Electrostatic Levitation (ESL) relies on absolute environmental isolation. To accurately measure the density of refractory metals, industrial-grade high vacuum systems are mandatory to prevent chemical degradation at temperatures exceeding 3000 K. Furthermore, this vacuum environment is essential for maintaining the stability of the electrostatic field, ensuring the sample remains suspended long enough for comprehensive data collection.
The necessity of high vacuum systems stems from two critical requirements: eliminating gas molecules that cause rapid oxidation of superheated metals and ensuring the stable electrostatic forces required for extended levitation.
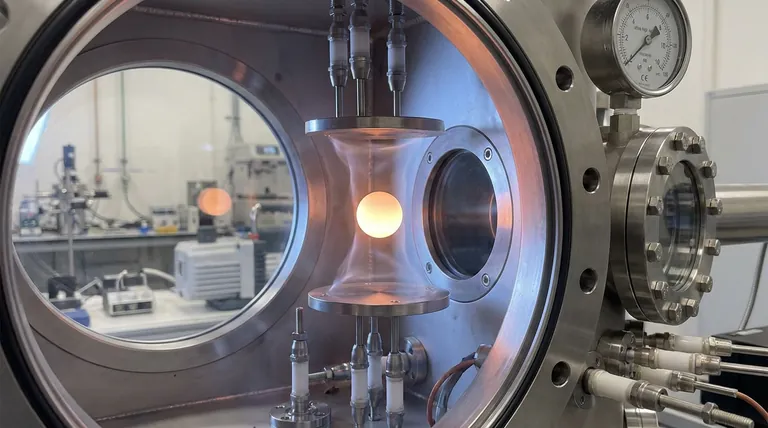
Preserving Chemical Purity
The primary challenge in measuring refractory metals—such as tungsten, rhenium, and tantalum—is their extreme reactivity at high temperatures.
Preventing Oxidation and Reaction
At temperatures above 3000 K, these metals become highly susceptible to chemical changes.
If oxygen or other active gases are present, the metal will instantly oxidize or react.
An industrial-grade high vacuum removes these gas molecules, ensuring the sample remains chemically pure throughout the experiment.
Ensuring Accurate Thermophysical Data
To characterize properties like density, the sample must remain in its native state.
Any reaction with the environment alters the mass and volume of the sample.
A vacuum environment guarantees that the measurements reflect the actual metal, rather than a contaminated compound or oxide layer.
Maintaining Levitation Stability
Beyond chemistry, the vacuum plays a critical physical role in the mechanics of Electrostatic Levitation.
Stabilizing the Electrostatic Field
ESL relies on delicate electric fields to counteract gravity.
The presence of gas molecules can disrupt this field, potentially leading to ionization or arcing.
A vacuum environment eliminates these disturbances, allowing for precise control over the positioning forces.
Enabling Extended Observation
Characterizing thermophysical properties often requires measuring the sample across a wide temperature range.
This process takes time, requiring the sample to remain suspended for extended periods.
The stability provided by a high vacuum ensures the sample does not become unstable or drop before the data collection is complete.
Understanding the Operational Stakes
While a high vacuum is necessary, it introduces specific operational constraints that must be managed.
The "Industrial-Grade" Requirement
Standard vacuum levels are often insufficient for these specific materials.
Because refractory metals require such extreme heat (3000 K+), even trace amounts of residual gas can ruin the experiment.
Success depends on using industrial-grade systems capable of achieving deep vacuum levels, rather than simple laboratory roughing pumps.
The Risk of Field Collapse
There is very little margin for error regarding pressure levels.
If the vacuum pressure rises, the electrostatic field can fluctuate unpredictable.
This instability inevitably leads to the loss of the sample, forcing a restart of the entire heating and levitation process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure successful density measurements of refractory metals, your equipment setup must prioritize the specific needs of the material.
- If your primary focus is data accuracy: Prioritize a high-vacuum environment to completely eliminate the risk of oxidation altering the mass or volume of tungsten, rhenium, or tantalum.
- If your primary focus is experimental duration: Ensure your vacuum system is industrial-grade to maintain the unwavering field stability required for long-term suspension and cooling curves.
By rigorously controlling the vacuum environment, you transform a volatile, superheated sample into a stable subject for precise physical analysis.
Summary Table:
| Requirement | Role in ESL Measurement | Benefit for Refractory Metals |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Purity | Eliminates oxygen/reactive gases | Prevents oxidation of Tungsten, Rhenium, and Tantalum |
| Field Stability | Removes gas molecules | Prevents ionization and arcing for stable levitation |
| Data Integrity | Maintains native metal state | Ensures accurate density and thermophysical measurements |
| Process Duration | Stabilizes electrostatic forces | Allows for extended observation and cooling curve analysis |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precise thermophysical analysis of refractory metals demands uncompromising environmental control. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance vacuum systems and high-temp furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and CVD systems—all customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs. Whether you are measuring density at 3000 K or developing new alloys, our industrial-grade solutions provide the stability and purity required for breakthrough results.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature experiments? Contact our experts today to discuss your custom furnace requirements!
References
- Lei Wang, Geun Woo Lee. Precise density measurements of refractory metals over 3000 K: Revisiting UV imaging technique at ultrahigh temperatures. DOI: 10.1063/5.0203390
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- Ultra High Vacuum Stainless Steel KF ISO CF Flange Pipe Straight Pipe Tee Cross Fitting
- 304 316 Stainless Steel High Vacuum Ball Stop Valve for Vacuum Systems
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three Section Clamp
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for gold electrode deposition? Key to Solar Cell Efficiency
- Why is vacuum heat treatment necessary? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Performance
- How do vacuum furnaces improve efficiency for processes requiring carburizing? Boost Quality and Cut Costs
- What is a vacuum atmosphere and when is it used? Achieve Material Purity and Integrity in High-Temp Processes
- What are the advantages of using vacuum furnaces for sintering applications? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a laboratory vacuum drying oven play in the treatment of filtered Y2O3-MgO precursors? Expert Insights
- What are the benefits of using vacuum heat treating furnaces for metal alloys? Achieve Superior Metal Properties and Performance
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace prevent contamination? Ensure Purity in High-Temperature Processes



















