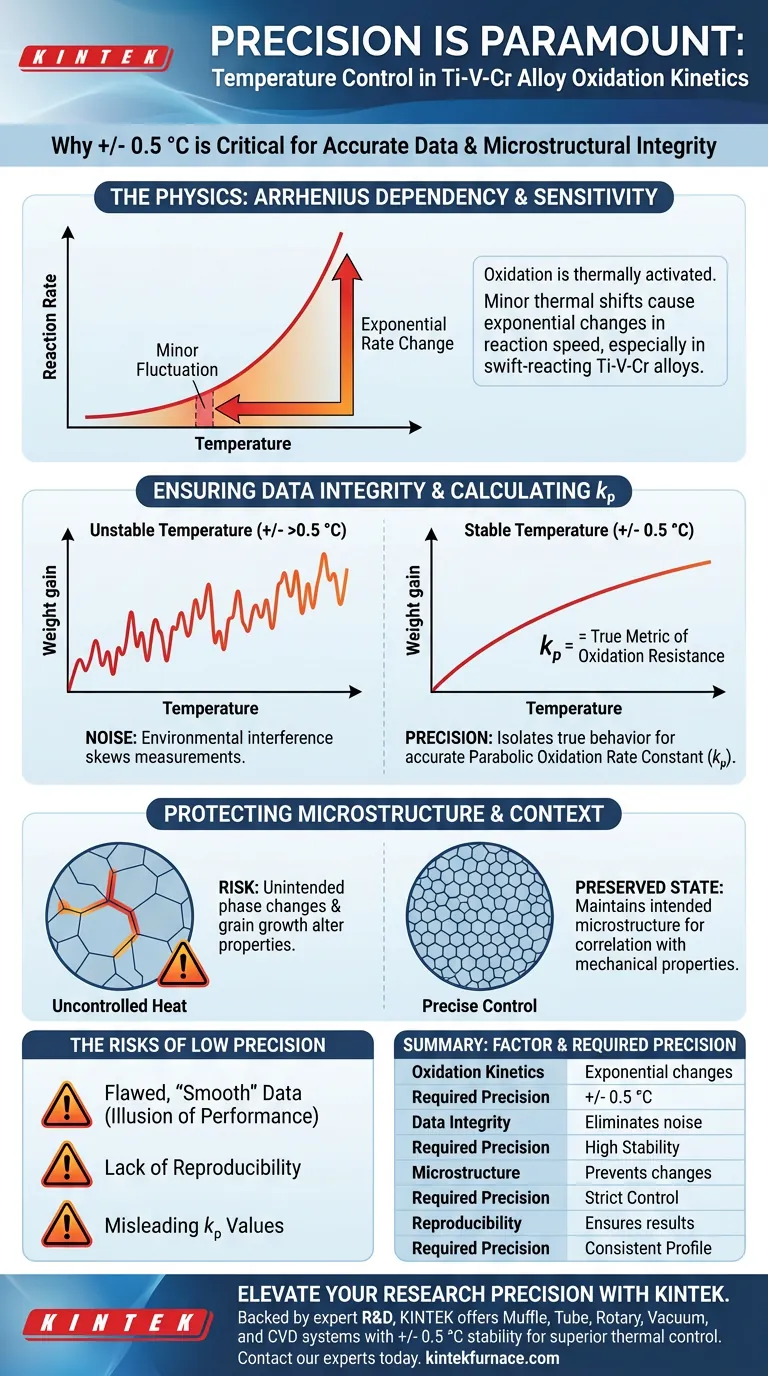
Precision in temperature control is the single most critical variable in high-temperature oxidation kinetics testing for Ti-V-Cr alloys. Because oxidation rates follow the Arrhenius equation, even minor thermal fluctuations can cause exponential changes in reaction speed, rendering weight-gain data unreliable. Maintaining a specific precision, typically +/- 0.5 °C, is necessary to ensure that the measured data reflects the alloy's intrinsic properties rather than environmental interference.
Precise thermal regulation is the only way to isolate the true oxidation behavior of the material. Without it, the calculation of the parabolic oxidation rate constant ($k_p$) becomes skewed, making it impossible to accurately assess the alloy's oxidation resistance.
The Physics of Oxidation Kinetics
The Arrhenius Dependency
Oxidation is a thermally activated process. This means the relationship between temperature and the reaction rate is exponential, not linear.
As described by the Arrhenius equation, a slight increase in temperature provides a disproportionate amount of energy to the system. Consequently, a fluctuation of just a few degrees can significantly accelerate the oxidation rate.
Sensitivity of Ti-V-Cr Alloys
Ti-V-Cr alloys are specifically analyzed to understand their oxidation resistance. These materials react readily with oxygen at high temperatures.
Because the reaction is so swift and sensitive, stability is paramount. The furnace must maintain a flat thermal profile to ensure the reaction proceeds at a constant, predictable rate.
Ensuring Data Integrity
Eliminating Environmental Noise
In kinetics testing, you are measuring the change in mass (weight gain) over time.
If the temperature fluctuates, the rate of weight gain fluctuates with it. This introduces "noise" into your data, making it difficult to distinguish between the actual oxidation curve and artifacts caused by the furnace's heating cycles.
Calculating the Rate Constant ($k_p$)
The ultimate goal of this testing is to derive the parabolic oxidation rate constant ($k_p$).
This constant is the mathematical representation of the alloy's ability to resist oxidation. High-precision control ensures that $k_p$ is calculated based on a stable thermal environment, providing a true metric of the material's performance.
The Impact on Microstructure
Avoiding Unintended Phase Changes
While the primary focus is kinetics, temperature control also safeguards the material's physical structure.
Titanium-based alloys are microstructurally sensitive to heat. Variations in temperature can trigger unintended grain growth or phase transitions (such as shifting from gamma to lamellar structures).
Preserving Mechanical Context
To correlate oxidation resistance with mechanical properties, the microstructure must remain consistent.
Precise temperature control ensures that the sample you analyze at the end of the test represents the specific microstructural state you intended to study, rather than a sample altered by thermal instability.
Understanding the Risks of Low Precision
The Illusion of Performance
Poor temperature control leads to data that may look "smooth" after averaging but is fundamentally flawed.
If a furnace oscillates beyond +/- 0.5 °C, you may calculate a $k_p$ value that suggests the alloy is more (or less) resistant to oxidation than it actually is.
Lack of Reproducibility
Scientific validity relies on reproducibility.
If your furnace lacks precision, repeating the experiment will likely yield different results. This inconsistency prevents you from comparing different Ti-V-Cr compositions effectively or publishing verifiable research.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring your experimental setup, consider your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is determining Intrinsic Kinetics: You must prioritize a furnace with +/- 0.5 °C precision to satisfy the Arrhenius requirements for accurate $k_p$ calculation.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Analysis: strict thermal control is required to prevent unintended phase transformations or grain growth that could skew mechanical property correlations.
- If your primary focus is Comparative Screening: Ensure identical thermal protocols are used for all samples to minimize relative error, even if absolute precision is slightly lower.
True insight into alloy performance is impossible without the rigorous elimination of thermal variables.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Testing | Required Precision |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation Kinetics | Exponential rate changes via Arrhenius equation | +/- 0.5 °C |
| Data Integrity | Eliminates noise in weight-gain measurements | High Stability |
| Microstructure | Prevents unintended phase changes or grain growth | Strict Control |
| Reproducibility | Ensures verifiable and comparable research results | Consistent Profile |
Elevate Your Research Precision with KINTEK
Don't let thermal fluctuations compromise your critical oxidation kinetics data. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs. Whether you are analyzing Ti-V-Cr alloys or developing next-generation materials, our furnaces provide the +/- 0.5 °C stability required for precise $k_p$ calculations and microstructural integrity.
Ready to achieve superior thermal control?
Contact our experts today to find your perfect heating solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Yuanzhi Sun, Liangju He. Prediction of oxidation resistance of Ti-V-Cr burn resistant titanium alloy based on machine learning. DOI: 10.1038/s41529-025-00553-2
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a sealed ceramic boat impact SPAN sulfur content? Unlock 53.62% Retention for High-Energy Cathodes
- Why is a specialized roasting simulation device necessary? Optimize Iron Ore Pellet Quality and Strength
- What are the process advantages of using a powder mixture for siliconization? Ensure Uniformity on Complex Geometries
- What is the function of a constant temperature blast drying oven? Achieve Uniform Chemical Activation and Porosity
- What is the function of an industrial drying oven in EFB fiber pretreatment? Optimize Biochar Yield & Quality
- How does heat treatment affect the TPU encapsulation layer? Optimize Flexible Sensor Durability & Bonding
- What is the role of homogeneous catalysts such as Na2CO3 or KOH in HTL? Boost Bio-crude Yield & Quality
- Why is the precision of an automatic temperature-controlled furnace critical in glass synthesis? Achieve 1350°C Accuracy



















