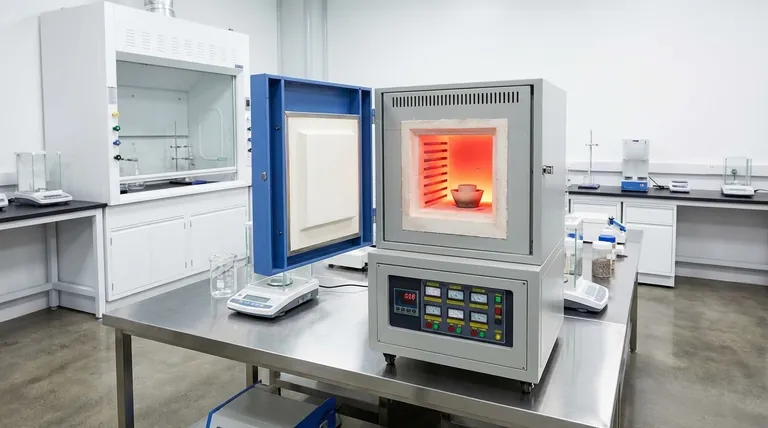
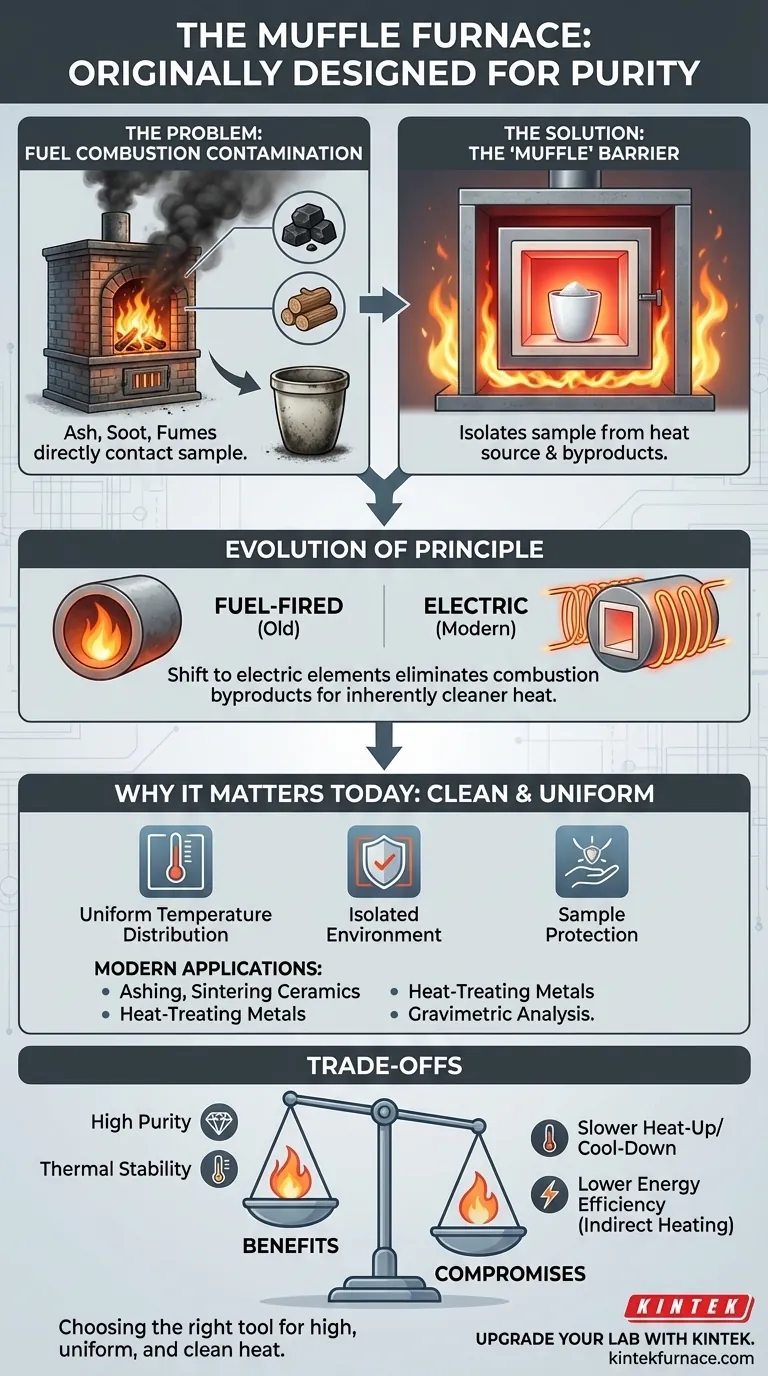
At its core, the muffle furnace was invented to solve a single, critical problem: isolating a sample from the byproducts of the very fuel used to heat it. In early high-temperature applications that relied on burning coal or other combustible fuels, the sample being processed was at constant risk of being contaminated by ash, soot, and chemical fumes. The muffle furnace was designed to create a protective barrier, ensuring the purity of the material inside.
The defining feature of a muffle furnace isn't just its ability to generate high heat, but to provide clean heat. Its design is based on the fundamental principle of creating a physical barrier—the "muffle"—that separates the process chamber from the direct heat source and any contaminants it produces.

The Original Problem: Contamination by Combustion
To understand the muffle furnace, you must first understand the challenges of historical high-temperature work. The goal was to achieve intense heat, but the methods were inherently "dirty."
The Challenge of Early Heat Sources
Early industrial and laboratory furnaces generated heat by burning materials like coal, coke, or wood. This combustion process was effective at creating high temperatures but was also uncontrolled and messy.
Contaminants: Ash, Soot, and Fumes
The direct byproducts of combustion were a significant issue. Ash particles, unburnt carbon (soot), and various gaseous fumes would inevitably come into contact with any material placed directly within the furnace, altering its chemical composition and purity.
The 'Muffle' as the Solution
The solution was to build a furnace with an inner chamber, or "muffle," made from a refractory material that could withstand extreme temperatures. The fuel was burned outside this chamber, heating the muffle's walls. The heat would then radiate into the chamber, heating the sample without any direct contact with the flame or its exhaust.
How the Principle Evolved with Technology
While the original problem was contamination from combustion, the core principle of isolation remains relevant even in modern, technologically advanced furnaces.
The Shift to Electric Heating
Most contemporary muffle furnaces use electric resistance heating elements. These coils are wrapped around the outside of the muffle chamber, eliminating the combustion byproducts of older fuel-fired models. This makes modern furnaces inherently cleaner.
Why the Muffle Still Matters
Even with a clean electric heat source, the muffle chamber is critical. It provides an enclosed, tightly controlled environment that ensures uniform temperature distribution around the sample. It also isolates the sample from any potential contaminants in the surrounding lab atmosphere and protects the electric heating elements from any fumes or off-gassing produced by the sample itself.
Modern High-Temperature Applications
This combination of high, uniform, and clean heat makes the muffle furnace essential for many processes today. Common applications include ashing organic materials, sintering ceramics, heat-treating metals, and performing gravimetric analysis where sample integrity is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The muffle furnace's design is highly specialized, which comes with specific operational trade-offs that are important to recognize.
A Focus on High, Continuous Heat
These furnaces are engineered for high-temperature applications, typically operating from several hundred to well over 1000°C. They are not efficient or suitable for low-temperature or rapid-cycling processes.
Indirect Heating Means Slower Response
Because the heat must first saturate the muffle chamber before radiating to the sample, these furnaces generally have slower heat-up and cool-down rates compared to direct-heating methods. This provides excellent thermal stability but is not ideal for processes requiring rapid temperature changes.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
The indirect nature of the heating can be less energy-efficient than direct-flame impingement or other methods. Heat is lost in the process of saturating the insulating and muffle materials, a necessary compromise to achieve the primary goal of process purity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the founding principle of the muffle furnace—protection from contamination—clarifies its role and helps you choose the right tool for your thermal processing needs.
- If your primary focus is sample purity and avoiding contamination: The muffle furnace is the definitive standard, as its entire design is built on the principle of isolation.
- If your process involves ashing, sintering, or heat-treating sensitive materials: A modern electric muffle furnace provides the necessary combination of high, uniform, and clean heat required for repeatable results.
- If your priority is rapid heating and maximum energy efficiency: A direct-heating furnace might be more suitable, but only if potential contamination from the heat source is not a concern for your material.
Understanding its origin in purity reveals its fundamental purpose in any modern laboratory or industrial setting.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Initial Purpose | Isolate samples from combustion byproducts like ash and soot to maintain purity. |
| Core Principle | Uses a physical barrier (muffle) to separate the heating source from the process chamber. |
| Evolution | Shifted from fuel-fired to electric heating for cleaner operation and better control. |
| Modern Applications | Ashing, sintering ceramics, heat-treating metals, and gravimetric analysis. |
| Trade-offs | Slower heat response and lower energy efficiency due to indirect heating design. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide muffle, tube, rotary, vacuum, atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems tailored to your unique experimental needs. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise performance for applications like ashing and sintering. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your sample purity and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do repeat sintering processes and specialized sintering molds address the technical challenges of manufacturing oversized flywheel rotor components? Expand Scale and Integrity
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis
- Why are precision stirring and drying equipment necessary for photocatalytic materials? Master Microstructure Control
- What is the primary use of a muffle furnace in the assembly of side-heated resistive gas sensors? Expert Annealing Guide
- How does a stainless steel reactor function within a muffle furnace for PET to graphene? Master Carbon Synthesis



















