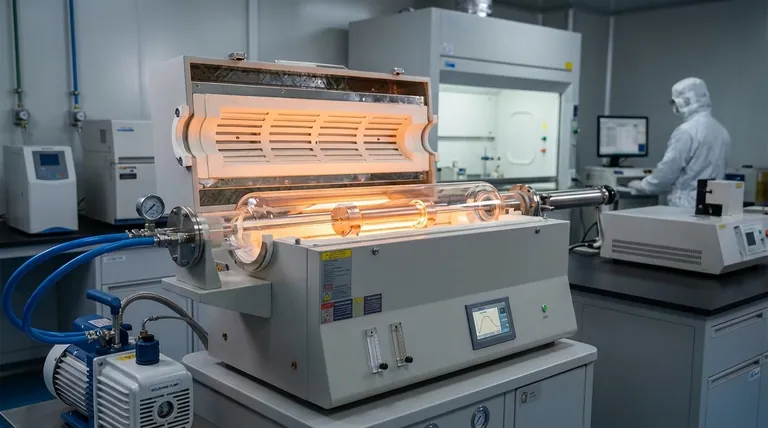
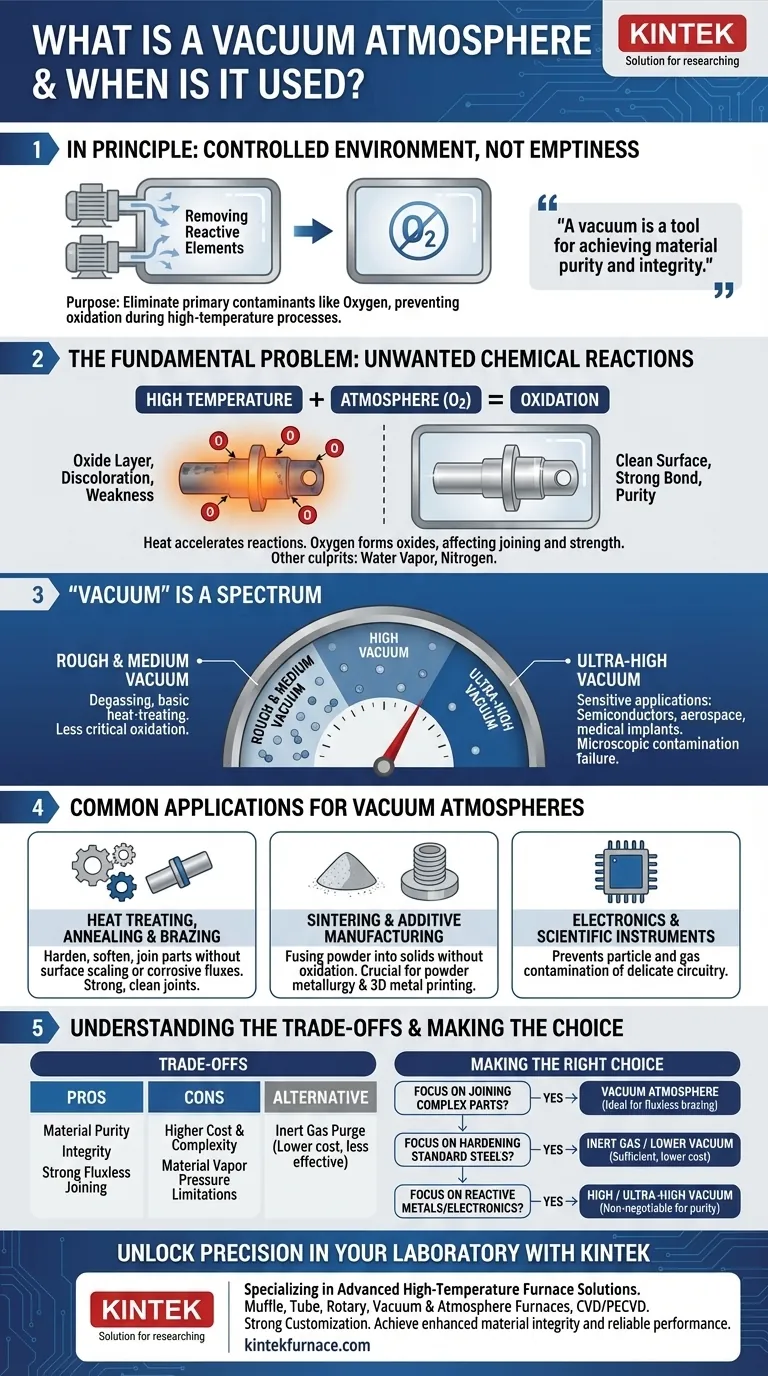
In principle, a vacuum atmosphere is a controlled environment created by removing air and other gases from a sealed chamber. Its purpose is not to create "emptiness" but to eliminate reactive elements, primarily oxygen, that cause unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, especially during high-temperature industrial processes.
The crucial insight is that a vacuum is a tool for achieving material purity and integrity. By removing the atmosphere, you remove the reactants that would otherwise contaminate or weaken materials during sensitive manufacturing and treatment processes.

The Fundamental Problem: Unwanted Chemical Reactions
At its core, the need for a vacuum atmosphere is driven by the desire to control a material’s chemistry during processing. Many valuable industrial processes require high heat, which acts as a catalyst for destructive reactions.
The Role of High Temperature
Heat is essential for processes like brazing, sintering, and annealing. It allows metals to fuse, powders to bond, and material microstructures to be altered for greater strength.
However, this same heat dramatically accelerates chemical reactions between the material and any gases present in the atmosphere.
The Primary Culprit: Oxygen
Oxygen is highly reactive, especially at high temperatures. When it reacts with metals, it forms oxides on the surface, a process commonly known as oxidation.
This oxide layer can prevent metals from joining properly during brazing, cause discoloration, and weaken the final product. A vacuum furnace removes the oxygen, allowing for clean, strong, and bright parts.
Other Contaminants
While oxygen is the main concern, other gases in the air, like water vapor and sometimes nitrogen, can also cause undesirable effects. A vacuum effectively removes these elements, preventing hydrogen embrittlement and unwanted nitride formation in sensitive alloys.
"Vacuum" Is a Spectrum, Not an Absolute
The term "vacuum" does not refer to a single state of absolute emptiness. Instead, it describes a range of pressures, and the level required depends entirely on the sensitivity of the application.
Rough and Medium Vacuums
These are the most common and easiest to achieve. They are used for processes like degassing, where the goal is simply to remove trapped gases from a liquid or porous material. They are sufficient for many basic heat-treating applications where slight oxidation is not critical.
High and Ultra-High Vacuums
These levels of vacuum remove exponentially more gas molecules from the chamber. They are required for highly sensitive applications where even microscopic contamination can cause failure.
This includes manufacturing semiconductors, processing medical implants, and fabricating components for aerospace and particle accelerators, where material purity is paramount.
Common Applications for Vacuum Atmospheres
A vacuum environment is essential wherever high heat and material purity intersect. It is a critical enabler for modern manufacturing.
Heat Treating, Annealing, and Brazing
Vacuum furnaces are used to harden, soften, or stress-relieve metal parts without causing the surface discoloration and scaling that occurs in air. Vacuum brazing allows complex assemblies to be joined with exceptional strength and cleanliness, eliminating the need for corrosive fluxes.
Sintering and Additive Manufacturing
Sintering is the process of fusing metal or ceramic powders into a solid mass using heat. Performing this in a vacuum prevents the powder particles from oxidizing, which would inhibit them from bonding properly. This is crucial for powder metallurgy and 3D metal printing.
Electronics and Scientific Instruments
Semiconductors and other sensitive electronic components are manufactured in high-vacuum conditions to prevent airborne particles and reactive gases from contaminating їх delicate circuitry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a vacuum atmosphere involves significant considerations. It is a powerful tool, but not always the right or most cost-effective one.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces and pumping systems are significantly more expensive and complex to operate and maintain than standard atmosphere furnaces. Achieving and holding a high vacuum requires specialized equipment and longer cycle times.
Material Limitations
A primary limitation of vacuum processing is the vapor pressure of the materials being heated. In a vacuum, elements with a high vapor pressure (like zinc, cadmium, or magnesium) can "boil off" or outgas from the base metal, altering its composition.
Vacuum vs. Inert Gas
For some processes, a simpler and cheaper alternative is to purge the furnace with a positive pressure of inert gas, like argon or nitrogen. This displaces the oxygen but is less effective at removing all contaminants compared to a vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the proper atmosphere is a critical decision based on your material, your process, and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is joining complex, high-value parts: A vacuum atmosphere is ideal for fluxless brazing, ensuring maximum joint strength and cleanliness.
- If your primary focus is hardening or annealing standard steels: An inert gas or a lower-level vacuum may provide sufficient protection from oxidation at a lower cost.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals or electronics: A high or ultra-high vacuum is non-negotiable to prevent any level of contamination.
Ultimately, using a vacuum atmosphere is a deliberate engineering choice to achieve control over your material's final properties.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Controlled environment with air/gases removed to eliminate reactive elements like oxygen. |
| Key Benefit | Prevents unwanted chemical reactions (e.g., oxidation) for material purity and strength. |
| Common Uses | Heat treating, brazing, sintering, electronics manufacturing, and aerospace components. |
| Vacuum Levels | Rough/Medium (basic heat treating) to High/Ultra-High (sensitive applications like semiconductors). |
| Considerations | Higher cost and complexity; material vapor pressure limits; inert gas as an alternative. |
Unlock Precision in Your Laboratory Processes with KINTEK
Are you struggling with material contamination or oxidation during high-temperature operations? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure our furnaces precisely meet your experimental requirements, whether for heat treating, brazing, sintering, or electronics fabrication.
Why Choose KINTEK?
- Enhanced Material Integrity: Achieve superior purity and strength in your materials by eliminating reactive gases.
- Custom Solutions: Get equipment designed to fit your specific processes, from rough vacuums for basic tasks to ultra-high vacuums for sensitive applications.
- Reliable Performance: Benefit from durable, high-quality furnaces that reduce downtime and improve efficiency.
Don't let atmospheric issues compromise your results. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can optimize your laboratory's performance and drive innovation in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of CVD tube furnaces for 2D material processing? Unlock Precision Synthesis for Superior Materials
- What future trends are expected in the development of CVD tube furnaces? Discover Smarter, More Versatile Systems
- What are the practical applications of gate media prepared by CVD tube furnaces? Unlock Advanced Electronics and More
- What are the advantages of CVD tube furnace sintering systems? Achieve Superior Material Control and Purity
- What are 2D heterostructures and how are they created using CVD tube furnaces? Unlock Atomic-Scale Material Engineering



















