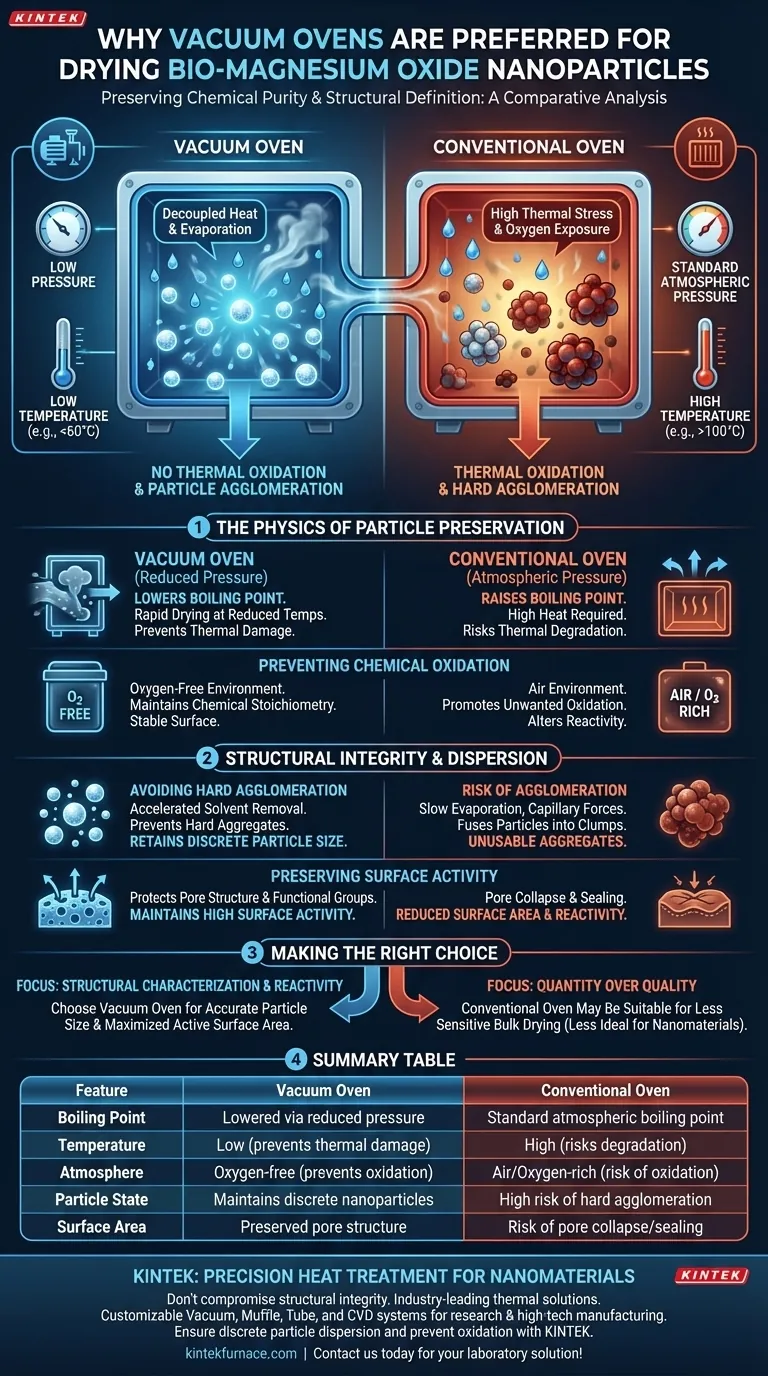
The preservation of chemical purity and structural definition is the deciding factor. A vacuum oven is preferred for drying synthesized bio-magnesium oxide nanoparticles because it lowers the boiling point of solvents, enabling rapid drying at significantly reduced temperatures. This specific environment prevents the thermal oxidation and particle agglomeration that frequently occur in conventional high-temperature air ovens, thereby maintaining the material's original particle size and surface activity.
The core advantage of vacuum drying lies in decoupling heat from evaporation. By reducing pressure, you remove moisture without subjecting delicate bio-magnesium oxide nanoparticles to the high thermal stress and oxygen exposure that degrade their quality in standard ovens.
The Physics of Particle Preservation
Lowering the Thermal Threshold
In a conventional oven, drying relies on raising the temperature to the solvent's boiling point (e.g., 100°C for water) at standard atmospheric pressure. This high heat can be destructive to sensitive nanomaterials.
A vacuum oven alters the thermodynamic environment by reducing the internal pressure. This depression allows water and other solvents to volatilize at much lower temperatures. Consequently, the bio-magnesium oxide can be dried thoroughly without ever reaching temperatures that would trigger degradation.
Preventing Chemical Oxidation
Standard ovens operate in an air environment, which is rich in oxygen. When combined with the high temperatures required for conventional drying, this creates an ideal environment for unwanted oxidation.
For bio-magnesium oxide, preserving the specific chemical stoichiometry is vital. The vacuum environment effectively excludes oxygen during the heating process. This ensures that the nanoparticles remain chemically stable and do not undergo surface oxidation, which would alter their intended reactivity.
Structural Integrity and Dispersion
Avoiding Hard Agglomeration
One of the most significant risks in drying nanoparticles is agglomeration—where individual particles fuse together into larger, unusable clumps. In conventional drying, the slow evaporation of liquid creates strong capillary forces that pull particles together.
Vacuum drying mitigates this by accelerating solvent removal from deep pores and surfaces simultaneously. This rapid release reduces the time particles spend in a liquid-bridge state, preventing the formation of hard aggregates. The result is a powder that retains its original, discrete particle size.
Preserving Surface Activity
The effectiveness of bio-magnesium oxide often depends on its specific surface area and the presence of active functional groups. High temperatures in standard ovens can cause surface pores to collapse or seal off.
By operating at lower temperatures, a vacuum oven protects the internal pore structure and surface functional groups. This ensures the material maintains high surface activity, which is critical if the nanoparticles are intended for applications requiring high reactivity or specific structural characterization.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Equipment Complexity vs. Sample Quality
While vacuum ovens offer superior results for nanomaterials, they introduce operational complexity compared to standard ovens. They require a vacuum pump, regular maintenance of seals, and careful monitoring of pressure levels.
Batch Limitations
Vacuum drying is generally a batch process with limited throughput compared to continuous air drying methods. However, for high-value synthesized nanomaterials where quality supersedes quantity, this trade-off is necessary to ensure the material is usable for characterization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
If you are synthesizing bio-magnesium oxide nanoparticles, your choice of drying method dictates the final quality of your material.
- If your primary focus is Structural Characterization: Choose a vacuum oven to ensure the particle size you measure is accurate and not skewed by heat-induced agglomeration.
- If your primary focus is Surface Reactivity: Choose a vacuum oven to prevent oxidation and pore collapse, maximizing the available active surface area.
By controlling both pressure and temperature, you transition from simply drying a sample to actively engineering its final quality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Oven | Conventional Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling Point | Lowered via reduced pressure | Standard atmospheric boiling point |
| Temperature | Low (prevents thermal damage) | High (risks degradation) |
| Atmosphere | Oxygen-free (prevents oxidation) | Air/Oxygen-rich (risk of oxidation) |
| Particle State | Maintains discrete nanoparticles | High risk of hard agglomeration |
| Surface Area | Preserved pore structure | Risk of pore collapse/sealing |
Precision Heat Treatment for Nanomaterials
Don't compromise the structural integrity of your synthesized nanoparticles. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Our customizable Vacuum, Muffle, Tube, and CVD systems are engineered to meet the rigorous demands of laboratory research and high-tech manufacturing.
Whether you need to prevent oxidation or ensure discrete particle dispersion, KINTEK has the high-temperature furnace for your unique application. Contact us today to find your perfect laboratory solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Sarita Shaktawat, Jay Singh. Biogenic-magnesium oxide nanoparticles from <i>Bauhinia variegata</i> (Kachnar) flower extract: a sustainable electrochemical approach for vitamin-B <sub>12</sub> determination in real fruit juice and milk. DOI: 10.1039/d3fb00198a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a rapid vacuum chamber play in measuring the evaporation rates? Achieve Precision Timing at t=0
- What are the main types of vacuum furnaces classified by use? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Thermal Process
- What is the principle behind microwave sintering furnaces? Discover Fast, Uniform Volumetric Heating
- How do the operation and maintenance features of vacuum sintering furnaces enhance efficiency? Boost Productivity and Cut Costs
- Why is a laboratory vacuum oven necessary for drying degraded LTGP samples? Ensure Pure Surface Analysis Results
- What industrial applications do vacuum annealing furnaces have? Unlock Material Perfection for Your Industry
- How are vacuum furnaces used in metal heat treatment? Enhance Metal Quality with Precision Heat Processing
- What role does a vacuum drying oven play in the preparation of anhydrous calcium chloride? Ensuring High-Purity Results



















