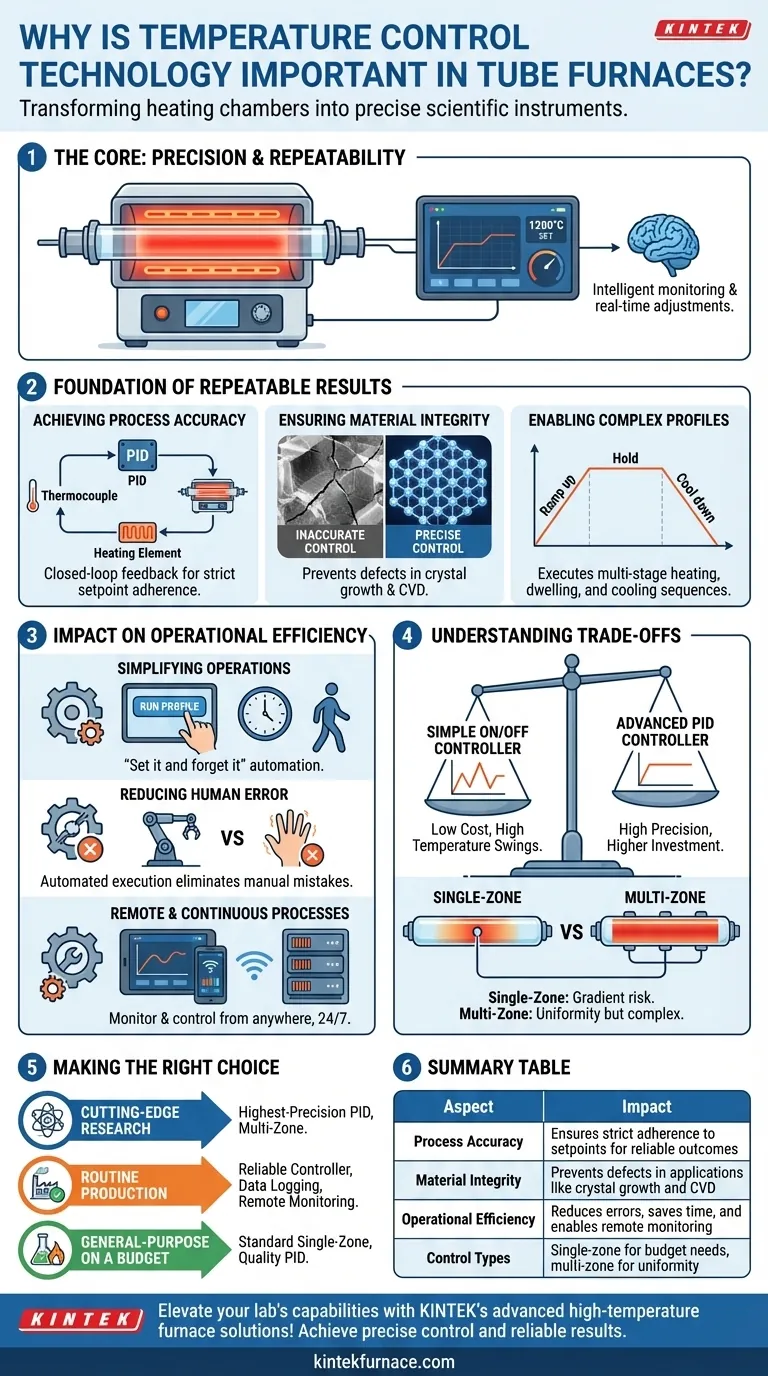
At its core, temperature control technology is the single most important factor for achieving precise, repeatable, and safe outcomes in a tube furnace. It is the system that transforms a simple heating chamber into a scientific instrument by continuously monitoring the internal temperature and making real-time adjustments to the heating elements, ensuring the process unfolds exactly as intended.
The quality of your temperature control system directly determines the quality and reliability of your results. It is not an optional feature but the fundamental mechanism that governs process accuracy, operational efficiency, and the integrity of the materials you are working with.
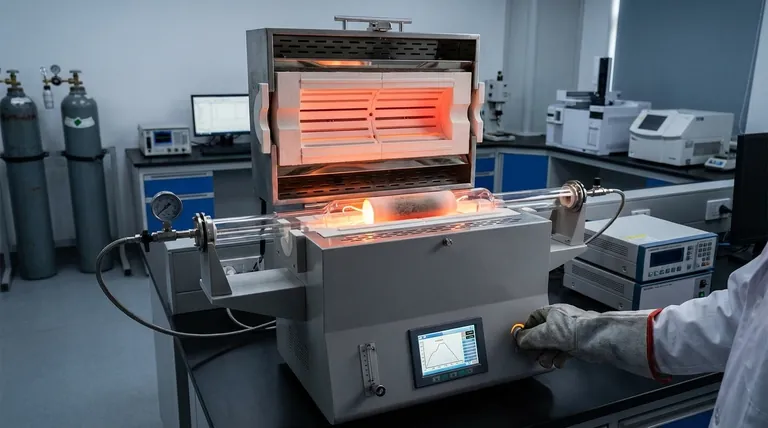

The Foundation of Repeatable Results
A tube furnace's primary function is to subject a material to a specific thermal profile. Without precise control, this function fails, rendering the results unreliable and unrepeatable.
Achieving Process Accuracy
Advanced control systems use sensors, such as thermocouples, to get a live reading of the furnace temperature. This data is fed to a controller (often a PID controller) that instantly adjusts the power sent to the heating elements. This closed-loop feedback ensures the temperature doesn't just get "close" but adheres strictly to the programmed setpoint, meeting the exact requirements of a given process.
Ensuring Material Integrity
For applications like crystal growth, annealing, or chemical vapor deposition, even minor temperature deviations can have a catastrophic effect on the material's final properties. Inaccurate control can lead to failed experiments, inconsistent product quality, and wasted materials. Precise control guarantees that the material's microstructure is formed under the intended conditions.
Enabling Complex Thermal Profiles
Modern material science rarely involves holding a single temperature. Processes often require complex "recipes" with multiple stages, such as ramping up to a temperature at a specific rate, holding it for a set duration (dwelling), and then executing a controlled cooling sequence. Only an intelligent control system can execute these multi-step thermal profiles with high fidelity.
The Impact on Operational Efficiency
Beyond the quality of the results, modern temperature control systems provide significant operational benefits that save time, reduce costs, and enhance safety.
Simplifying Complex Operations
Intelligent control systems allow operators to program, save, and run complex heating cycles with minimal intervention. This "set it and forget it" capability frees up valuable time for researchers and technicians.
Reducing Human Error
By automating the heating process, the risk of human error is virtually eliminated. The system doesn't get distracted or forget to make an adjustment; it executes the program flawlessly every time, leading to more consistent production and fewer failed runs.
Enabling Remote and Continuous Processes
Many modern furnaces are equipped with controllers that allow for remote monitoring and operation. This is invaluable for long-duration experiments or continuous industrial processes, allowing a single operator to oversee multiple units from a central control room.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While advanced control is critical, it's important to understand the associated considerations. Choosing the right system involves balancing needs and budget.
Cost vs. Precision
The most significant trade-off is cost. A simple on/off controller is inexpensive but results in significant temperature swings around the setpoint. A sophisticated, multi-zone PID controller offers incredible precision but comes at a much higher price. The level of precision you require dictates the level of investment.
System Complexity and Calibration
More advanced systems can have a steeper learning curve for programming and setup. Furthermore, the accuracy of any control system is entirely dependent on the accuracy of its sensor. Thermocouples degrade over time and require periodic recalibration or replacement to maintain the system's integrity.
Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone Control
For long tube furnaces, a single temperature sensor in the center may not reflect the temperature at the ends, creating a significant temperature gradient. Multi-zone furnaces use multiple independent heating zones and sensors to ensure a uniform temperature profile along the entire length of the tube, but this adds significant cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate level of temperature control depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge research or material development: Invest in the highest-precision PID controller and consider a multi-zone furnace to ensure your results are accurate and repeatable.
- If your primary focus is routine production or quality control: Prioritize a reliable controller with an intuitive interface, data logging, and remote monitoring capabilities to maximize efficiency and minimize operator error.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment on a budget: A standard single-zone furnace with a quality PID controller will be a robust and effective solution for many applications.
Ultimately, investing in the right temperature control transforms a tube furnace from a simple heat source into a precise and predictable scientific tool.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Process Accuracy | Ensures strict adherence to setpoints for reliable outcomes |
| Material Integrity | Prevents defects in applications like crystal growth and CVD |
| Operational Efficiency | Reduces errors, saves time, and enables remote monitoring |
| Control Types | Single-zone for budget needs, multi-zone for uniformity |
Elevate your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Achieve precise temperature control and reliable results—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















