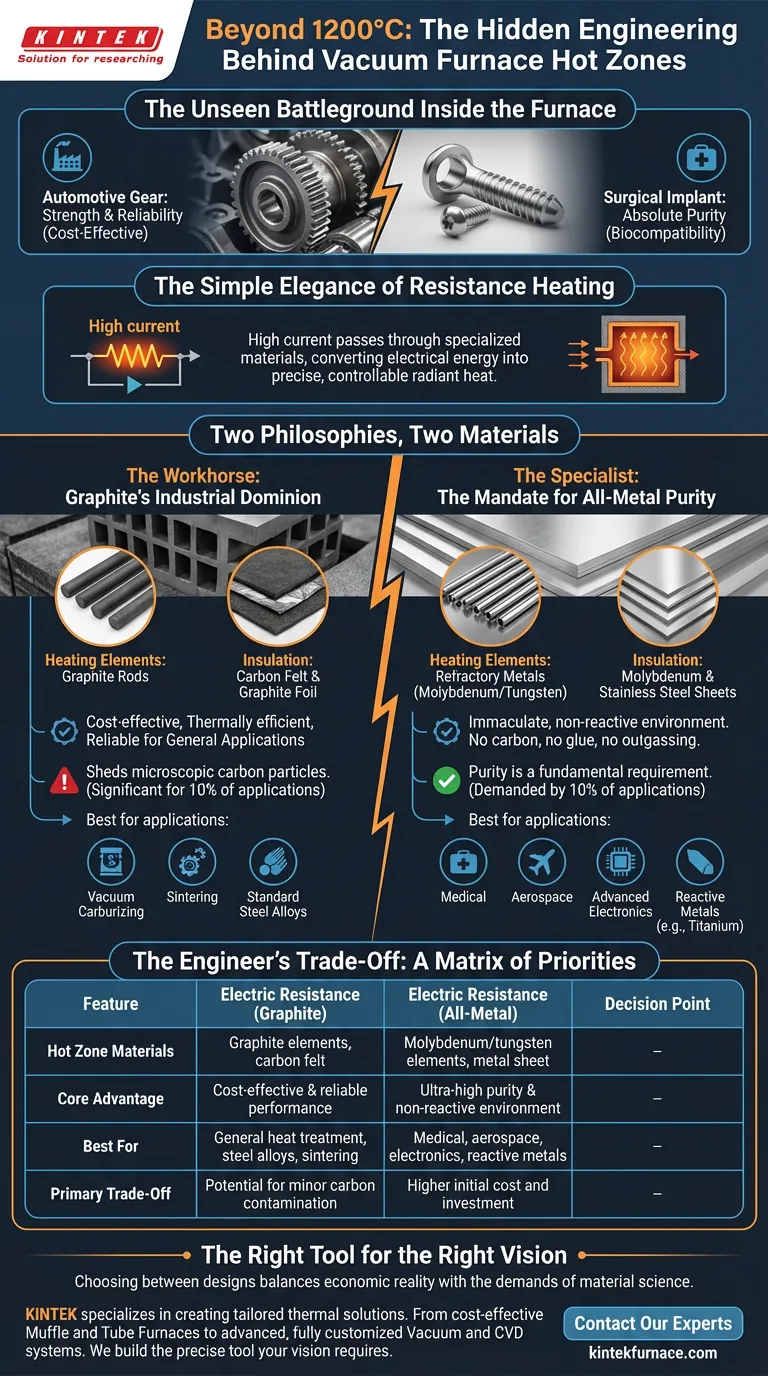
The Unseen Battleground Inside the Furnace
Imagine two scenarios.
In one, an engineer is heat-treating a steel alloy for a high-stress automotive gear. The goal is brute strength and reliability at a manageable cost.
In another, a materials scientist is processing a titanium alloy for a surgical implant. The goal is absolute purity; a single stray carbon molecule could compromise biocompatibility.
The success of both depends entirely on the controlled, violent environment inside a vacuum furnace. But the furnace that forges the gear would fail the implant. The difference lies in a single, critical engineering decision: the material composition of its "hot zone."
The Simple Elegance of Resistance Heating
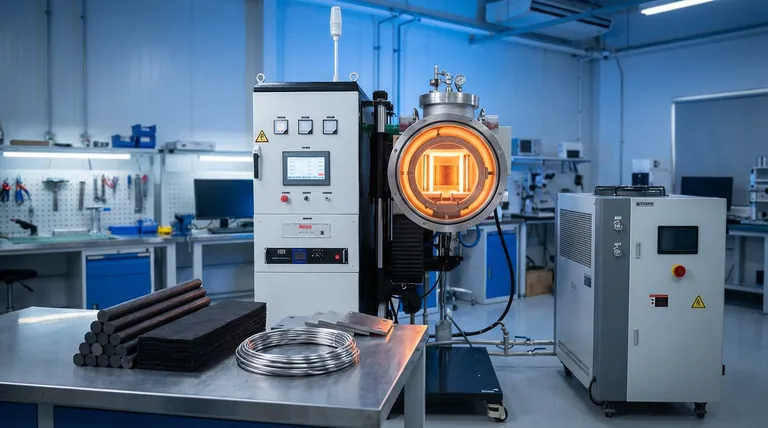
At their heart, most modern vacuum furnaces operate on a principle of beautiful simplicity: electrical resistance.
A high current is passed through specialized materials that resist its flow. This struggle converts electrical energy into raw, radiant heat. It’s a clean, precise, and wonderfully controllable method for achieving temperatures that can reshape the molecular structure of metals.
This all happens inside an insulated chamber—the hot zone. This zone is the furnace's soul. Its design and materials don't just contain the heat; they define the furnace's character and capability.
Two Philosophies, Two Materials
The engineering world has converged on two dominant designs for this critical component, each representing a different philosophy of thermal processing.
The Workhorse: Graphite's Industrial Dominion
The most common hot zone is built from graphite. The heating elements are robust graphite rods, and the insulation is a layered sandwich of carbon felt and graphite foil.
This design is the backbone of modern industry. It's cost-effective, thermally efficient, and perfect for a vast range of applications like vacuum carburizing, sintering, and treating standard steel alloys. It gets the job done reliably and economically.
However, graphite has a nature it cannot deny: it sheds microscopic carbon particles. For 90% of applications, this is insignificant. For the other 10%, it's a critical failure point.
The Specialist: The Mandate for All-Metal Purity
For that 10%, a different philosophy is required. Enter the all-metal hot zone.
Here, the insulation is made of layered sheets of molybdenum and stainless steel. The heating elements are crafted from refractory metals like molybdenum or tungsten. There is no carbon, no glue, no potential for outgassing or contamination.
This is the environment demanded by the medical, aerospace, and advanced electronics industries. When you are building components that will fly at Mach 3 or be placed inside a human body, purity is not a feature; it's a fundamental requirement.
The Engineer's Trade-Off: A Matrix of Priorities
Choosing between these two designs is a classic engineering dilemma. It’s a multi-variable equation with no single right answer, only the answer that is right for your specific process.
-
Purity vs. Cost: This is the primary axis of decision. An all-metal furnace provides an immaculate, non-reactive environment but comes at a significant premium. A graphite furnace is far more economical but introduces an acceptable level of carbon into the environment. The decision is a reflection of your process's tolerance for contamination.
-
Durability vs. Brittleness: Graphite, while robust in many ways, can be brittle and susceptible to mechanical shock. All-metal hot zones, if operated correctly, offer a longer operational lifespan and greater physical resilience, justifying their higher initial investment over time.
-
Process vs. Material: The materials themselves dictate the choice. Processing reactive metals like titanium, which readily forms carbides, makes an all-metal furnace non-negotiable. For standard tool steels, a graphite furnace is not only sufficient but often superior in its thermal performance for that specific task.
The table below simplifies this decision matrix:
| Feature | Electric Resistance (Graphite) | Electric Resistance (All-Metal) |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Zone Materials | Graphite elements, carbon felt insulation | Molybdenum/tungsten elements, metal sheet insulation |
| Core Advantage | Cost-effective & reliable performance | Ultra-high purity & non-reactive environment |
| Best For | General heat treatment, steel alloys, sintering | Medical, aerospace, electronics, reactive metals |
| Primary Trade-Off | Potential for minor carbon contamination | Higher initial cost and investment |
The Right Tool for the Right Vision
The choice is not about which furnace is better, but about which furnace aligns with the fundamental goal of the work. It’s a decision that balances economic reality with the uncompromising demands of material science.
This is where expertise becomes critical. Navigating these trade-offs requires a partner who understands the deep connection between furnace design and process outcomes. With expert R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK specializes in creating tailored thermal solutions. Our portfolio includes everything from cost-effective Muffle and Tube Furnaces to advanced, fully customized Vacuum and CVD systems.
Whether your project demands the economical power of a graphite workhorse or the pristine purity of an all-metal system, we build the precise tool your vision requires. The material science of tomorrow is forged in the hot zones of today, and making the right choice is paramount. Contact Our Experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
Related Articles
- Mastering the Void: How Custom Vacuum Furnaces Forge the Future of Materials
- Beyond the Heat: The Psychology of Perfect Vacuum Furnace Operation
- The Most Important Number in a Vacuum Furnace Isn't Its Temperature
- The Physics of Perfection: How Vacuum Furnaces Redefine Material Integrity
- The Pursuit of Nothing: How Vacuum Furnace Control Defines Material Destiny




















