An electric muffle furnace earns its reputation as a multifunctional tool because it delivers a precisely controlled, high-temperature environment suitable for a wide range of material processing and analytical chemistry tasks. Its core design allows it to perform functions from altering the physical properties of metals to preparing samples for elemental analysis, making it an indispensable instrument in laboratories and industrial settings.
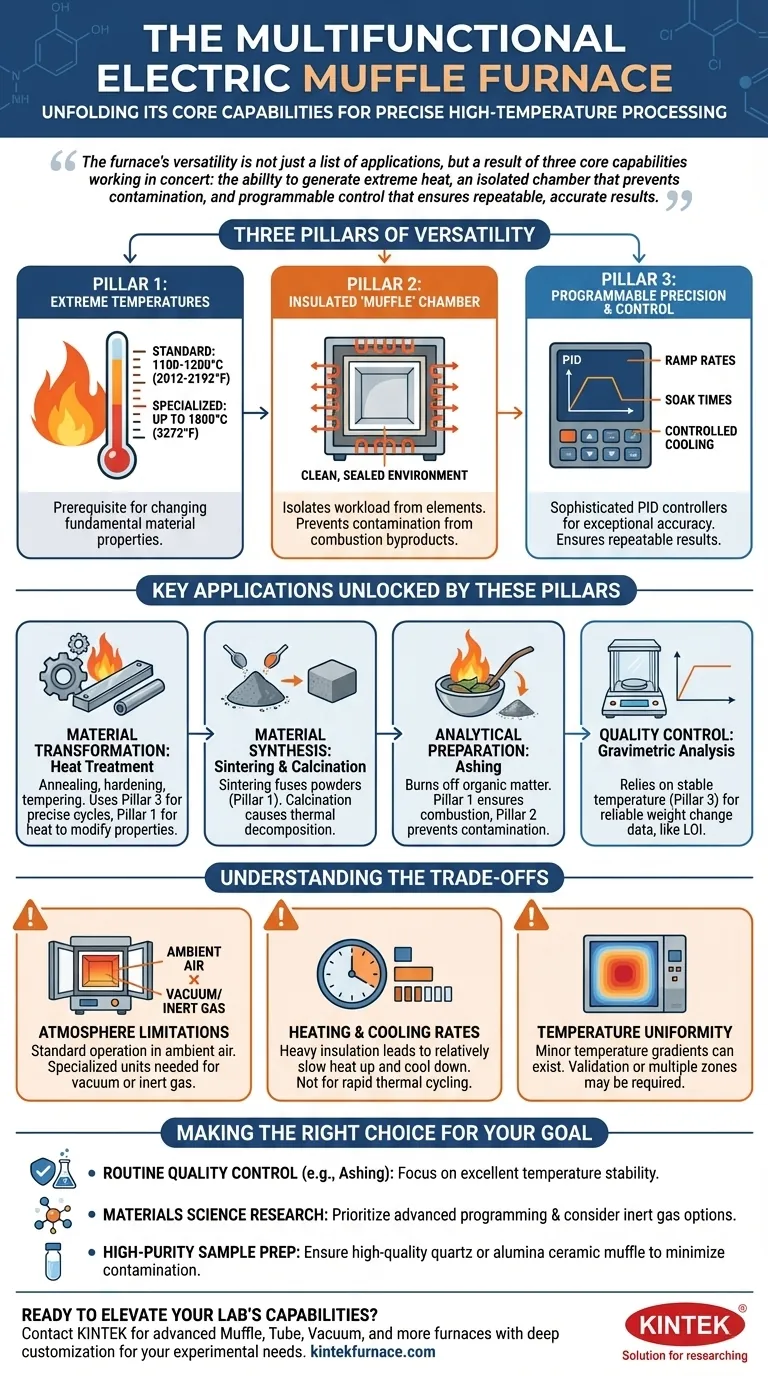
The furnace's versatility is not just a list of applications, but a result of three core capabilities working in concert: the ability to generate extreme heat, an isolated chamber that prevents contamination, and programmable control that ensures repeatable, accurate results.
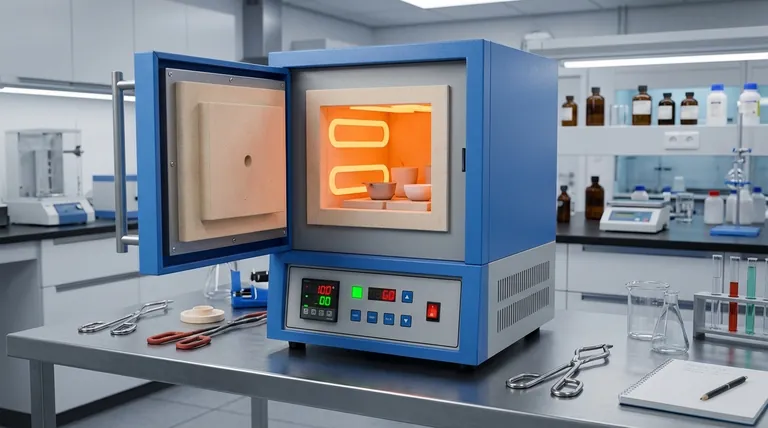

The Three Pillars of Versatility
The power of a muffle furnace comes from the integration of three fundamental design principles. Understanding these pillars reveals why it is so much more than just a simple oven.
Pillar 1: Reaching Extreme Temperatures
A muffle furnace's primary function is to generate significant heat, with most standard models reaching 1100-1200°C (2012-2192°F). Specialized units can even exceed 1800°C (3272°F).
This ability to produce and sustain high temperatures is the prerequisite for applications that involve changing a material's fundamental physical or chemical state.
Pillar 2: The Insulated 'Muffle' Chamber
The name "muffle furnace" comes from its key feature: the muffle, a refractory ceramic chamber that isolates the workload from the heating elements.
This creates a clean, sealed environment. It prevents direct contact with the heating coils and protects the sample from any gaseous byproducts of combustion, which is critical for preventing contamination during sensitive analytical procedures.
Pillar 3: Programmable Precision and Control
Modern furnaces use sophisticated PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controllers to manage temperature with exceptional accuracy.
Users can program complex heating cycles, including specific ramp rates (how fast it heats up), soak times (how long it holds a temperature), and controlled cooling. This level of precision transforms the furnace from a brute-force heater into a fine-tuned scientific instrument.
Key Applications Unlocked by These Pillars
The combination of high heat, isolation, and precision unlocks a vast array of processes across different fields.
Material Transformation: Heat Treatment
Applications like annealing, hardening, and tempering rely on precise temperature cycles (Pillar 3) to alter the microstructure of metals and alloys. The high heat (Pillar 1) enables these changes, modifying properties like hardness and ductility.
Material Synthesis: Sintering and Calcination
Sintering uses high heat (Pillar 1) to fuse powders into a solid mass without melting them, a key step in creating ceramics and certain metal parts. Calcination uses heat to cause thermal decomposition, often to create oxides from carbonates.
Analytical Preparation: Ashing
Ashing is a common analytical technique that involves heating a sample to burn off all organic matter, leaving only the inorganic ash behind for analysis.
The furnace's high temperature (Pillar 1) ensures complete combustion, while the isolated muffle (Pillar 2) prevents contaminants from skewing the final weight measurement.
Quality Control: Gravimetric Analysis
Similar to ashing, loss-on-ignition (LOI) and other gravimetric analysis methods depend on the furnace's ability to hold a precise, stable temperature (Pillar 3). This ensures that any weight change is due only to the intended process, leading to reliable quality control data.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly versatile, the muffle furnace is not without its limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging them.
Atmosphere Limitations
A standard muffle furnace operates in an ambient air atmosphere. For processes that require a vacuum or an inert gas environment (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation, a specially designed and more expensive furnace is necessary.
Heating and Cooling Rates
The heavy insulation that enables a furnace to reach and hold extreme temperatures also means it heats up and cools down relatively slowly. This makes it unsuitable for applications requiring rapid thermal cycling.
Temperature Uniformity
While controllers offer precise readings at the thermocouple, minor temperature gradients can exist across the chamber. For exceptionally sensitive processes where uniformity is paramount, validation or the use of a furnace with multiple heating zones may be required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" use of a muffle furnace depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control (like ashing): A standard, reliable furnace with excellent temperature stability is your most critical requirement.
- If your primary focus is materials science research: Prioritize a furnace with advanced programming for complex heat cycles and consider a model with an optional inert gas port.
- If your primary focus is high-purity sample preparation: Ensure the furnace uses a high-quality quartz or alumina ceramic muffle to minimize any potential for sample contamination.
By understanding its core principles, you can leverage the muffle furnace as a powerful and adaptable tool for nearly any high-temperature challenge.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Temperatures (up to 1800°C) | Enables material transformation and synthesis | Heat treatment, sintering, calcination |
| Insulated Muffle Chamber | Prevents contamination for pure results | Ashing, gravimetric analysis |
| Programmable PID Control | Ensures repeatable, accurate processes | Complex heating cycles, quality control |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a custom high-temperature furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















