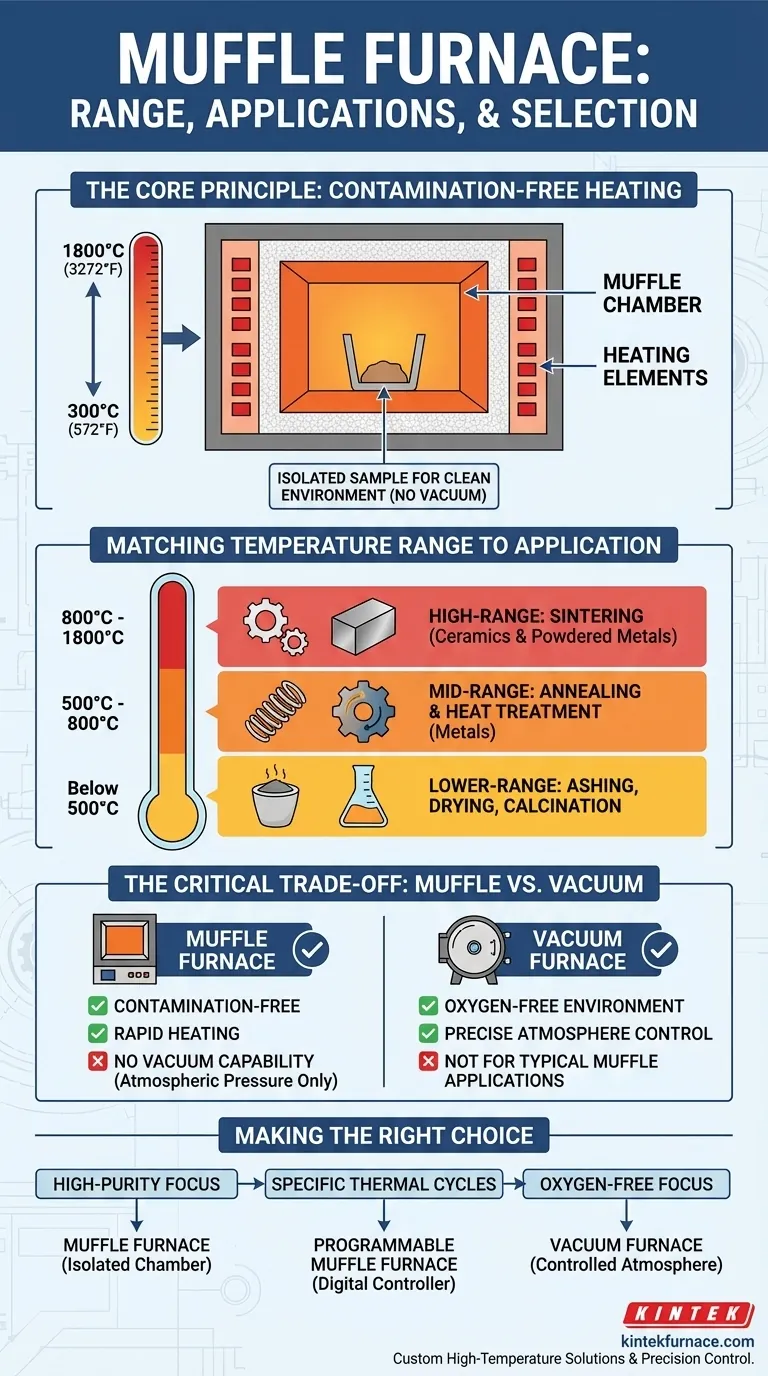
To be direct, a typical muffle furnace has an operational temperature range from approximately 300°C to 1800°C (572°F to 3272°F). However, the specific range depends heavily on the model and its intended application, with different temperature zones being optimal for distinct material processes.
The crucial insight is not the temperature range itself, but what enables it: a muffle furnace isolates the sample in a separate chamber from the heating elements. This design ensures a contamination-free environment for high-temperature work, but it cannot create a vacuum.

How a Muffle Furnace Operates
To understand its capabilities, you must first understand its core design principle. The name "muffle" refers to the insulated inner chamber that separates your sample from the furnace's heating elements.
The Principle of the Isolated Chamber
A muffle furnace's primary function is to provide a clean, controlled heating environment. By enclosing the sample within this "muffle," it is protected from any gases or byproducts generated by the heating source.
This separation is critical for applications like ashing, sintering, or heat-treating sensitive materials where contamination would compromise the results.
Precision Temperature Management
Modern muffle furnaces use a digital temperature controller connected to a thermometer to precisely manage the heat.
These controllers allow users to program specific heating cycles. This includes setting the ramp-up rate (how fast it heats), the hold time (how long it stays at a target temperature), and the cooling period, ensuring accurate and repeatable processes.
Matching Temperature Range to Application
The wide temperature range of a muffle furnace makes it a versatile tool, but specific processes fall into distinct temperature brackets. Knowing these helps in selecting the right equipment.
High-Range Applications (800°C – 1800°C)
The upper end of the temperature spectrum is primarily used for demanding processes that require significant thermal energy.
Sintering ceramics and powdered metals is a common application in this range, as these temperatures are needed to fuse particles together into a solid mass.
Mid-Range Applications (500°C – 800°C)
This intermediate range is ideal for modifying the properties of metals and other materials.
Processes like annealing (to reduce hardness and increase ductility) and various other heat treatments are performed here to alter a material's microstructure.
Lower-Range Processes (Below 500°C)
The lower temperature capabilities are often used for analytical or preparatory work.
Applications include ashing (burning off organic substances to determine inorganic content), drying, and calcination (heating solids to drive off volatile substances).
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single piece of equipment is perfect for every task. Acknowledging the inherent advantages and limitations of a muffle furnace is key to making an informed decision.
Key Advantages
The primary benefit is contamination-free heating due to the isolated chamber.
Additionally, muffle furnaces are known for their rapid heating capabilities, durability, and versatility across a wide range of materials and applications.
The Critical Limitation: No Vacuum Capability
A muffle furnace operates at atmospheric pressure. It is not suitable for any process that requires a vacuum.
For heat treatments or sintering of materials that are highly sensitive to oxygen or other atmospheric gases, a vacuum furnace is the correct choice. It is specifically designed to eliminate air for a pure, controlled environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To select the right equipment, align its core capabilities with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material processing: A muffle furnace is an excellent choice due to its isolated chamber, which prevents contamination from the heating source.
- If your primary focus is running specific thermal cycles: Seek a muffle furnace with a modern, programmable controller to precisely manage ramp rates, hold times, and cooling.
- If your primary focus is processing in an oxygen-free environment: A muffle furnace is unsuitable; you must use a vacuum furnace to achieve the necessary atmosphere control.
Understanding these core capabilities and limitations is the key to ensuring your equipment perfectly matches your technical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| 800°C – 1800°C | Sintering ceramics & powdered metals |
| 500°C – 800°C | Annealing, heat treatment of metals |
| Below 500°C | Ashing, drying, calcination |
Need a muffle furnace that perfectly matches your temperature and application requirements?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our Muffle Furnaces are designed with precision temperature control and contamination-free heating chambers, ideal for applications like sintering, annealing, and ashing.
With our strong deep customization capability, we can tailor a furnace to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you need specific temperature ranges, programmable controllers, or specialized chamber designs.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and results.
Get a Custom Quote for Your Muffle Furnace
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















