heat-treating powders or small particulates: The gravity-fed mechanism ensures every particle receives consistent thermal exposure for processes like calcination or pyrolysis.
- If your primary focus is batch processing larger, static components: A horizontal tube furnace for smaller items or a box furnace for bulkier objects is likely a more practical and efficient solution.
Understanding the unique process advantages of the vertical design empowers you to select the precise tool needed for advanced material manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Design | Enables gravity-assisted flow for powders and particulates | Powder synthesis, pyrolysis |
| Precise Atmosphere Control | Maintains inert or reactive gas environments | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), battery material production |
| Uniform Heating | Ensures consistent thermal exposure for all materials | Sintering ceramics, alloy development |
| Continuous Flow | Supports semi-continuous processing for efficiency | High-purity material manufacturing |
Optimize your industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide drop tube furnaces and other systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and material quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your advanced material manufacturing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















