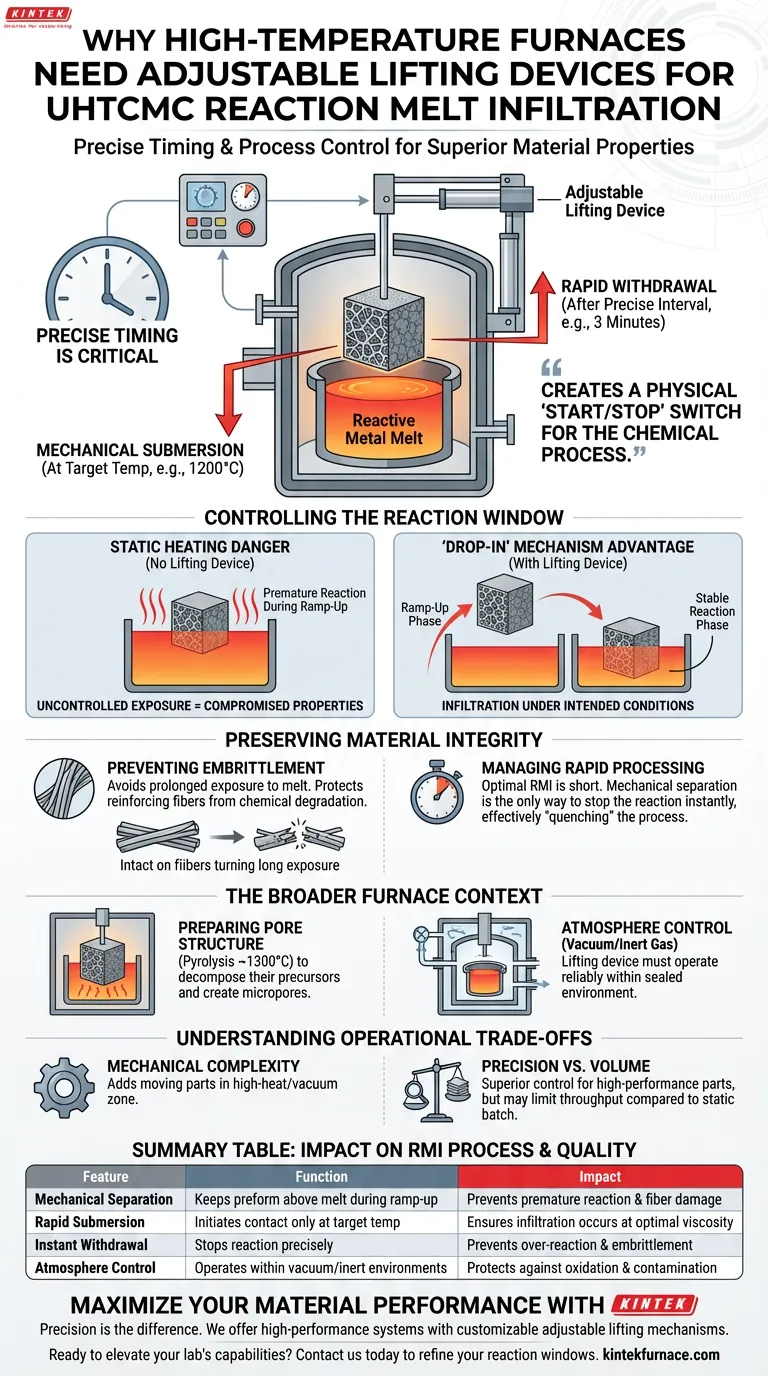
Precise timing is critical in Reaction Melt Infiltration (RMI). High-temperature furnaces utilize adjustable lifting devices to mechanically separate the ceramic preform from the reactive metal melt until the exact target temperature is reached. This mechanism allows operators to submerge the preform only once the environment is stabilized at infiltration temperatures (e.g., 1200°C) and rapidly withdraw it after a precise interval (e.g., 3 minutes), ensuring the reaction does not exceed strict time limits.
The adjustable lifting device turns a static heating environment into a dynamic reaction chamber. It creates a physical "start/stop" switch for the chemical process, preventing fiber degradation caused by prolonged exposure to the melt during heating and cooling ramps.

Controlling the Reaction Window
The Danger of Static Heating
In a standard furnace setup without a lifting device, the preform and the metal melt would sit together from the start of the heating cycle.
As the furnace ramps up to temperature, the metal melts and begins reacting with the preform prematurely.
This uncontrolled exposure prevents precise data collection and compromises the final material properties.
The "Drop-In" Mechanism
The lifting device allows the preform to remain suspended above the melt while the furnace heats up.
Contact is initiated only when the target temperature (typically around 1200°C) is stable.
This ensures that the infiltration process occurs exclusively under the intended thermal conditions.
Preserving Material Integrity
Preventing Embrittlement
The primary goal of the lifting device is to protect the reinforcing fibers within the composite.
If the reaction between the melt and the fibers continues for too long, the fibers can degrade chemically.
This over-reaction leads to material embrittlement, drastically reducing the toughness and utility of the final composite.
Managing Rapid Processing Times
The optimal RMI process is often surprisingly short, sometimes lasting only a few minutes.
A furnace cannot heat up or cool down fast enough to control a 3-minute reaction window thermally.
Mechanical separation is the only way to stop the reaction instantly, effectively "quenching" the process by removing the part from the melt source.
The Broader Furnace Context
Preparing the Pore Structure
Before infiltration occurs, the high-temperature furnace often performs pyrolysis at even higher temperatures (around 1300°C).
This step decomposes carbon-based precursors and removes volatiles, creating an interconnected micropore system.
These micropores act as the critical channels that the melt will eventually infiltrate.
Atmosphere Control
The furnace must maintain a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation during these high-heat steps.
The lifting device must operate reliably within this sealed, controlled environment without compromising the vacuum integrity.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Mechanical Complexity
Introducing moving parts into a high-temperature (1200°C+) vacuum zone adds significant engineering complexity.
The lifting mechanism must withstand thermal expansion and potential chemical vapors without seizing or jamming.
Precision vs. Volume
While lifting devices offer superior control for research and high-performance parts, they may limit the volume of material that can be processed at once compared to static batch processing.
This setup prioritizes quality and material properties over sheer throughput quantity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize the manufacturing of Ultra-High Temperature Ceramic Matrix Composites, align your equipment capabilities with your material requirements:
- If your primary focus is Fiber Integrity: Prioritize a lifting system with high-speed actuation to minimize exposure time and prevent embrittlement.
- If your primary focus is Infiltration Density: Ensure your furnace provides precise temperature control during the pyrolysis stage to optimize the micropore network before infiltration begins.
True process control requires the ability to dictate not just the temperature, but the exact moment the reaction begins and ends.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in RMI Process | Impact on Material Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Separation | Keeps preform above melt during ramp-up | Prevents premature reaction and fiber damage |
| Rapid Submersion | Initiates contact only at target temperature | Ensures infiltration occurs at optimal viscosity/temp |
| Instant Withdrawal | Stops reaction precisely (e.g., after 3 mins) | Prevents over-reaction and material embrittlement |
| Atmosphere Control | Operates within vacuum/inert environments | Protects against oxidation and contamination |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a high-performance composite and a brittle failure. At KINTEK, we understand that advanced materials like UHTCMCs require more than just heat—they require dynamic process control.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all featuring customizable configurations like adjustable lifting mechanisms to suit your unique RMI and pyrolysis needs.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact us today to discuss how our tailored high-temperature furnace solutions can refine your reaction windows and protect your fiber integrity.
Visual Guide
References
- Luis Baier, Vito Leisner. Development of ultra-high temperature ceramic matrix composites for hypersonic applications via reactive melt infiltration and mechanical testing under high temperature. DOI: 10.1007/s12567-024-00562-y
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace in iron-modified activated carbon prep? Optimize Adsorption Sites
- What is the difference between a retort and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Atmosphere-Controlled Furnace
- Why is a high-precision high-temperature furnace required for chemical activation? Ensure Superior Carbon Quality
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the thermal processing of crystal synthesis? Master Precise Crystal Growth
- Why is a programmable temperature control box furnace required for Bi-2223? Ensure High-Purity Superconductor Synthesis
- What maintenance is required for a muffle furnace? Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Safety
- What is the range of a muffle furnace? Choosing the Right Temperature for Your Application
- What electrical precautions should be taken when setting up a muffle furnace? Essential Safety Tips for Your Lab



















